erp-mes-backend
 erp-mes-backend copied to clipboard
erp-mes-backend copied to clipboard
ERP-MES RESTful Web Service created with @patsaf [2018]
ERP-MES (Back-end)
- Overview
- Back-end technologies
-
ERP features
- Staff management
- Delivery and warehouse management
- Finance management and reporting
- Production planning
- Mailbox
-
MES features
- Key Performance Indicators
- Instant Messenger
- Kaizen Teian
- Kanban Board
- Task scheduling algorithm
- Security
- Project structure
- Example local configuration
- Front-end repository
- Heroku platform
Overview ›››
Back-end layer of RESTful web service created as engineering thesis by @patsaf and @plkpiotr.
ERP-MES is intended for management of a forwarding company.
The application was equipped with features typical of Enterprise Resource Planning and Manufacturing Execution System.
Back-end technologies ›››
- Java 8
- Spring Framework (MVC, Security, Data JPA)
- Spring Boot (Mail, Websocket)
- JSON Web Token
- JUnit
- Lombok
- Hibernate
- PostgreSQL 9
- Maven 4
- Heroku
ERP features ›››
Staff management ›
The company staff is divided into managers and employees, each of whom is the application's user. In their own profile, each user can, for example, submit holiday requests. Managers can approve such requests for their subordinates. Basic contact (and contract - although only for the logged in user) information may be found in a user's profile.
Delivery and warehouse management ›
Keeping track of the items stored in the warehouse. Automatic generation of recommended deliveries, based on customer demand and lean management principles. All online store operations (orders, complaints, returns) are immediately reflected on the warehouse state.
Finance management and reporting ›
Storing, updating and analysing all the company's financial operations. Automatic generation of monthly reports. Financial estimates for a given period of time (by default: month), which are calculated based on data gatheres by previous reports.
Production planning ›
Monitoring if the amount of work planned for a given day does not exceed the assumed daily plan and if so - notifying the person responsible. Possibility to introduce special production plans. Making sure all orders, complaints and returns are resolved without delays.
Mailbox ›
Automatic generation of first login password and sending it via e-mail when registering a new user. Automatic notifications of order/complaint/return status change sent to customers. Possibility of e-mail communication between the company and its customers.
MES features ›››
Key Performance Indicators ›
Evaluation of the work-in-progress expressed in mean times, number of tasks and suggestions by category - for one employee and the whole team.

Instant Messenger ›
Providing communication between employees in real time and documenting time and author's initials.

Kaizen Teian ›
Employee suggestion system with possibility of searching records.
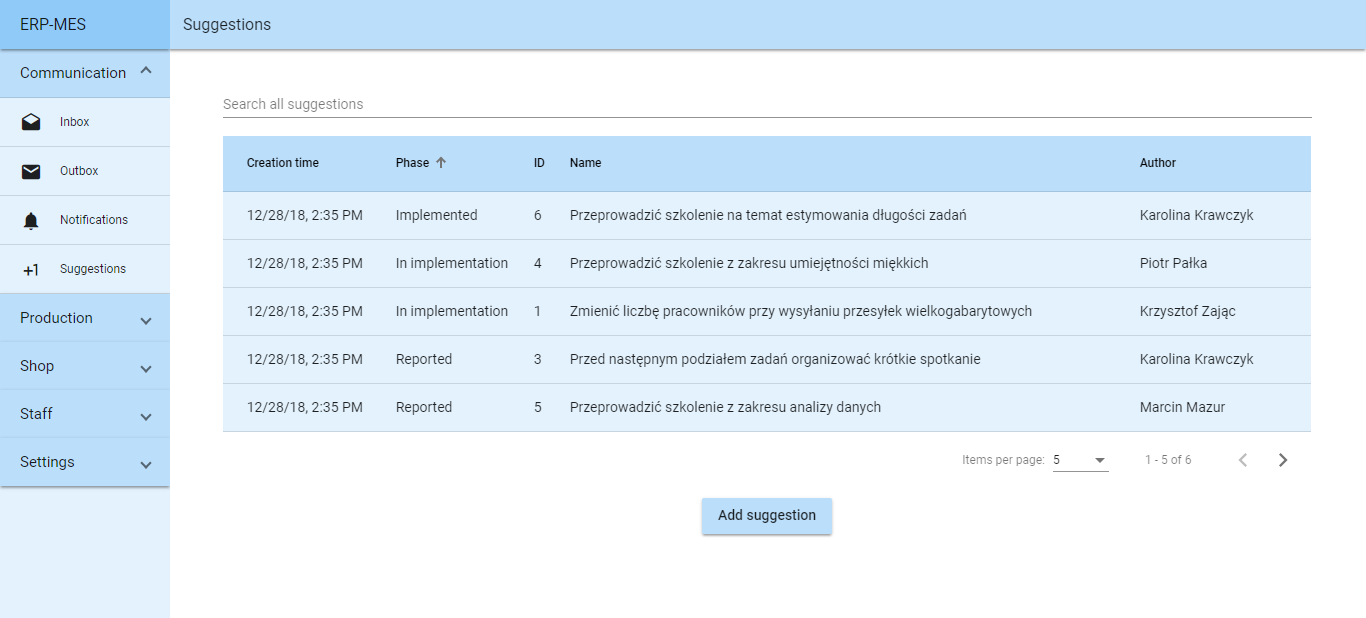
Kanban Board ›
Visualization of tasks created in the last four weeks for one person.
Task scheduling algorithm ›
Planning and reduction of total time allowed for tasks through scheduling algorithm.

Security ›››
- Only registered users can acces the application.
- Access is granted based on the JWT token sent as request header.
- Upon first login attempt, a first login password is used and the user needs to set their own password.
- Each request is filtered by Spring Security mechanisms and access to given resources is granted based on the user's role in the company.
Project structure ›››
└────src
├───main
│ ├───java
│ │ └───com
│ │ └───herokuapp
│ │ └───erpmesbackend
│ │ └───erpmesbackend
│ │ ├───communication
│ │ │ ├───config
│ │ │ ├───controller
│ │ │ ├───dto
│ │ │ ├───factory
│ │ │ ├───model
│ │ │ ├───repository
│ │ │ ├───request
│ │ │ └───service
│ │ ├───exceptions
│ │ ├───production
│ │ │ ├───controller
│ │ │ ├───dto
│ │ │ ├───factory
│ │ │ ├───model
│ │ │ ├───repository
│ │ │ ├───request
│ │ │ └───service
│ │ ├───security
│ │ ├───shop
│ │ │ ├───controller
│ │ │ ├───factory
│ │ │ ├───model
│ │ │ ├───repository
│ │ │ ├───request
│ │ │ └───service
│ │ └───staff
│ │ ├───controller
│ │ ├───dto
│ │ ├───factory
│ │ ├───model
│ │ ├───repository
│ │ ├───request
│ │ └───service
│ └───resources
│ └───db
│ └───changelog
└───test
└───java
└───com
└───herokuapp
└───erpmesbackend
└───erpmesbackend
└───erpmesbackend
└───controllers
Example local configuration ›››
application.properties file:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/erpmes
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=postgres1
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create
Front-end repository ›››
Find front-end repository on Github: plkpiotr/erp-mes-frontend
Heroku platform ›››
Check out ERP-MES: erp-mes-backend.herokuapp.com and erp-mes-frontend.herokuapp.com.
Visit both of the links. First of them launches back-end layer and the database (if it is inactive) while the second contains front-end layer with login form.
Then use one of the following data:
Email: [email protected]
Password: haslo123
or
Email: [email protected]
Password: haslo123