awesome-commonsense
 awesome-commonsense copied to clipboard
awesome-commonsense copied to clipboard
[Work in progress] A reading list for machine commonsense reasoning
Awesome Commonsense
A collection of papers and resources about common-sense knowledge graphs (CSKG) and reasoning (CSR).
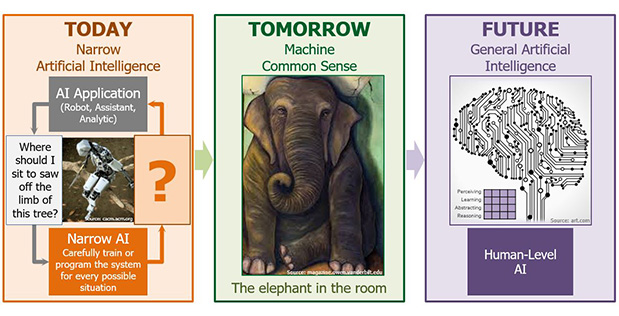
Research in MCS aims to create machine common sense services that can help break down the barrier between the narrowly focused AI applications of today and the more general AI applications of the future.
https://www.darpa.mil/news-events/2018-10-11
Contents
- Common-Sense Knoweldge Graphs
- Tasks & Datasets
- Papers
- Tutorials/Workshops/Blogs
Common-Sense Knoweldge Graphs
-
ConceptNet
- Intro: ConceptNet is a general, human-annotated commonsense knowledge graph, representing common concepts (words and phrases) that people use and the common-sense relationships between them. The knowledge in ConceptNet is collected from a variety of resources, including crowd-sourced resources (such as Wiktionary and Open Mind Common Sense), games with a purpose (such as Verbosity and nadya.jp), and expert-created resources (such as WordNet and JMDict). ConceptNet is the most widely-used general commonsense knowledge graph.
- Authors: MIT Media Lab and Luminoso Technologies, Inc.
- Paper: [ConceptNet 5.5: An Open Multilingual Graph of General Knowledge] in AAAI 2017
- Website: [http://conceptnet.io/]
-
WebChild
- Intro: WebChild is a large collection of commonsense knowledge, automatically extracted and disambiguated from Web contents. WebChild contains triples that connect nouns with adjectives via fine-grained relations like hasShape, hasTaste, evokesEmotion, etc. The arguments of these assertions, nouns and adjectives, are disambiguated by mapping them onto their proper WordNet senses.
- Authors: Niket Tandon, Gerard de Melo, and Gerhard Weikum
- Paper: [WebChild 2.0: Fine-Grained Commonsense Knowledge Distillation] in ACL 2017 (demo)
- [Website @ MPI-INF]
-
ATOMIC
- Intro: ATOMIC, extended from Event2Mind, is a commonsense knowledge base that focuses on inferential knowledge organized as typed if-then relations with variables (e.g., “if X pays Y a compliment, then Y will likely return the compliment”). It has nine if-then relation types to distinguish causes vs. effects, agents vs. themes, voluntary vs. involuntary events, and actions vs. mental states. Most assertions are about human social behaviors.
- Authors: Maarten Sap et al. (AI2 & UW)
- Paper: [ATOMIC: An Atlas of Machine Commonsense for If-Then Reasoning] in AAAI 2019
- Website: [https://homes.cs.washington.edu/~msap/atomic/]
Tasks and Datasets
-
Script-based Commonsense Reasonig
- Description: The seting is similar to multi-choice passage-based question asnwering. Given passages are usually script-based stroies, the correct ansqwer cannot be inferred by literally matching. Answering the questions correctly requires common knowledge that are not obvious in the given script.
- Example:
- Dataset: SemEval-2018 Task 11 (an incoming extended shared task will be at EMNLP2019 workshop COIN).
- Paper: [SemEval-2018 Task 11: Machine Comprehension Using Commonsense Knowledge] (ACL 2018 SemEval)
-
Situition Commonsense Reasonig
- Description: The (evaluation) seting is given a situition (a single sentence or a four-sentence story) as input, we need to anticipate which situition (out of multiple choices) will happen next ("story-end prediction" or "story cloze test" or "situition inference").
- Example:
- Dataset: ROCStories, SWAG.
- Papers:
-
General Commonsense Reasoning
- Description: Given a natural language question (without any passage as context) and multiple answers, we are asked to choose one (extensively) based on cmmonsense knowledge. The main difference is that we have no script as context here.
- Example:
- Dataset: CommonsenseQA
- Paper: [CommonsenseQA: A Question Answering Challenge Targeting Commonsense Knowledge] (NAACL-HLT 2019)
-
Unsupervised General Commonsense Reasoning
- Winograd Schema Challenge(WSC) is a evaluation dataset (150 cases) that test machines' commonsense reasoning capacity in the sense of whether they can correctly resolve ambiguous coreferences (Pronoun Disambiguation Problems, PDPs).
- Choice Of Plausible Alternatives (COPA) has a evaluation dataset (1000 sentences). Each question is composed of a premise and two alternatives, where the task is to select the alternative that more plausibly has a causal relation with the premise. This can be seen as a special case of "Situition Commonsense Reasonig", where we also infer the causes other than results.
-
Visual Commonsense Reasoning
-
Commonsense Knowledge Graph Representation
-
Commonsense Knowledge Graph Construction

