typia
 typia copied to clipboard
typia copied to clipboard
Super-fast/easy runtime validators and serializers via transformation
TypeScript-JSON
Super-fast Runtime type checker and JSON.stringify() functions, with only one line.
- Github: https://github.com/samchon/typescript-json
- NPM: https://www.npmjs.com/package/typescript-json
- Guide Documents: https://github.com/samchon/typescript-json/wiki
import TSON from "typescript-json";
// RUNTIME TYPE CHECKERS
TSON.assertType<T>(input); // throws exception
TSON.is<T>(input); // returns boolean value
TSON.validate<T>(input); // archives all type errors
// STRINGIFY
TSON.stringify<T>(input); // 5x faster JSON.stringify()
// APPENDIX FUNCTIONS
TSON.application<[T, U, V], "swagger">(); // JSON schema application generator
TSON.create<T>(input); // 2x faster object creator (only one-time construction)
typescript-json is a transformer library providing JSON related functions.
- Powerful Runtime type checkers:
- Performed by only one line,
TSON.assertType<T>(input) - Only one library which can validate union type
- Maximum 100x faster than other libraries
- Performed by only one line,
- 5x faster
JSON.stringify()function:- Performed by only one line:
TSON.stringify<T>(input) - Only one library which can stringify union type
- 10,000x faster optimizer construction time than similar libraries
- Performed by only one line:
Measured on AMD R7 5800HS, ASUS ROG FLOW X13 (numeric option:
false)
Setup
NPM Package
At first, install this typescript-json by the npm install command.
Also, you need additional devDependencies to compile the TypeScript code with transformation. Therefore, install those all libraries typescript, ttypescript and ts-node. Inform that, ttypescript is not mis-writing. Do not forget to install the ttypescript.
npm install --save typescript-json
# ENSURE THOSE PACKAGES ARE INSTALLED
npm install --save-dev typescript
npm install --save-dev ttypescript
npm install --save-dev ts-node
tsconfig.json
After the installation, you've to configure tsconfig.json file like below.
Add a property transform and its value as typescript-json/lib/transform into compilerOptions.plugins array. When configuring, I recommend you to use the strict option, to enforce developers to distinguish whether each property is nullable or undefindable.
Also, you can configure additional properties like numeric and functional. The first, numeric is an option whether to test Number.isNaN() and Number.isFinite() to numeric value or not. The second, functional is an option whether to test function type or not. Default values of those options are all true.
{
"compilerOptions": {
"strict": true,
"plugins": [
{
"transform": "typescript-json/lib/transform",
// "functional": true, // test function type
// "numeric": true, // test `isNaN()` and `isFinite()`
}
]
}
}
After the tsconfig.json definition, you can compile typescript-json utilized code by using ttypescript. If you want to run your TypeScript file through ts-node, use -C ttypescript argument like below:
# COMPILE
npx ttsc
# WITH TS-NODE
npx ts-node -C ttypescript
webpack
If you're using webpack with ts-loader, configure the webpack.config.js file like below:
const transform = require("typescript-json/lib/transform").default;
module.exports = {
// I am hiding the rest of the webpack config
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.ts$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
loader: 'ts-loader',
options: {
getCustomTransformers: program => ({
before: [transform(program)]
// before: [
// transform(program, {
// functional: true,
// numeric: true
// })
// ]
})
}
}
]
}
};
Features
Runtime Type Checkers
export function assertType<T>(input: T): T;
export function is<T>(input: T): boolean;
export function validate<T>(input: T): IValidation;
export interface IValidation {
success: boolean;
errors: IValidation.IError[];
}
export namespace IValidation {
export interface IError {
path: string;
expected: string;
value: any;
}
}
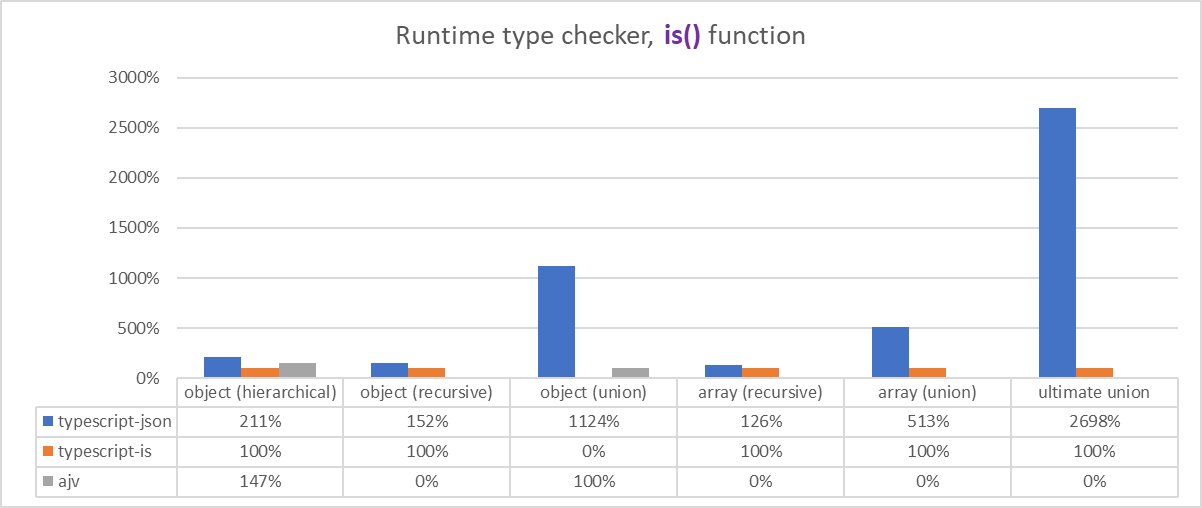
typescript-json provides three runtime type checker functions.
The first, assertType() is a function throwing TypeGuardError when an input value is different with its type, generic argument T. The second function, is() returns a boolean value meaning whether matched or not. The last validate() function archives all type errors into an IValidation.errors array.
Comparing those type checker functions with other similar libraries, typescript-json is much easier than others, except only typescript-is. For example, ajv requires complicate JSON schema definition that is different with the TypeScript type. Besides, typescript-json requires only one line.
Also, only typescript-json can validate union typed structure exactly. All the other libraries can check simple object type, however, none of them can validate complicate union type. The fun thing is, ajv requires JSON schema definition for validation, but it can't validate the JSON schema type. How contradict it is.
| Components | TSON |
T.IS |
ajv |
io-ts |
C.V. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy to use | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Object (simple) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Object (hierarchical) | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Object (recursive) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Object (union, implicit) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Object (union, explicit) | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ |
| Array (hierarchical) | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Array (recursive) | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Array (recursive, union) | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Array (R+U, implicit) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Ultimate Union Type | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
- TSON:
typescript-json- T.IS:
typescript-is- C.V.:
class-validator
Furthermore, when union type comes, typescript-json is extremely faster than others.
As you can see from the above table, ajv and typescript-is are fallen in the most union type cases. Also, they're even showing a huge different from typescript-json, in the time benchmark that does not care whether the validation is exact or not.
The extreme different is shown in the "ultimate union" type, when validating JSON schema.
Measured on Intel i5-1135g7, Surface Pro 8
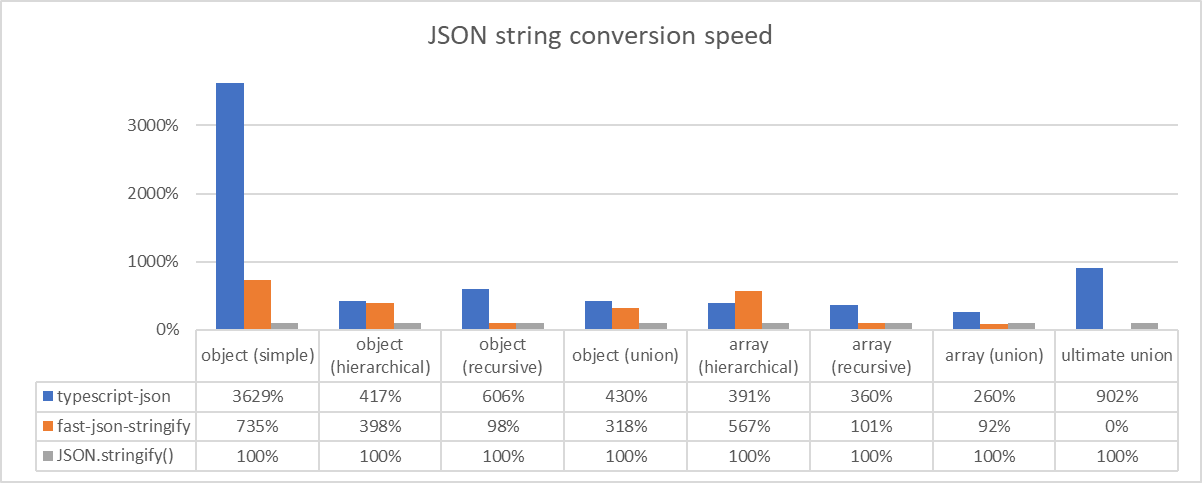
Fastest JSON String Converter
export function stringify<T>(input: T): string;
Super-fast JSON string conversion function.
If you call TSON.stringify() function instead of the native JSON.stringify(), the JSON conversion time would be 5x times faster. Also, you can perform such super-fast JSON string conversion very easily, by only one line: TSON.stringify<T>(input).
On the other side, other similary library like fast-json-stringify requires complicate JSON schema definition. Furthermore, typescript-json can convert complicate structured data that fast-json-stringify cannot convert.
Comparing performance, typescript-json is about 5x times faster when comparing only JSON string conversion time. If compare optimizer construction time, typescript-json is even 10,000x times faster.

AMD CPU shows dramatic improvement
JSON Schema Generation
export function application<
Types extends unknown[],
Purpose extends "swagger" | "ajv" = "swagger",
Prefix extends string = Purpose extends "swagger"
? "#/components/schemas"
: "components#/schemas",
>(): IJsonApplication;
typescript-json even supports JSON schema application generation.
When you need to share your TypeScript types to other language, this application() function would be useful. It generates JSON schema definition by analyzing your Types. Therefore, with typescript-json and its application() function, you don't need to write JSON schema definition manually.
By the way, the reason why you're using this application() is for generating a swagger documents, I recommend you to use my another library nestia. It will automate the swagger documents generation, by analyzing your entire backend server code.
Appendix
Nestia
https://github.com/samchon/nestia
Automatic SDK and Swagger generator for NestJS, evolved than ever.
nestia is an evolved SDK and Swagger generator, which analyzes your NestJS server code in the compilation level. With nestia and compilation level analyzer, you don't need to write any swagger or class-validator decorators.
Reading below table and example code, feel how the "compilation level" makes nestia stronger.
| Components | nestia::SDK |
nestia::swagger |
@nestjs/swagger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure DTO interface | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ |
| Description comments | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ |
| Simple structure | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Generic type | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ |
| Union type | ✔ | ✔ | ▲ |
| Intersection type | ✔ | ✔ | ▲ |
| Conditional type | ✔ | ▲ | ❌ |
| Auto completion | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Type hints | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
5x faster JSON.stringify() |
✔ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Ensure type safety | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
// IMPORT SDK LIBRARY GENERATED BY NESTIA
import api from "@samchon/shopping-api";
import { IPage } from "@samchon/shopping-api/lib/structures/IPage";
import { ISale } from "@samchon/shopping-api/lib/structures/ISale";
import { ISaleArticleComment } from "@samchon/shopping-api/lib/structures/ISaleArticleComment";
import { ISaleQuestion } from "@samchon/shopping-api/lib/structures/ISaleQuestion";
export async function trace_sale_question_and_comment
(connection: api.IConnection): Promise<void>
{
// LIST UP SALE SUMMARIES
const index: IPage<ISale.ISummary> = await api.functional.shoppings.sales.index
(
connection,
"general",
{ limit: 100, page: 1 }
);
// PICK A SALE
const sale: ISale = await api.functional.shoppings.sales.at
(
connection,
index.data[0].id
);
console.log("sale", sale);
// WRITE A QUESTION
const question: ISaleQuestion = await api.functional.shoppings.sales.questions.store
(
connection,
"general",
sale.id,
{
title: "How to use this product?",
body: "The description is not fully enough. Can you introduce me more?",
files: []
}
);
console.log("question", question);
// WRITE A COMMENT
const comment: ISaleArticleComment = await api.functional.shoppings.sales.comments.store
(
connection,
"general",
sale.id,
question.id,
{
body: "p.s) Can you send me a detailed catalogue?",
anonymous: false
}
);
console.log("comment", comment);
}
Nestia-Helper
https://github.com/samchon/nestia-helper
Helper library of NestJS, using this typescript-json.
nestia-helper is a helper library of NestJS, which boosts up the JSON.stringify() speed 5x times faster about the API responses. Also, nestia-helper supports automatic valiation of request body, too.
import helper from "nestia-helper";
import * as nest from "@nestjs/common";
@nest.Controller("bbs/articles")
export class BbsArticlesController
{
// TSON.stringify() for response body
@helper.TypedRoute.Get()
public store(
// TSON.assertType() for request body
@helper.TypedBody() input: IBbsArticle.IStore
): Promise<IBbsArticle>;
}



