enhancements
 enhancements copied to clipboard
enhancements copied to clipboard
[Serve] Add Cpp Deployment in Ray Serve
Summary
General Motivation
In scenarios such as search, inference, and others, system performance is of utmost importance. Taking the model inference and search engines of Ant Group as an example, these systems require high throughput, low latency, and high concurrency as they handle a massive amount of business. In order to meet these requirements, they have all chosen C++ for designing and developing their systems, ensuring high efficiency and stability. Currently, these systems plan to run on Ray Serve to enhance their distributed capabilities. Therefore, Ray Serve needs to provide C++ deployment so that users can easily deploy their services.
Should this change be within ray or outside?
main ray project. Changes are made to the Ray Serve level.
Stewardship
Required Reviewers
@sihanwang41 @edoakes @akshay-anyscale
Shepherd of the Proposal (should be a senior committer)
@sihanwang41 @edoakes @akshay-anyscale
Design and Architecture
Example Model
Taking the recommendation system as an example, when user inputs a search word, the system returns recommended words that are similar to it.

The RecommendService receives user requests and calls the FeatureService, SimilarityService, and RankService to calculate similar words, then return the results to users:
#pragma once
#include <memory>
#include "FeatureService.h"
#include "SimilarityService.h"
#include "RankService.h"
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class RecommendService {
public:
RecommendService() {
feature_service_ = std::make_shared<FeatureService>();
similarity_service_ = std::make_shared<SimilarityService>();
rank_service_ = std::make_shared<RankService>();
}
std::vector<std::string> Recommend(const std::string &request, const int num) {
// 1. Calculate vector
std::vector<float> features = feature_service_->GetVector(request);
// 2. Calculate similarity
std::unordered_map<std::string, float> similarities = similarity_service_->GetSimilarity(features);
// 3. Get similar words
std::vector<std::string> result = rank_service_->Rank(similarities, num);
return result;
}
private:
std::shared_ptr<FeatureService> feature_service_;
std::shared_ptr<SimilarityService> similarity_service_;
std::shared_ptr<RankService> rank_service_;
};
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
The FeatureService convert requests to vector:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <word2vec.h>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class FeatureService {
public:
FeatureService() {
model_.load("model/word2vec.bin");
}
~FeatureService() {
delete model_;
model_ = nullptr;
}
std::vector<float> GetVector(const std::string &request) {
return model_.getVector(request);
}
private:
word2vec::Word2Vec model_;
};
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
The SimilarityService is used to calculate similarity:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <unordered_map>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class SimilarityService {
public:
std::unordered_map<std::string, float> GetSimilarity(std::vector<float> request_vec) {
std::unordered_map<std::string, float> result;
for (auto it = recommend_cache_.begin(); it != recommend_cache_.end(); it++) {
result.insert({it->first, ComputeCosineSimilarity(request_vec, it->second)});
}
return result;
}
private:
float ComputeCosineSimilarity(std::vector<float> v1, std::vector<float> v2) {
int len = v1.size();
float dotProduct = 0;
float magnitude1 = 0;
float magnitude2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dotProduct += v1[i] * v2[i];
magnitude1 += v1[i] * v1[i];
magnitude2 += v2[i] * v2[i];
}
magnitude1 = std::sqrt(magnitude1);
magnitude2 = std::sqrt(magnitude2);
return dotProduct / (magnitude1 * magnitude2);
}
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<float>> recommend_cache_ = {
{"mac", {1.5, 2.3, 3.5, 5.5}},
{"car", {1.5, 3.2, 3.9, 7.5}},
{"phone", {1.5, 2.0, 4.5, 8.1}},
};
};
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
The RankService is used to sort based on similarity:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class RankService {
public:
std::vector<std::string> Rank(std::unordered_map<std::string, float> recommends, int num) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<std::string, float>, std::vector<std::pair<std::string, float>>, std::greater<std::pair<std::string, float>>> pq;
for (auto& pair : recommends) {
pq.push(pair);
if (pq.size() > num) {
pq.pop();
}
}
std::vector<std::string> result;
while (!pq.empty()) {
result.push_back(pq.top().first);
pq.pop();
}
std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
};
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
This is the code that uses the RecommendService class:
#include "RecommendService.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
ray::serve::RecommendService recommend_service;
std::vector<std::string> recommends = recommend_service.Recommend("computer", 1);
for(std::string recommend_word : recommends) {
printf("Recommend word is %s", recommend_word.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
In this way, all services need to be deployed together, which increases the system load and is not conducive to expansion.
Converting to a Ray Serve Deployment
Through Ray Serve, the core computing logic can be deployed as a scalable distributed service.
First, convert these Services to run on Ray Serve.
FeatureService:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <word2vec.h>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class FeatureService {
public:
FeatureService() {
model_.load("model/word2vec.bin");
}
~FeatureService() {
delete model_;
model_ = nullptr;
}
std::vector<float> GetVector(const std::string &request) {
return model_.getVector(request);
}
static FeatureService *FactoryCreate() {
return new FeatureService();
}
private:
word2vec::Word2Vec model_;
};
// Register function
SERVE_DEPLOYMENT(FeatureService::FactoryCreate);
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
SimilarityService:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <unordered_map>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class SimilarityService {
public:
std::unordered_map<std::string, float> GetSimilarity(std::vector<float> request_vec) {
std::unordered_map<std::string, float> result;
for (auto it = recommend_cache_.begin(); it != recommend_cache_.end(); it++) {
result.insert({it->first, ComputeCosineSimilarity(request_vec, it->second)});
}
return result;
}
static SimilarityService *FactoryCreate() {
return new SimilarityService();
}
private:
float ComputeCosineSimilarity(std::vector<float> v1, std::vector<float> v2) {
int len = v1.size();
float dotProduct = 0;
float magnitude1 = 0;
float magnitude2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dotProduct += v1[i] * v2[i];
magnitude1 += v1[i] * v1[i];
magnitude2 += v2[i] * v2[i];
}
magnitude1 = std::sqrt(magnitude1);
magnitude2 = std::sqrt(magnitude2);
return dotProduct / (magnitude1 * magnitude2);
}
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::vector<float>> recommend_cache_ = {
{"mac", {1.5, 2.3, 3.5, 5.5}},
{"car", {1.5, 3.2, 3.9, 7.5}},
{"phone", {1.5, 2.0, 4.5, 8.1}},
};
};
// Register function
SERVE_DEPLOYMENT(SimilarityService::FactoryCreate);
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
RankService:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
namespace ray {
namespace serve {
class RankService {
public:
std::vector<std::string> Rank(std::unordered_map<std::string, float> recommends, int num) {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<std::string, float>, std::vector<std::pair<std::string, float>>, std::greater<std::pair<std::string, float>>> pq;
for (auto& pair : recommends) {
pq.push(pair);
if (pq.size() > num) {
pq.pop();
}
}
std::vector<std::string> result;
while (!pq.empty()) {
result.push_back(pq.top().first);
pq.pop();
}
std::reverse(result.begin(), result.end());
return result;
}
static RankService *FactoryCreate() {
return new RankService();
}
};
// Register function
SERVE_DEPLOYMENT(RankService::FactoryCreate);
} // namespace serve
} // namespace ray
RecommendService is a sequential invocation of other services without complex processing logic, so we can directly use the DAG ability to connect these services, eliminating the need for RecommendService and simplifying user logic. Next, we start the Ray Serve runtime and use Python Serve API deploy these Service as Deployment:
feature_service = serve.deployment(_func_or_class='FeatureService::FactoryCreate', name='feature_service', language='CPP')
similarity_service = serve.deployment(_func_or_class='SimilarityService::FactoryCreate', name='similarity_service', language='CPP')
rank_service = serve.deployment(_func_or_class='RankService::FactoryCreate', name='rank_service', language='CPP')
with InputNode() as input:
features = feature_service.GetVector.bind(input[0])
similarities = similarity_service.GetSimilarity.bind(features)
rank_result = rank_service.Rank.bind(similarities, input[1])
graph = DAGDriver.bind(rank_result, http_adapter=json_request)
handle = serve.run(graph)
ref = handle.GetVector.remote()
result = ray.get(ref)
print(result)
Calling Ray Serve Deployment with HTTP
curl http://127.0.0.1:8000?request=computer&num=1
Overall Design

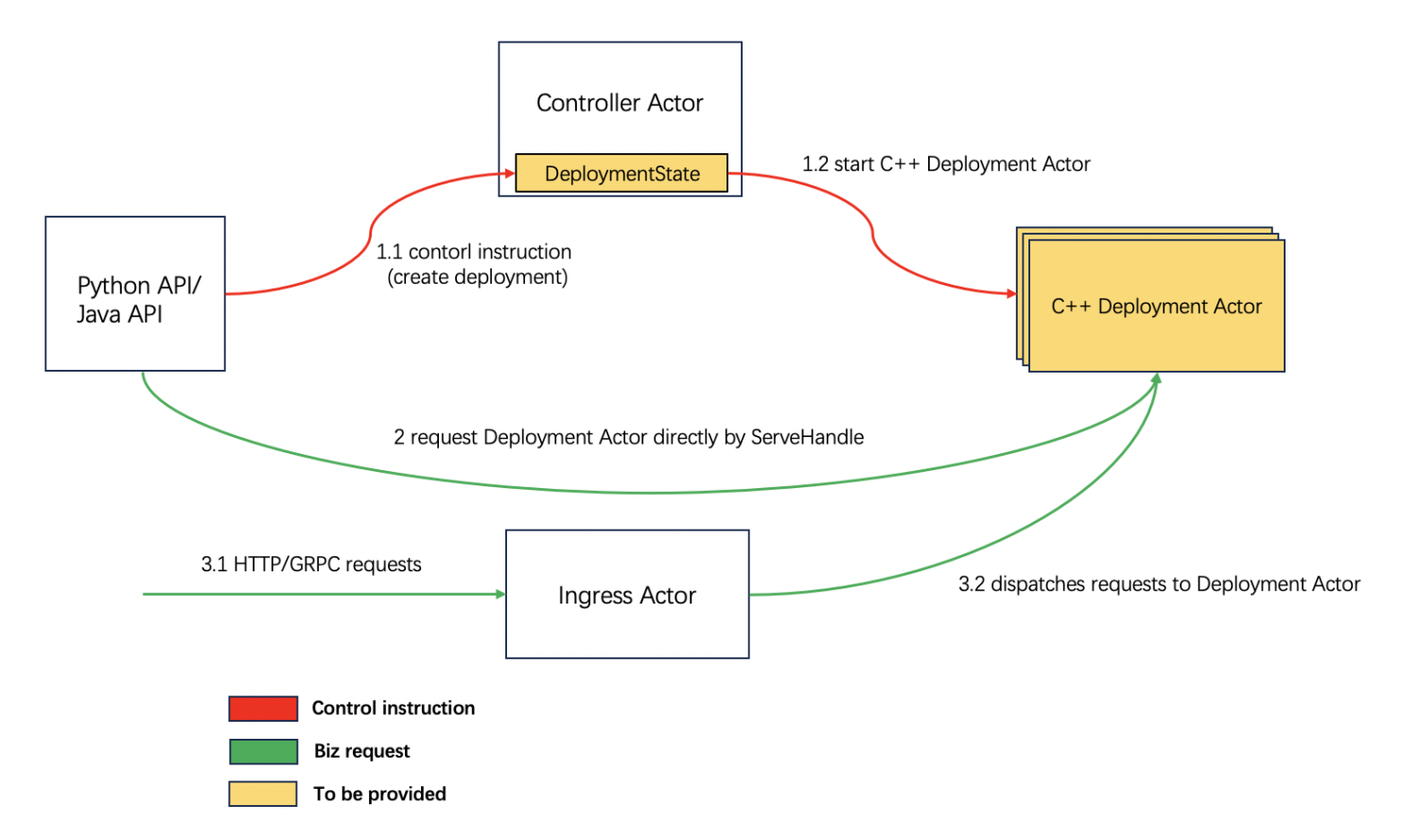
Ray Serve maintains Controller Actor and Ingress Actor. So these two roles are not related to the language of the user's choice. And they have the ability to manage cross-language deployments and route requests.
C++ Case Deduction
The businesses can send control commands to the Controller Actor of Ray Serve, which includes creating ingress, creating deployment, etc. When publishing C++ online services, the DeploymentState component needs to create C++ Deployment Actors. Users can call their business logic in Python/Java Driver, Ray task, or Ray Actor, and the requests will be dispatched to C++ Deployment Actors.
Package
C++ programs are typically compiled and packaged into three types of results: binary, static library, shared library.
- binary: C++ does not have a standard load binary API, and binaries compiled by different compilers may not be the same. Directly loading the binary can result in many uncontrollable factors.
- static library: Static library bundle all their dependencies together, whereas common utility libraries such as glog and boost may be loaded via dynamic dependencies in the Ray Serve Deployment. This can lead to a higher probability of conflicts when the same library exists as both a dynamic and static dependency.
- shared library: C++ provides a standard API for loading shared library, and it can reduce memory usage and prevent conflicts.
In conclusion, the business needs to package the system as a shared library to run it on Ray Serve.
Register function
Ray Serve will add SERVE_FUNC and SERVE_DEPLOYMENT macros to publish user Service as Deployment.
SERVE_FUNC: Resolving overloaded function registration;
SERVE_DEPLOYMENT: Publishing user Service as Deployment.
Example:
static RecommendService *CreateRecommendService(std::string request) {
return new RecommendService(request);
}
static RecommendService *CreateRecommendService(std::string request, int num) {
return new RecommendService(request, num);
}
static FeatureService *CreateFeatureService() {
return new FeatureService();
}
// Register function
SERVE_DEPLOYMENT(SERVE_FUNC(CreateRecommendService, std::string, int),
CreateFeatureService);
Compatibility, Deprecation, and Migration Plan
The new feature is to add C++ deployment for Ray Serve, without modifying or deprecating existing functionalities. The changes to the Ray Serve API are also adding new capabilities.
Test Plan and Acceptance Criteria
- Unit and integration test for core components
- Benchmarks on C++ Deployment
(Optional) Follow-on Work
- Init Ray Serve C++ project structure
- Create C++ Deployment through Python/Java API
- ServeHandler for C++
- Accessing C++ Deployment using Python/Java/C++ ServeHandle or HTTP