path_optimizer
 path_optimizer copied to clipboard
path_optimizer copied to clipboard
Optimization-based real-time path planning for vehicles.
path_optimizer
:bell: CHECK OUT THE NEWER VERSION path_optimizer_2

This ROS package generates feasible paths for non-holonomic vehicles.
Simulation videos
(1) Simulation in dynamic environment
(2) Simulation with complex static obstacles
Run demos
0. Install dependencies and build
- ROS kinetic on Ubuntu 16.04
- OpenCV 3
mkdir -p workspace/src && cd workspace/src
git clone [email protected]:LiJiangnanBit/path_optimizer.git
sudo bash path_optimizer/scripts/install_deps.sh
cd ..
catkin build path_optimizer
source devel/setup.bash
install_deps.sh will install other dependencies (Those already installed will be skipped). These dependencies include:
- ipopt 3.12.4
- cppad 20180000.0
- google benchmark
- glog
- gflags
- osqp-eigen
- grid_map
- ros_viz_tools
- tinyspline_ros.
1. Demo
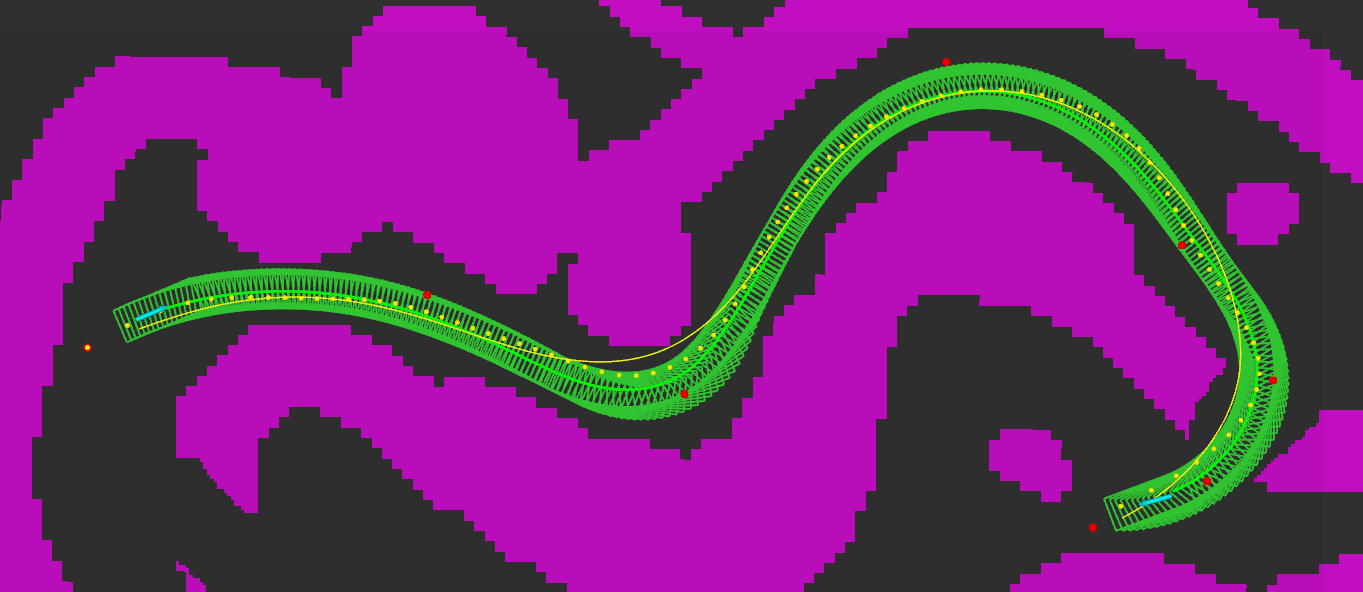
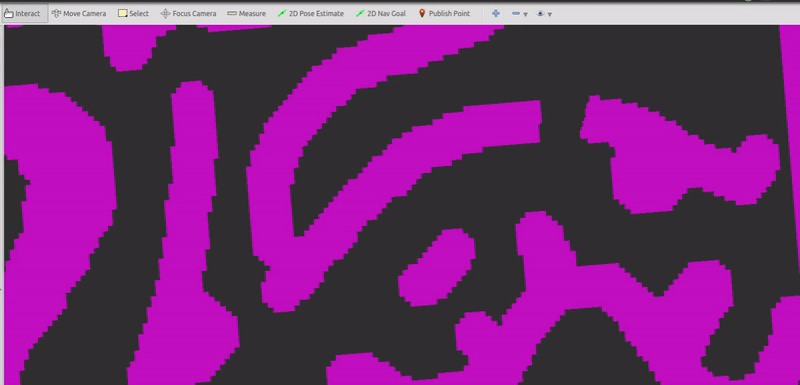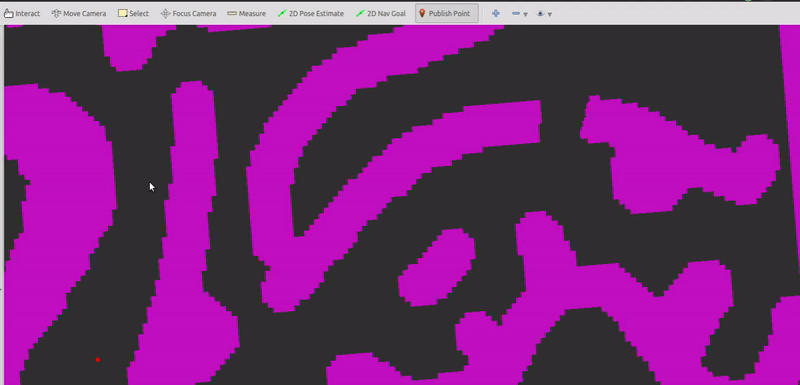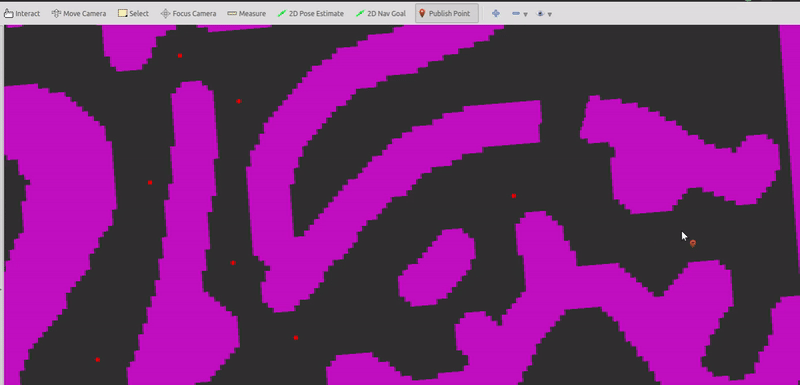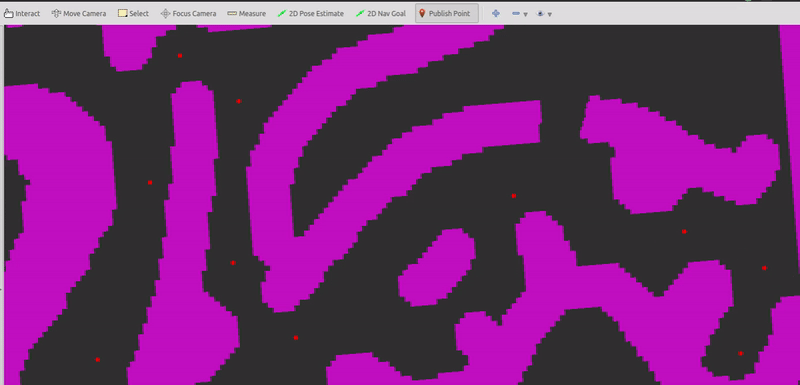
A png image is loaded as the grid map. You can click to specify the global reference path and the start/goal state of the vehicle.
roslaunch path_optimizer demo.launch
(1) Pick reference points using "Publish Point" tool in RViz.
- Pick at least six points.
- There are no hard and fast rules about the spacing of the points.
- If you want to abandon the chosen points, just double click anywhere when using the "Publish Point" tool.
- You can replace
gridmap.pngwith other black and white images. Note that the resolution indemo.cppis set to 0.2m, whick means that the length of one pixel is 0.2m on the map. - In application, the reference path is given by a global path or by a search algorithm like A*.
(2) Pick start state using "2D Pose Estimate" tool and pick goal state using "2D Nav Goal" tool.
- Currently, it's not strictly required to reach the goal state. But this can be changed.
- The start state must be ahead of the first reference point.
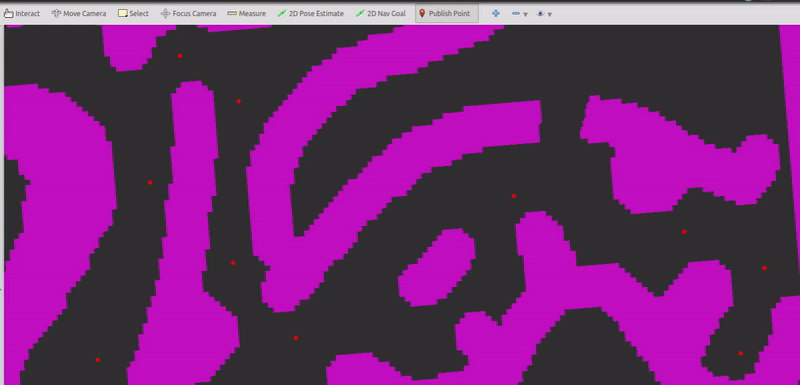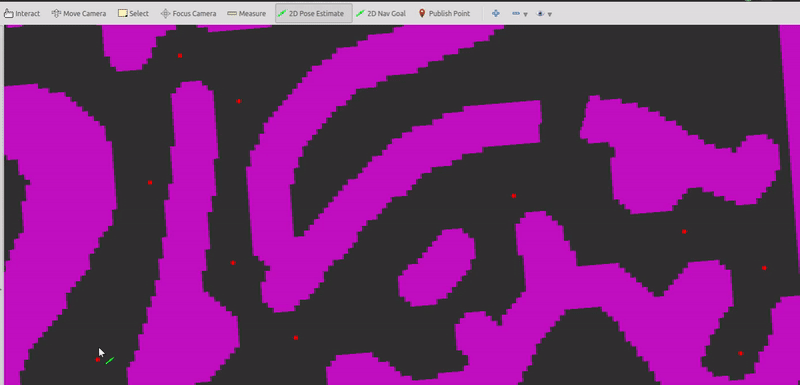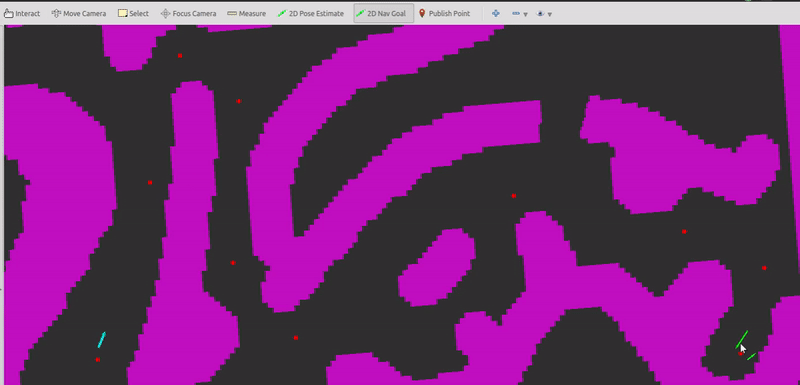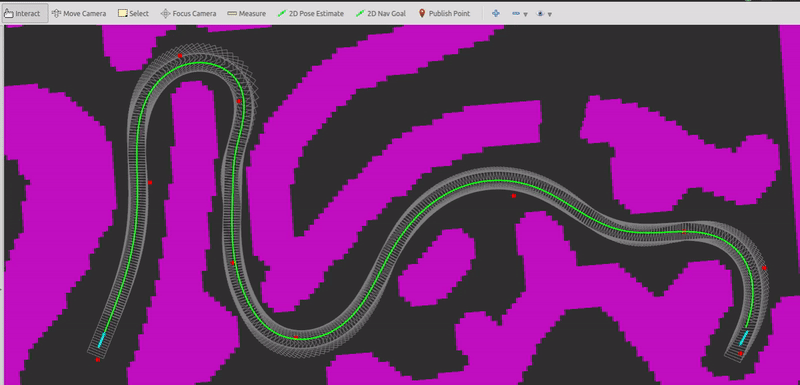
2. Benchmark test
This is a computation time test.
rosrun path_optimizer path_optimizer_benchmark
Usage
Refer to demo.cpp
The parameters that you can change can be found in planning_flags.cpp.
How it works
Refer here.
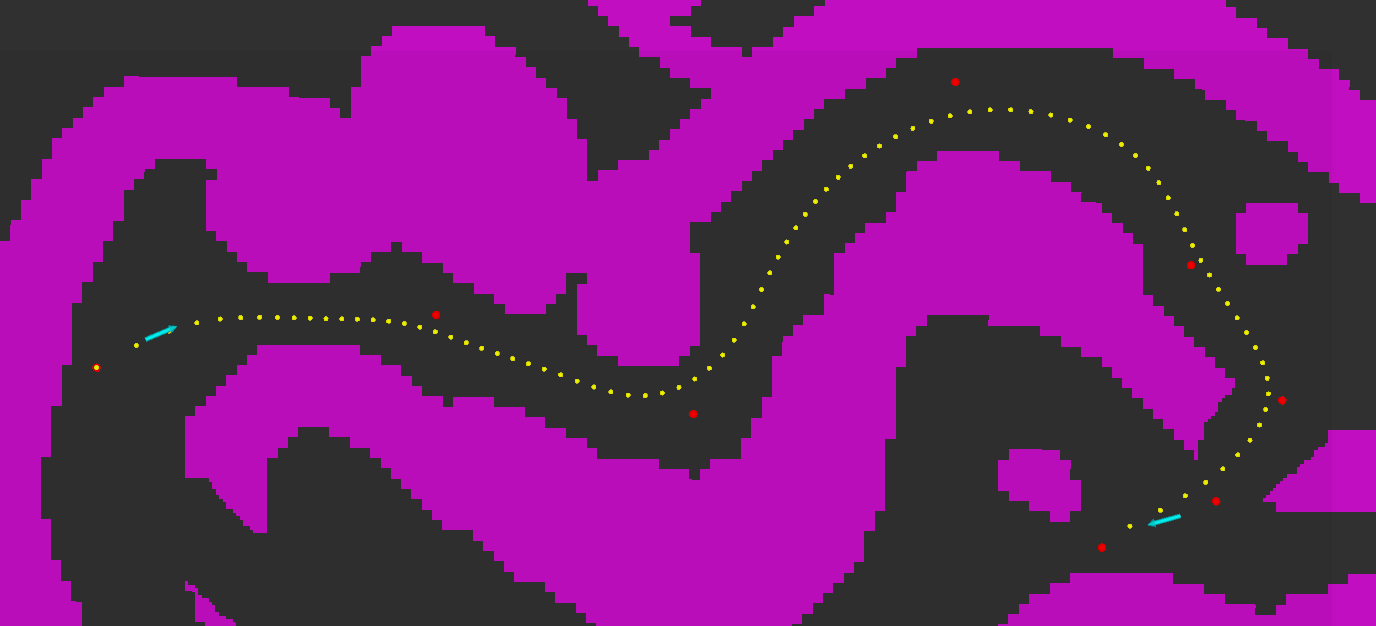
- Take inputs (red dots):
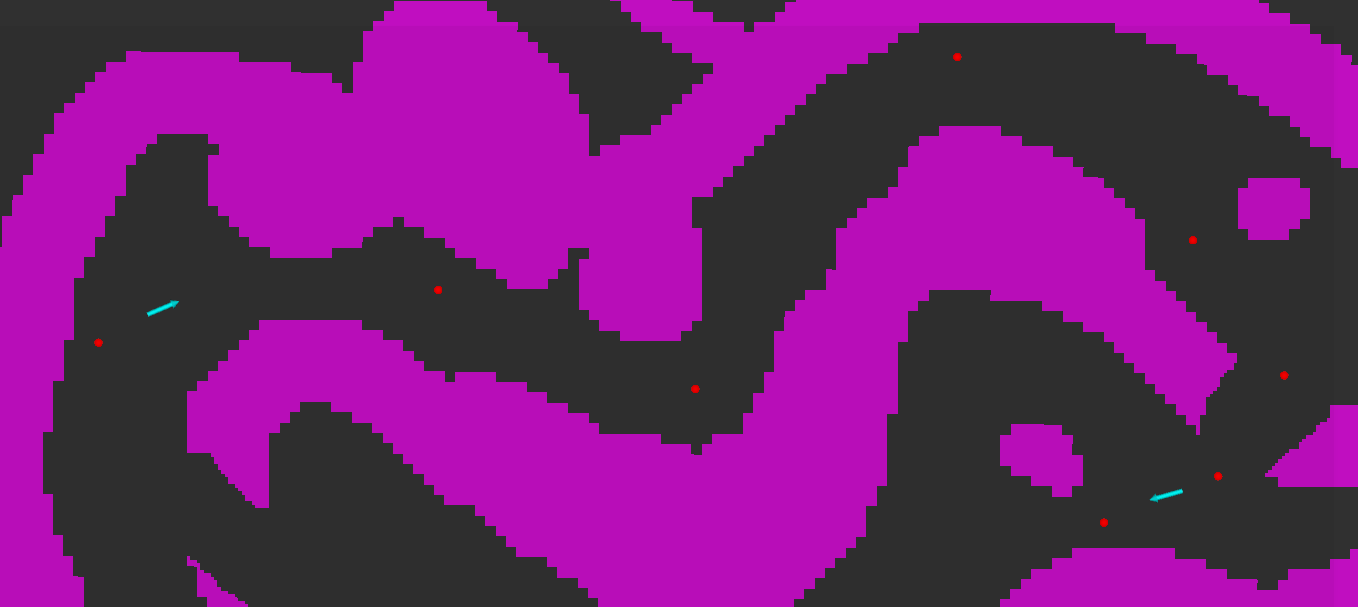

- (Optional) Use B spline curve fitting to make the path continuous and then search around it for a more reasonable reference path (yellow dots).
This step can be skipped by changing settings.
- Smooth the reference path using IPOPT (yellow curve).
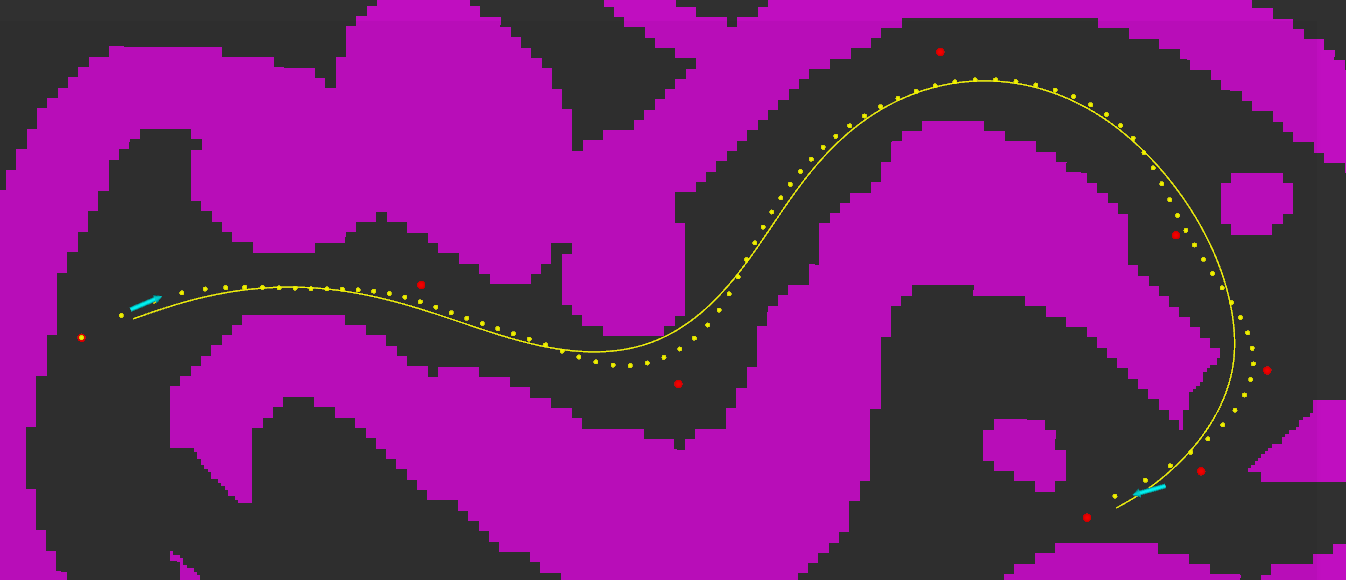
- Represent the path planning problem as a QP and solve it using OSQP.