PapersAnalysis
 PapersAnalysis copied to clipboard
PapersAnalysis copied to clipboard
Generative Models - Basic Elements
Overview
Basic Elements about Generative Models
TODO
- After having it properly extended
- [ ] Release as Medium Article
Generative Models and PDF
- Let's consider a target domain
- E.g. a high dimensional domain like the
D: domain of images
- E.g. a high dimensional domain like the
Discriminative Model
- Description: let's assume it has been trained to discriminate images of cats from non cats
- Input:
D - Output: Scalar Value representing the probability of belonging to cat category
- This value can then be thresholded to get to a binary result
- Comments
- so from a statistical point of view the discriminative model (or discriminator) has learned the Cats PDF hence a function associating to a certain point in its domain (whatever it is) a scalar value that can be interpreted as a probability
- from a set theory point of view, this function has split
Dinto 2 subsets: theD_{cats}(images of cats) and~D_{cats}(images of non cats)
Generative Model
- Description: let's assume it has been trained to produce realistic cats images
- Input: Random Value (e.g. a random scalar value)
- Output: an element in
Dwhich, more precisely, is in its subsetD_{cats}(realistic cat) - Comments
- this is also a function but totally different from the previous PDF as its domain is completely different and its codomain is PDF domain
- this codomain-domain connection is what makes GAN work
Examples of Generative Models
VAE
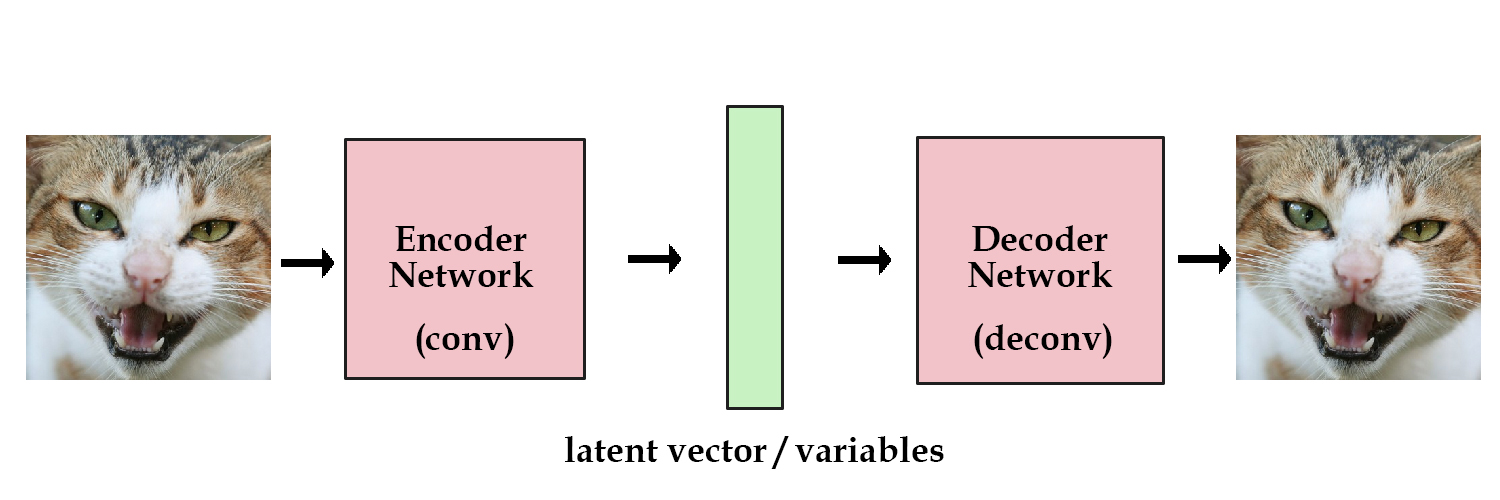
- Specifically the Decoder Network connecting Latent Space to Output Space
- The Encoder Network is used for training purpose
- Generation is done by (random) sampling the Latent Space
GAN

- Specifically the Generator Network
- Generation is done taking noise as input, equivalent to (random) sampling the latent space