adaptive
 adaptive copied to clipboard
adaptive copied to clipboard
:chart_with_upwards_trend: Adaptive: parallel active learning of mathematical functions
.. summary-start
|logo| adaptive
|PyPI| |Conda| |Downloads| |Pipeline status| |DOI| |Binder| |Gitter| |Documentation| |Coverage| |GitHub|
Adaptive: parallel active learning of mathematical functions.
.. include:: logo.rst
adaptive is an open-source Python library designed to
make adaptive parallel function evaluation simple. With adaptive you
just supply a function with its bounds, and it will be evaluated at the
“best” points in parameter space, rather than unnecessarily computing all points on a dense grid.
With just a few lines of code you can evaluate functions on a computing cluster,
live-plot the data as it returns, and fine-tune the adaptive sampling algorithm.
adaptive shines on computations where each evaluation of the function
takes at least ≈100ms due to the overhead of picking potentially interesting points.
Run the adaptive example notebook live on Binder <https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/python-adaptive/adaptive/master?filepath=example-notebook.ipynb>_
to see examples of how to use adaptive or visit the
tutorial on Read the Docs <https://adaptive.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial/tutorial.html>__.
.. summary-end
Implemented algorithms
The core concept in adaptive is that of a learner. A learner
samples a function at the best places in its parameter space to get
maximum “information” about the function. As it evaluates the function
at more and more points in the parameter space, it gets a better idea of
where the best places are to sample next.
Of course, what qualifies as the “best places” will depend on your
application domain! adaptive makes some reasonable default choices,
but the details of the adaptive sampling are completely customizable.
The following learners are implemented:
.. not-in-documentation-start
Learner1D, for 1D functionsf: ℝ → ℝ^N,Learner2D, for 2D functionsf: ℝ^2 → ℝ^N,LearnerND, for ND functionsf: ℝ^N → ℝ^M,AverageLearner, for random variables where you want to average the result over many evaluations,AverageLearner1D, for stochastic 1D functions where you want to estimate the mean value of the function at each point,IntegratorLearner, for when you want to intergrate a 1D functionf: ℝ → ℝ.BalancingLearner, for when you want to run several learners at once, selecting the “best” one each time you get more points.
Meta-learners (to be used with other learners):
BalancingLearner, for when you want to run several learners at once, selecting the “best” one each time you get more points,DataSaver, for when your function doesn't just return a scalar or a vector.
In addition to the learners, adaptive also provides primitives for
running the sampling across several cores and even several machines,
with built-in support for
concurrent.futures <https://docs.python.org/3/library/concurrent.futures.html>,
mpi4py <https://mpi4py.readthedocs.io/en/stable/mpi4py.futures.html>,
loky <https://loky.readthedocs.io/en/stable/>,
ipyparallel <https://ipyparallel.readthedocs.io/en/latest/> and
distributed <https://distributed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/>_.
Examples
Adaptively learning a 1D function (the gif below) and live-plotting the process in a Jupyter notebook is as easy as
.. code:: python
from adaptive import notebook_extension, Runner, Learner1D
notebook_extension()
def peak(x, a=0.01):
return x + a**2 / (a**2 + x**2)
learner = Learner1D(peak, bounds=(-1, 1))
runner = Runner(learner, goal=lambda l: l.loss() < 0.01)
runner.live_info()
runner.live_plot()
.. raw:: html
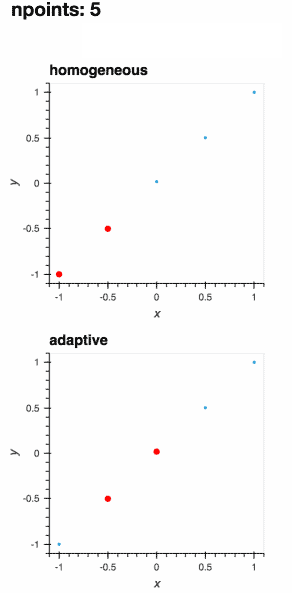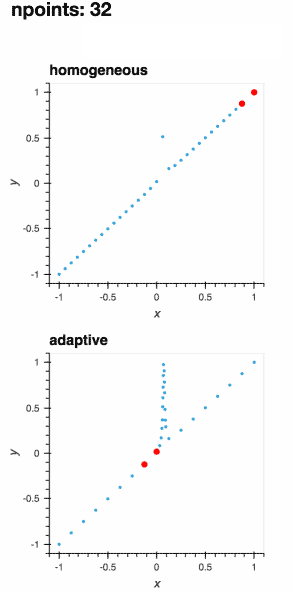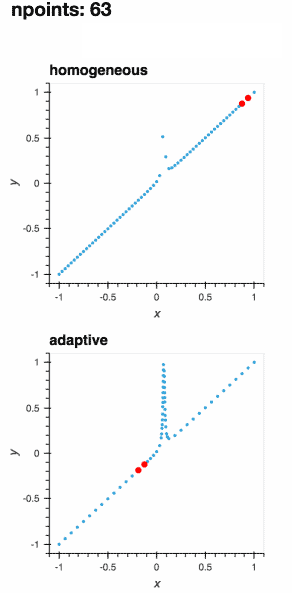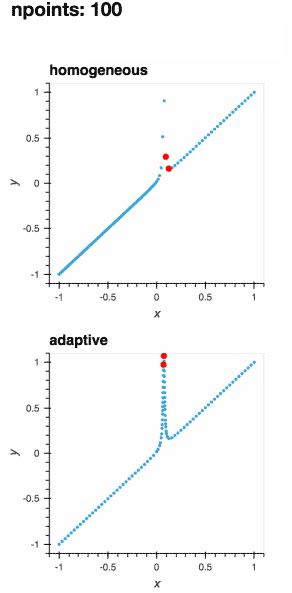


.. not-in-documentation-end
Installation
adaptive works with Python 3.7 and higher on Linux, Windows, or Mac,
and provides optional extensions for working with the Jupyter/IPython
Notebook.
The recommended way to install adaptive is using conda:
.. code:: bash
conda install -c conda-forge adaptive
adaptive is also available on PyPI:
.. code:: bash
pip install adaptive[notebook]
The [notebook] above will also install the optional dependencies for
running adaptive inside a Jupyter notebook.
To use Adaptive in Jupyterlab, you need to install the following labextensions.
.. code:: bash
jupyter labextension install @jupyter-widgets/jupyterlab-manager
jupyter labextension install @pyviz/jupyterlab_pyviz
Development
Clone the repository and run setup.py develop to add a link to the
cloned repo into your Python path:
.. code:: bash
git clone [email protected]:python-adaptive/adaptive.git
cd adaptive
python3 setup.py develop
We highly recommend using a Conda environment or a virtualenv to manage
the versions of your installed packages while working on adaptive.
In order to not pollute the history with the output of the notebooks, please setup the git filter by executing
.. code:: bash
python ipynb_filter.py
in the repository.
We implement several other checks in order to maintain a consistent code style. We do this using pre-commit <https://pre-commit.com>_, execute
.. code:: bash
pre-commit install
in the repository.
Citing
If you used Adaptive in a scientific work, please cite it as follows.
.. code:: bib
@misc{Nijholt2019,
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.1182437},
author = {Bas Nijholt and Joseph Weston and Jorn Hoofwijk and Anton Akhmerov},
title = {\textit{Adaptive}: parallel active learning of mathematical functions},
publisher = {Zenodo},
year = {2019}
}
Credits
We would like to give credits to the following people:
- Pedro Gonnet for his implementation of
CQUAD <https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/manual/html_node/CQUAD-doubly_002dadaptive-integration.html>_, “Algorithm 4” as described in “Increasing the Reliability of Adaptive Quadrature Using Explicit Interpolants”, P. Gonnet, ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 37 (3), art. no. 26, 2010. - Pauli Virtanen for his
AdaptiveTriSamplingscript (no longer available online since SciPy Central went down) which served as inspiration for the~adaptive.Learner2D.
.. credits-end
For general discussion, we have a Gitter chat channel <https://gitter.im/python-adaptive/adaptive>. If you find any
bugs or have any feature suggestions please file a GitHub
issue <https://github.com/python-adaptive/adaptive/issues/new>
or submit a pull request <https://github.com/python-adaptive/adaptive/pulls>_.
.. references-start .. |logo| image:: https://adaptive.readthedocs.io/en/latest/_static/logo.png .. |PyPI| image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/adaptive.svg :target: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/adaptive .. |Conda| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/install%20with-conda-green.svg :target: https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/adaptive .. |Downloads| image:: https://img.shields.io/conda/dn/conda-forge/adaptive.svg :target: https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/adaptive .. |Pipeline status| image:: https://dev.azure.com/python-adaptive/adaptive/_apis/build/status/python-adaptive.adaptive?branchName=master :target: https://dev.azure.com/python-adaptive/adaptive/_build/latest?definitionId=6?branchName=master .. |DOI| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/doi-10.5281%2Fzenodo.1182437-blue.svg :target: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1182437 .. |Binder| image:: https://mybinder.org/badge.svg :target: https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/python-adaptive/adaptive/master?filepath=example-notebook.ipynb .. |Gitter| image:: https://img.shields.io/gitter/room/nwjs/nw.js.svg :target: https://gitter.im/python-adaptive/adaptive .. |Documentation| image:: https://readthedocs.org/projects/adaptive/badge/?version=latest :target: https://adaptive.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest .. |GitHub| image:: https://img.shields.io/github/stars/python-adaptive/adaptive.svg?style=social :target: https://github.com/python-adaptive/adaptive/stargazers .. |Coverage| image:: https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/python-adaptive/adaptive :target: https://codecov.io/gh/python-adaptive/adaptive .. references-end