k8s-when-ready
 k8s-when-ready copied to clipboard
k8s-when-ready copied to clipboard
Wait for Kubernetes Jobs or Services to be running.
k8s-when-ready
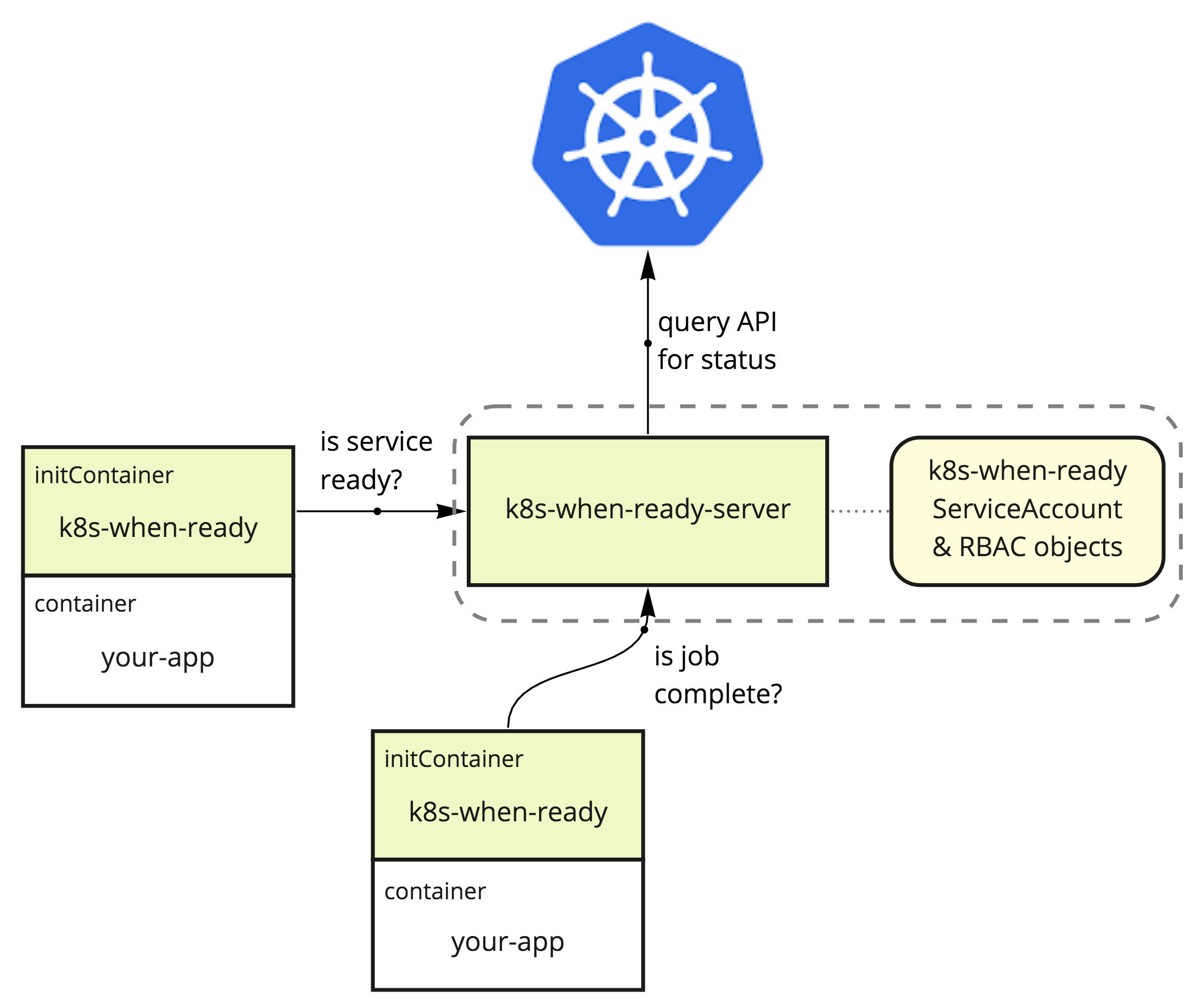
This utility is designed to be used as a Kubernetes initContainer that will wait for another Service or Job to become available before exiting.
The primary use for this tool would be to delay running a container until other dependency containers or jobs have run.
For example waiting to start a Job to create a database until the DB server is running, or waiting to run a Ruby Rake task like db:migrate until a DB server is running.
Why did you write this?
The original intent was to lessen the dependency on using Helm Hooks with the --wait flag to delay running jobs until services were started. Using Helm in this way had some issues because it waits for all pods to be running, not just certain ones that are actual dependencies.
This project was heavily inspired by groundnuty/k8s-wait-for but I had several issues using that script. I wanted to rewrite it in a language that could be easily unit tested. The resulting docker image for this project is larger than k8s-wait-for but in my opinion the easy of reading the code and the ability to rely on propper unit tests and separation of RBAC permissions outweighs the image size.
Why are there 2 images? (why a client and server?)
You will notice that this utility is split into a server portion that runs as it's own service, and a client portion that is intended to run in an init container.
This is because determining the status of jobs and services requires certain permissions on RBAC enabled clusters. Kubernetes requires that all containers defined by a deployment use the same ServiceAccount. This means that if the initContainers themselves were to check the pod states, you would have to add permissions to any ServiceAccounts in use, or add them to default. Adding permissions to default can be dangerous and expose information that should be secret.
To circumvent this, there is a server portion that can run with it's own ServiceAccount to grant it permissions. Then the initContainer-based client portion can simply query the server for status, without needing special permissions, and without risking exposing job and service definitions.
Usage
Server
The server portion is a central process for reporting the status of services and jobs. It is made separate from the client portion so that Kubernetes Roles and ServiceAccounts can be properly provisioned to isolate access to pod information.
The following yaml can be used to define the server.
Please find the latest versioned docker images from: https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready-server and https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready and use them in the yaml below.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: k8s-when-ready
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: k8s-when-ready
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services","pods"]
verbs: ["get","list"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs/status"]
verbs: ["get","list"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: k8s-when-ready
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: k8s-when-ready
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: k8s-when-ready
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: k8s-when-ready-server # If you change this, you will have to pass `--host={this name}` to the k8s-when-ready clients.
namespace: default
labels:
app: k8s-when-ready
spec:
ports:
- port: 3000 # If you change this, you will have to pass `--port={this port}` to the k8s-when-ready clients.
selector:
app: k8s-when-ready
type: ClusterIP
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: k8s-when-ready-server
namespace: default
spec:
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: k8s-when-ready
spec:
serviceAccountName: k8s-when-ready
containers:
- name: k8s-when-ready
image: jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready-server:latest # PLEASE use the newest versioned release from https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready-server
Client
The normal practice would be to use the jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready image as an initContainer for a job or service that you want to delay running until some other services are ready.
For example, if you have a Ruby on Rails project named my-api that you don't want to have run until your postgres DB is running, you could do:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-api
labels:
app: my-api
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: my-api
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cloud-services
tier: my-api
spec:
initContainers:
- name: init-wait-for-db
image: jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready:latest # PLEASE use the newest versioned release from https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready
args:
- --type=service
- --namespace=my-namespace
- --name=postgres
containers:
- image: 123abc.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/my-api:1.2.3
name: my-api
ports:
- containerPort: 80
env:
- name: RAILS_ENV
value: production
Available Arguments
You can pass these to the k8s-when-ready image using initContainers.[].args:
initContainers:
- name: ...
image: jeffvalore/k8s-when-ready:latest
args:
- --option=value
...
Options:
--type Whether to wait for a Service or a Job.
[required] [choices: "service", "job"]
--name The name of the service or job to wait for.
[string] [required]
--uptime The number of seconds of uptime an item should have before
considering it "running". If not specified, the default is 5
seconds for Services, 0 seconds for Jobs. [number]
--timeout The duration in seconds to wait before canceling the wait.
The process will exit with a non-0 exit code.
[number] [default: 300]
--poll-delay The duration in seconds to wait between each check to see if
the service is running. [default: 1]
--namespace, -n The namespace to check in. [default: "default"]
--host, -h The hostname of the k8s-when-ready-server.
[default: "k8s-when-ready-server"]
--port, -p The port for the k8s-when-ready-server. [default: "3000"]
Contributing
This project is built as a yarn monorepo and uses yarn "modern".
Set up yarn by enabling nodejs corepack (requires nodejs v16+)
corepack enable
To install dependencies:
yarn install
To run tests for both client and server:
yarn test
To build docker images for both client and server:
yarn build
To cut a new version:
./scripts/version.sh {next version number}
for example:
./scripts/version.sh 1.2.3
will build update package.json of all packages in the monorepo to the version, and make a git commit and tag with this version number.
GitHub actions will also run the unit tests when a push is detected.
To publish the docker images, create a new "Release" in GitHub using this version tag.