innopolis_vtol_dynamics
 innopolis_vtol_dynamics copied to clipboard
innopolis_vtol_dynamics copied to clipboard
Cyphal/DroneCAN UAV HITL simulator
UAV HITL Simulator 
UAV HITL Simulator brings up a set of ROS packages, config files and instructions to establish a full simulation for UAV based on PX4/Ardupilot autopilot.
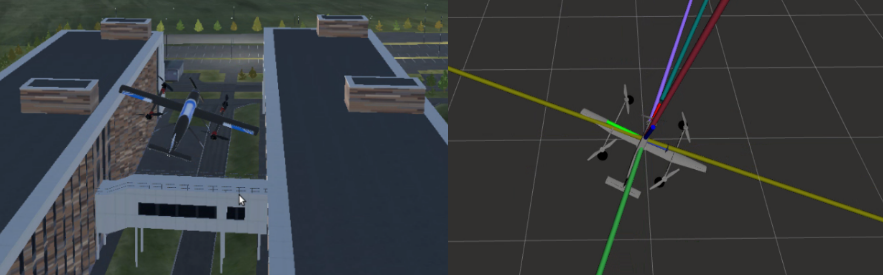
The key feature of this simulation is to run it in such a way that the hardware knows nothing about the simulation. This can be done with Cyphal/DroneCAN. It covers more PX4 modules than standard SITL and HITL.
Purpose
- Simulation of UAV onboard systems at a low hardware level
- Testing and debugging of UAV control systems using a CAN-bus
- Development and testing of intelligent automatic control systems for UAVs
- Training in the development and use of drones, including creating datasets and automated testing
Requirements
-
Operating System: We've tailored the simulator for modern versions of Windows, Linux, and Mac. Choose the build that matches your OS.
-
CPU: Aim for an Intel i7 from the 11th or 12th generation. For those using AMD, any equivalent processor will suffice.
-
RAM: 16GB is a recommended minimum, but more is always better for performance.
-
Hardware: CUAV V5+, CAN-sniffer
1. Design
VTOL HITL Dynamics Simulator is designed to be modular. It is divided into the following main components:
UAV dynamicsis the main node that handles actuator commands from the communicator, performs dynamics simulation, and publishes vehicle and sensors states.Communicatoris the set of nodes that communicate with thePX4 flight stackin HITL (via Cyphal/DroneCAN) and SITL (via MAVLink) modes.inno_sim_interfaceis a bridge for interaction with3D-Simulatorthrough ROS.
The design of the simulator is shown below.

2. Usage
The simulator is distributed as a Docker image. It is recommended to use the ./scripts/docker.sh script. It configures all the necessary Docker flags, performs automatic firmware upload,
configuration, creates a CAN interface, and generally provides a simple interface to interact with
the simulator.
Step 1. Clone repository with submodules
git clone https://github.com/ZilantRobotics/innopolis_vtol_dynamics.git --recursive
Whenever you pull this repository, don't forget to update submodules:
git submodule update --init --recursive
Step 2. Build/pull the docker image
To build docker image, type:
./scripts/docker.sh build
An image on dockerhub usually is not up to date, so it's better to build manually
Step 3. Connect everything together for HITL
You should skip this step if you want to run PX4 MAVLink SITL mode. Please follow docs/px4/mavlink for details.
Typically we use CUAV v5+ and RL-programmer-sniffer, but it might be anything else.
An example of a connection is shown in the picture below.
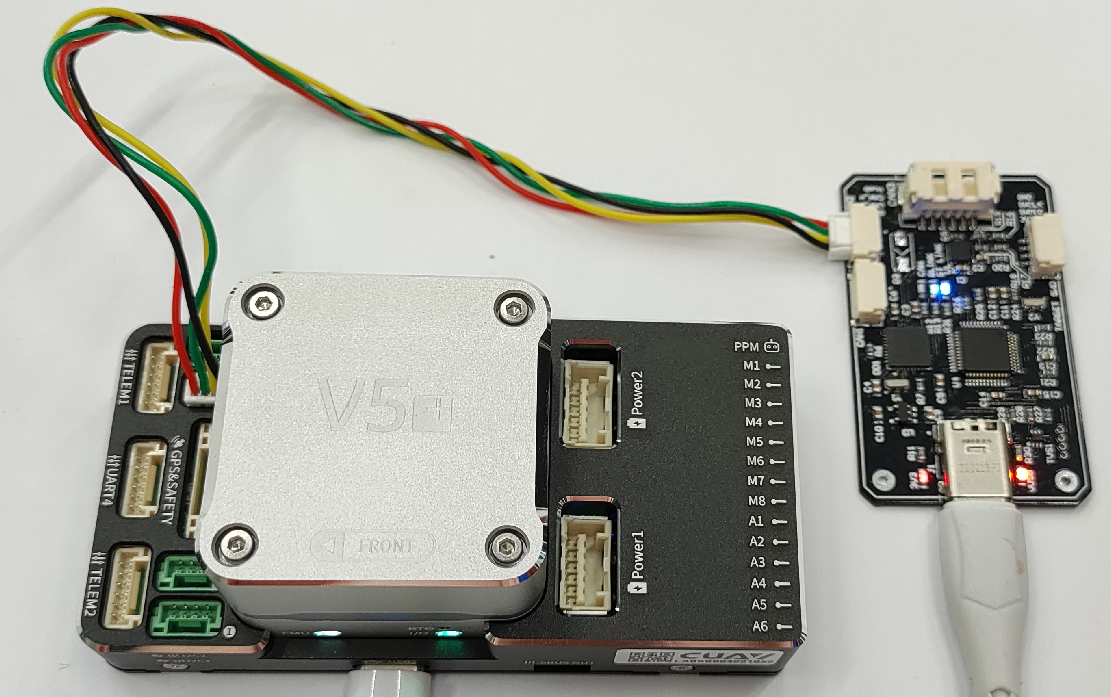
All default parameters expect that you use CAN1 on the autopilot side.
Step 4. Run the container in force mode
In --force mode the script automatically upload the required firmware and parameters corresponded
to the specified mode, create SLCAN and run the container with required docker flags.
To run force mode you need to install autopilot-tools python package: pip install autopilot-tools.
To get the list of all supported modes, just type:
./scripts/docker.sh --help
To run PX4 Cyphal quadcopter, type:
./scripts/docker.sh cq # cq = px4_v1_15_0_cyphal_quadcopter
To run PX4 Dronecan VTOL, type:
./scripts/docker.sh dv # cq = dronecan_vtol
Troubleshooting:
- If your sniffer connection is not found or something else is missing, it will exit in a few seconds.
If something doesn't work, please open an issue.
Step 5. Run ground control station
Here 2 options are suggested.
- You can run QGroundControl or MissionPlanner to have manual flight
- (soon) You can run a script to run one of the test scenario in automatic mode.
Step 6. (optional) 3D Simulator
A new 3D simulator will appear here soon.
3. Supported modes
You can obrain the actual list of the suported modes by typing ./scripts/docker.sh --help.
Well, here is the output of the command:
Primary supported modes (with aliases):
px4_v1_15_0_cyphal_quadcopter,cq | Cyphal PX4 v1.15-alpha Quadrotor x (4001)
px4_v1_15_0_cyphal_quadplane_vtol,csv | Cyphal PX4 v1.15-alpha Standard VTOL (13000)
px4_v1_14_0_dronecan_quadrotor,dq | DroneCAN PX4 v1.14-beta Quadrotor (4001)
px4_v1_14_0_dronecan_quadplane_vtol,dv | DroneCAN PX4 v1.14-beta Standard VTOL (13000)
px4_v1_13_0_dronecan_vtol,dv1130 | DroneCAN PX4 v1.13.0 vtol 13070
Other modes:
sitl_inno_vtol | MAVLink PX4 v1.12 vtol 13070
sitl_flight_goggles | MAVLink PX4 v1.12 Quadrotor (4001)
cyphal_and_dronecan | 2 CAN AP v4.4.0 Copter
px4_v1_15_0_cyphal_octorotor,co | Cyphal PX4 v1.15-alpha Octorotor Coaxial (12001)
New modes will be extended step by step.
4. Example
Check the video below.
5. Auxilliary documentation
Docs:
- Developer docs
- PX4 MAVLink SITL manual configuration instructions
Outdated manual instructions:
- PX4 Cyphal manual configuration instructions
- PX4 DroneCAN manual configuration instructions
- ArduPilot manual configuration instructions
