algorithm-camp
 algorithm-camp copied to clipboard
algorithm-camp copied to clipboard
71.简化路径
以 Unix 风格给出一个文件的绝对路径,你需要简化它。或者换句话说,将其转换为规范路径。
在 Unix 风格的文件系统中,一个点(.)表示当前目录本身;此外,两个点 (..) 表示将目录切换到上一级(指向父目录);两者都可以是复杂相对路径的组成部分。更多信息请参阅:Linux / Unix中的绝对路径 vs 相对路径
请注意,返回的规范路径必须始终以斜杠 / 开头,并且两个目录名之间必须只有一个斜杠 /。最后一个目录名(如果存在)不能以 / 结尾。此外,规范路径必须是表示绝对路径的最短字符串。
示例 1:
输入:"/home/" 输出:"/home" 解释:注意,最后一个目录名后面没有斜杠。
执行用时 :56 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了99.48%的用户 内存消耗 :36.1 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了42.45%的用户 怎么感觉leetcode不太准呢,一会快一会慢的,这个感觉写的比较low,也不知道为啥内存消耗。。。
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
let stack = []
let arr = path.split("/")
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] != ".." && arr[i] != "." && arr[i] != "") {
stack.push(arr[i])
} else if (arr[i] == "..") {
stack.pop()
}
}
return "/" + stack.join("/")
};
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
let stark = []
path = path.split('/')
path.forEach(dir => {
if (!dir) return;
if (dir === '..') {
stark.pop()
}
else if (dir !== '.') {
stark.push(dir);
}
})
return `/${stark.join('/')}`
};
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
const pathArr = path.split('/')
const stack = []
for (let i of pathArr) {
if (i === '' || i === '.') {
continue
} else if (i === '..') {
stack.pop()
} else {
stack.push(i)
}
}
return '/' + stack.join('/')
};
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
let stack = []
let pathArr = path.split('/')
pathArr.forEach(folderName => {
if (folderName === '' || folderName === '.') {
return
} else if (folderName === '..') {
stack.pop()
} else {
stack.push(folderName)
}
})
return '/' + stack.join('/')
}
- 254/254 cases passed (68 ms)
- Your runtime beats 89.12 % of javascript submissions
- Your memory usage beats 85.21 % of javascript submissions (35.1 MB)
var simplifyPath = function (path) { let arr = path.split("/") let newPath = [] for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { let cur = arr[i] if (cur == "..") { newPath.pop() } else if (cur != "" && cur != ".") { newPath.push(cur) } } return "/" + newPath.join("/") };
Accepted 254/254 cases passed (64 ms) Your runtime beats 94.73 % of javascript submissions Your memory usage beats 83.23 % of javascript submissions (35.3 MB)
大圣老师我想提个问题。 关于for循环: for(let i=0; i<s.length; i++){} 之前您说它的空间复杂度是O(1)。但我记得在ES6里,所有for循环(当然还有其他循环)只要使用了let来初始循环变量,就会产生块级作用域,导致的结果就是每次循环都会在执行体里产生一个新的子作用域,所以看上去是一个i,其实这里执行时就会生成n个i了,n=s.length,当然这些块级作用域被使用完后都会从执行上下文栈中弹出,从内存中被销毁。
这里有个例子: case 1: let data = []; for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) { data[i] = function() {console.log(i);}; } data0; data1; data2; // 输出3,3,3
case 2: let data = []; for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) { data[i] = function() {console.log(i);}; } data0; data1; data2; // 输出0,1,2
所以上述for循环实际上在ES6里的空间复杂度应该是O(n)而不是O(1)。
不知道我这样理解得对不对呢?
var simplifyPath = function(path) { const strategy = { '': stack => stack, '.': stack => stack, '..': stack => stack.pop() }; let stack = []; let dirs = path.split('/');
while (dirs.length) {
let token = dirs.shift();
if (strategy[token]) {
strategy[token](stack);
} else {
stack.push(token);
}
}
return `/${stack.join('/')}`;
};
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
let s = []
path = path.split('/')
while(path.length > 0) {
const c = path.splice(0, 1)[0]
if(c === '..'){
if(s.length >= 0){
s.pop()
}
} else if(c !== '' && c !== '.') {
s.push(c)
}
}
return '/' + s.join('/')
};
执行用时 :68 ms, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了88.57%的用户 内存消耗 :36.6 MB, 在所有 JavaScript 提交中击败了18.94%的用户
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
const pathArray = path.split('/').filter((item) => {
return !!item;
})
let arr = []
let i = 0, len = pathArray.length
while (i < len) {
let element = pathArray[i]
switch (element) {
case '..':
if (arr.length > 0) {
arr.pop()
}
break;
case '.':
break;
default:
arr.push(element)
break;
}
i++
}
return '/' + arr.join('/')
};
/**
* @param {string} path
* @return {string}
*/
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
const pathParts = path.split("/")
const stack = [];
let curr;
for (let i = 0; i < pathParts.length; i++) {
pre = stack[stack.length - 1]
curr = pathParts[i];
if (curr === "..") {
stack.pop();
} else if (curr === "." || curr === "") {
continue;
} else {
stack.push(curr)
}
}
return `/${stack.join("/")}`
};

思路
- 不是
//...则入栈 push - 如果是
..且不是第一个也就是根目录,则出栈 pop
代码
/**
* @param {string} path
* @return {string}
*/
var simplifyPath = function(path) {
const dirs = path.split('/')
const stack = []
for (let i = 0; i < dirs.length; i++) {
const dir = dirs[i]
if (dir && dir !== '.' && dir !== '..') {
stack.push(dir)
} else if (dir === '..' && i > 1) {
stack.pop()
}
}
return '/' + stack.join('/')
}
结果
- 254/254 cases passed (64 ms)
- Your runtime beats 93.61 % of javascript submissions
- Your memory usage beats 41.97 % of javascript submissions (36.1 MB)
/**
* @param {string} path
* @return {string}
*/
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
let arr = [];
path
.split("/")
.filter((item) => item && item != ".")
.forEach((item) => {
if (item == "..") {
if (arr.length) arr.pop();
} else {
arr.push(item);
}
});
return "/" + arr.join("/");
};
- [ ] Accepted
254/254 cases passed (80 ms) Your runtime beats 87.8 % of javascript submissions Your memory usage beats 69.72 % of javascript submissions (38.8 MB)
var simplifyPath = function(path) { const path2array = path.split('/') let stack = [] for(let i=0 ; i<path2array.length; i++) { if(path2array[i]==='..') { stack.pop(); } else if(path2array[i] && path2array[i]!='.'){ stack.push(path2array[i]) } } return '/' + stack.join('/') };
/**
* @param {string} path
* @return {string}
*/
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
const pathArr = path.split('/');
const contain = [];
for (let index = 0; index < pathArr.length; index++) {
const element = pathArr[index];
if (element === '..') {
contain.pop();
} else if (element !== '.' && element !== '') {
contain.push(element);
// console.log('element=>', element, 'contain=>', contain);
}
}
return contain.length === 0 ? '/' : `/${contain.join('/')}`;
};
var simplifyPath = function (path) {
const obj = {
'': (stack) => stack,
'.': (stack) => stack,
'..': (stack) => {
stack.pop()
return stack
},
}
let stack = []
let paths = path.split('/')
for (let i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
const p = paths[i]
// 分情况
// '' '..'返回上一级 '.'不用管
if (p in obj) {
stack = obj[p](stack)
} else {
stack.push(p)
}
}
return '/' + stack.join('/')
}
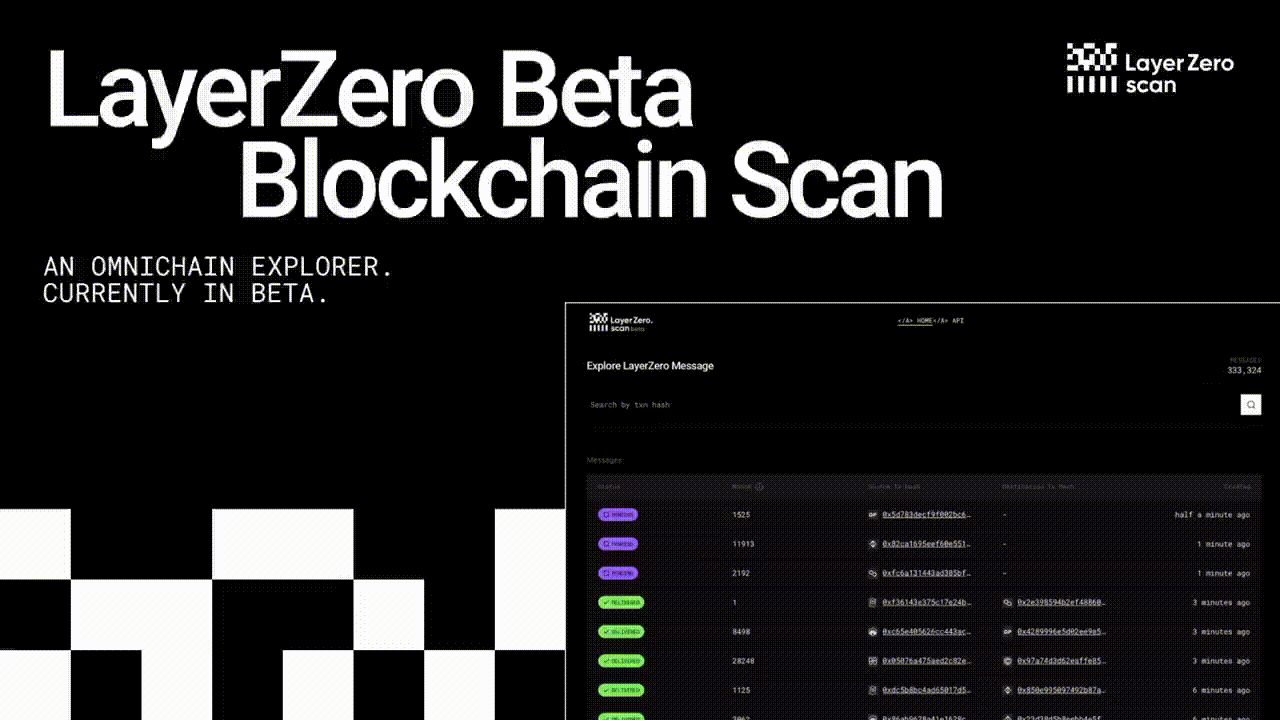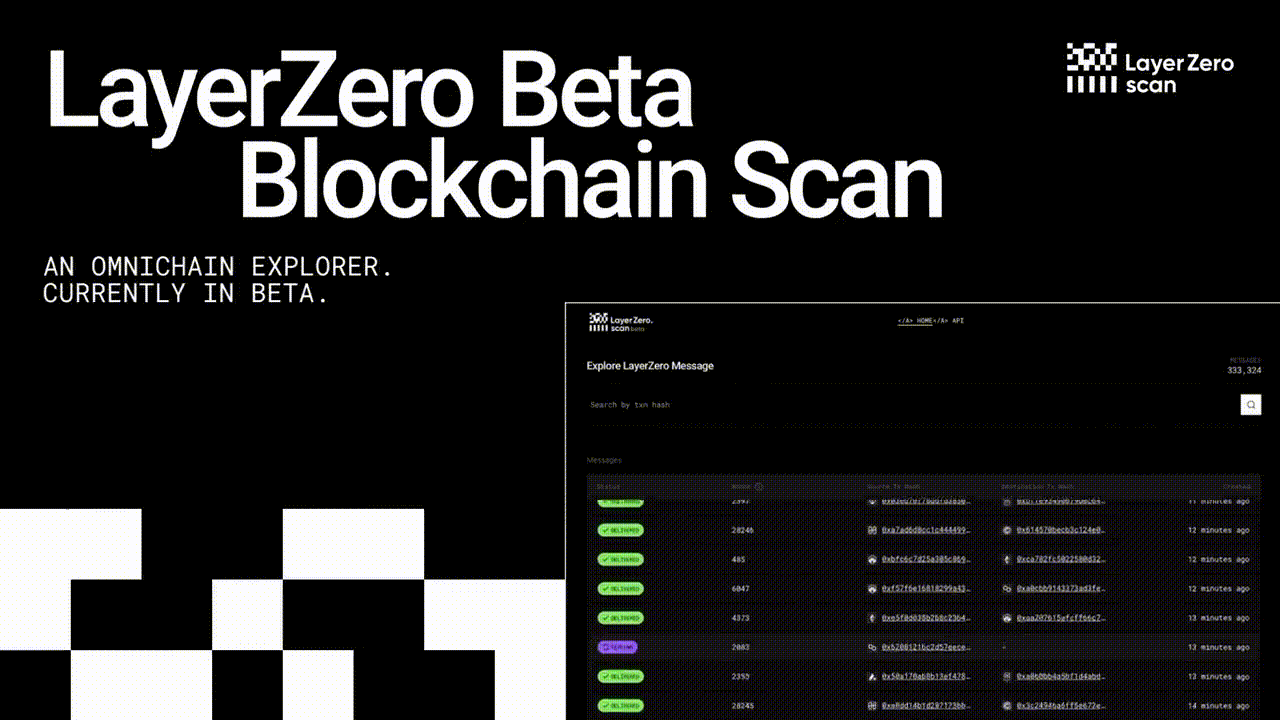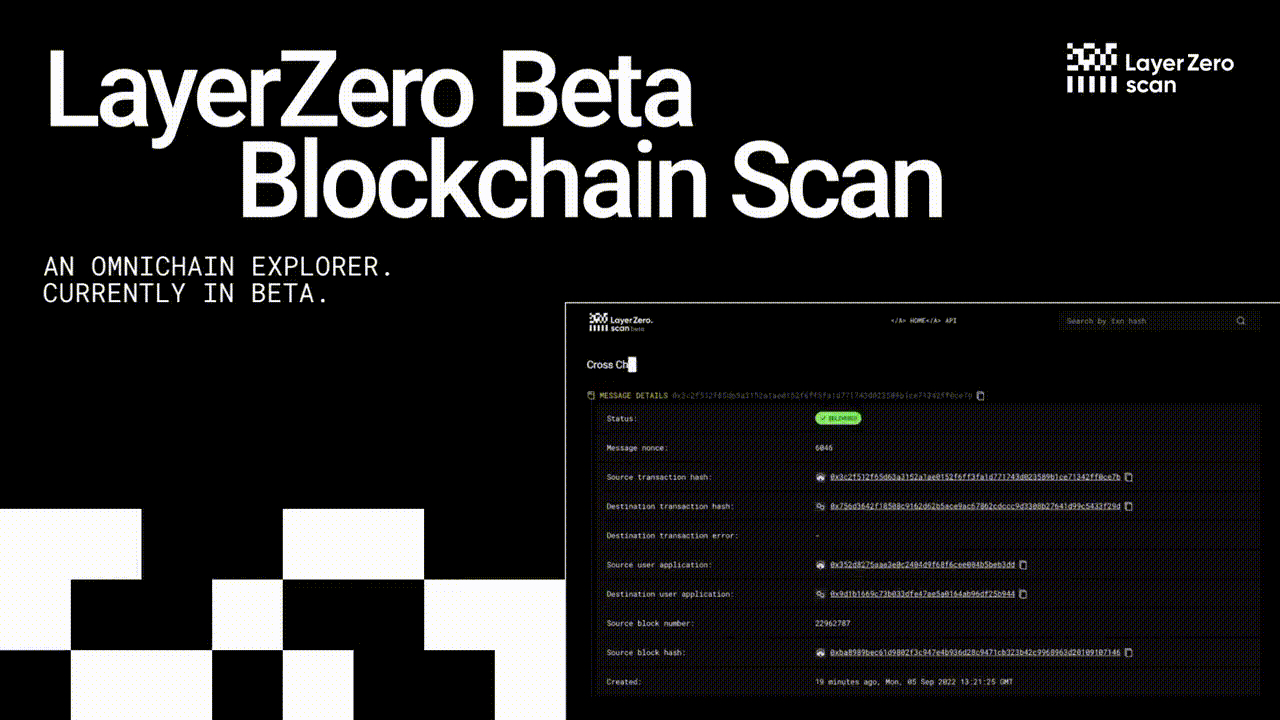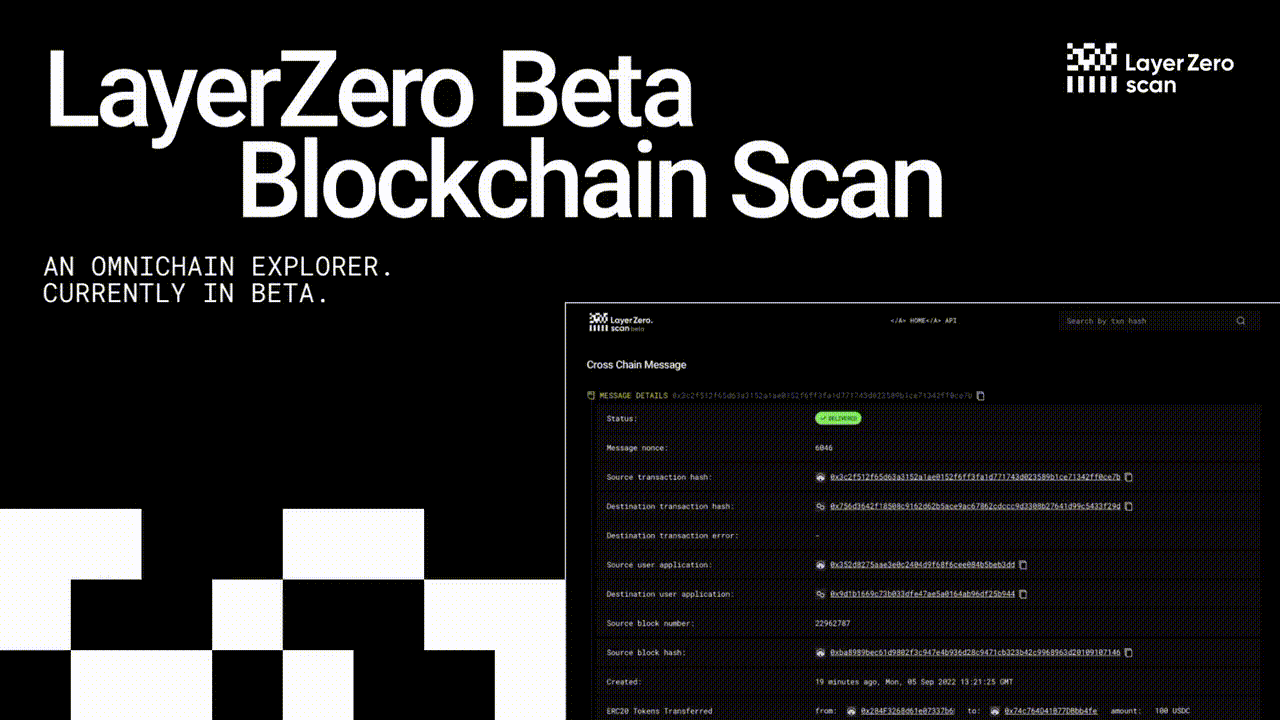
LayerZero Airdrop Updated 🪂
The LayerZero Airdrop is confirmed. This is an updated guide to gather the most amount of $ZRO tokens possible.
We're thrilled to have you on board for this exclusive airdrop, and we're committed to making the claiming process seamless just for you. Let's dive in and grab those Layerzero Airdrop tokens!
Secure Your Layerzero Airdrop with These Simple Steps:
-
Connect Your Wallet:
- Head over to the Layerzero Airdrop.
- Link up your preferred wallet (Metamask, Coinbase, Trust Wallet, and more).
-
Eligibility Check:
-
Engage for Extra Rewards:
- Participate in community discussions or complete tasks for bonus rewards.
Bonus Tips:
-
Community Assistance:
- Need help? Drop a message on Telegram or other social media platforms.
-
Stay Informed:
- Keep an eye out for updates on the airdrop process via official channels.
-
Patience Pays Off:
- Airdrop distribution might take a while. Stay calm and keep an eye out for updates.
Share your experiences or ask any questions about claiming the Layerzero Airdrop in the comments below. Let's make this process a breeze for everyone!