Open area/grid graph routing
In this question on Stackoverflow a user asked about Theta Star, and the name made me curious: https://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/380920/is-there-a-routing-solution-for-postgis-that-supports-theta-star
Right now pgRouting algorithms require a network model. Would it possible and interesting to also add routing functions for "open areas" or "grid graps"? There are various use cases. Routing on the sea for example is one.
Some links:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theta*
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Any-angle_path_planning
After browsing the web and some papers, here is an approach that I think pgRouting can use for routing through open spaces. We would basically generate grids/spiders on the open space and convert it into a routable node network. This could be used as a new form of pgr_dijkstra().
I am not sure if there has been a discussion on this somewhere else. You might have already thought about the below idea but for sake of discussion here I decided to post it.
Input
The input arguments could be as follows:
- Weighted geometries (say Polygon)
- ST_StartPoint
- ST_EndPoint
- grid node distance (optional)
Sample Input
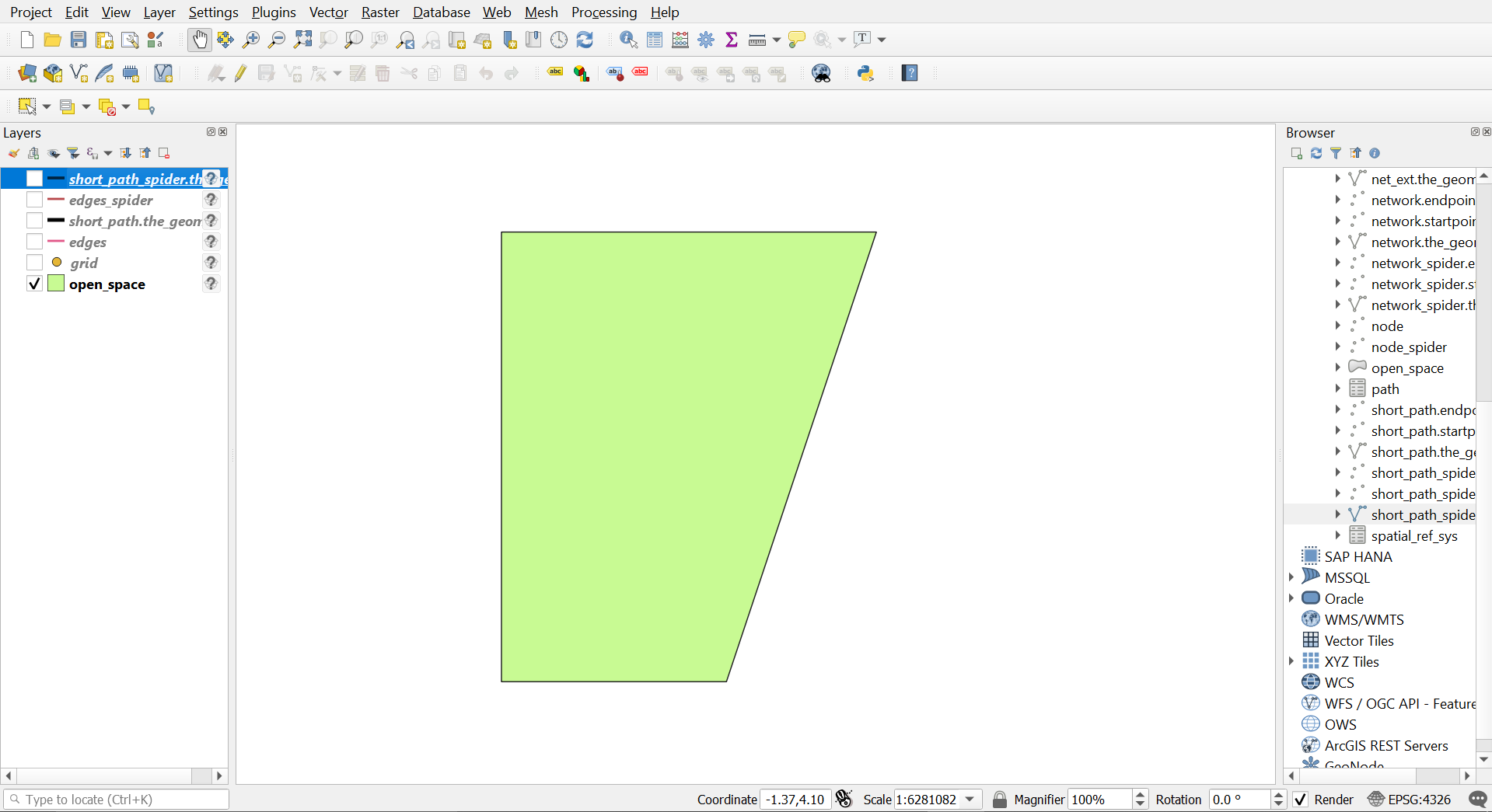
visualised using QGIS
Preprocessing
Since pgRouting deals with node networks, we can create grids/spiders of distance passed as an argument insider the open space. Followed by adding edges between the grid/spider nodes. After this step we will have sequence IDs assigned to each node in the grid, which will be used later.
Gridify
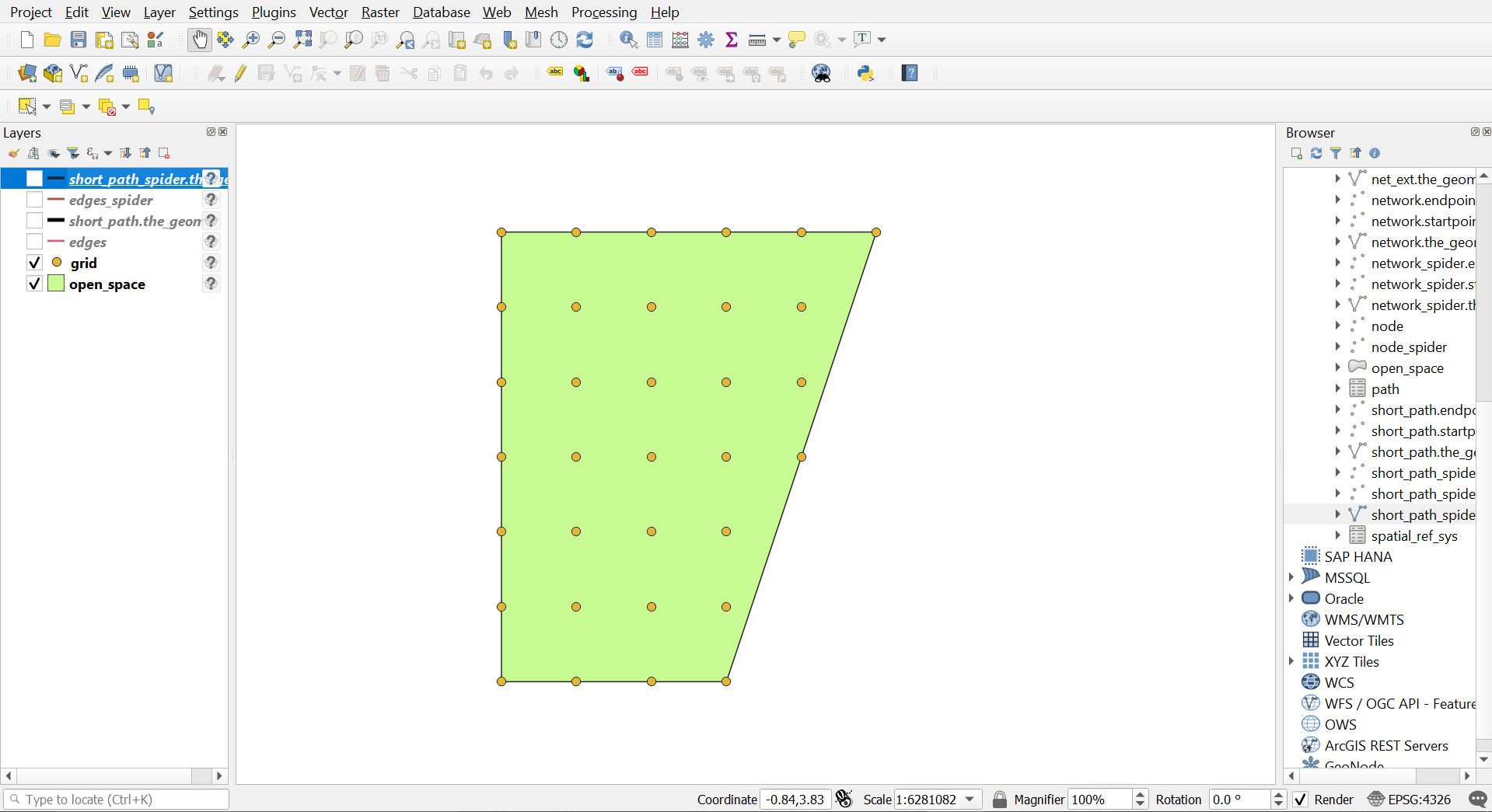
Grid 10 meter
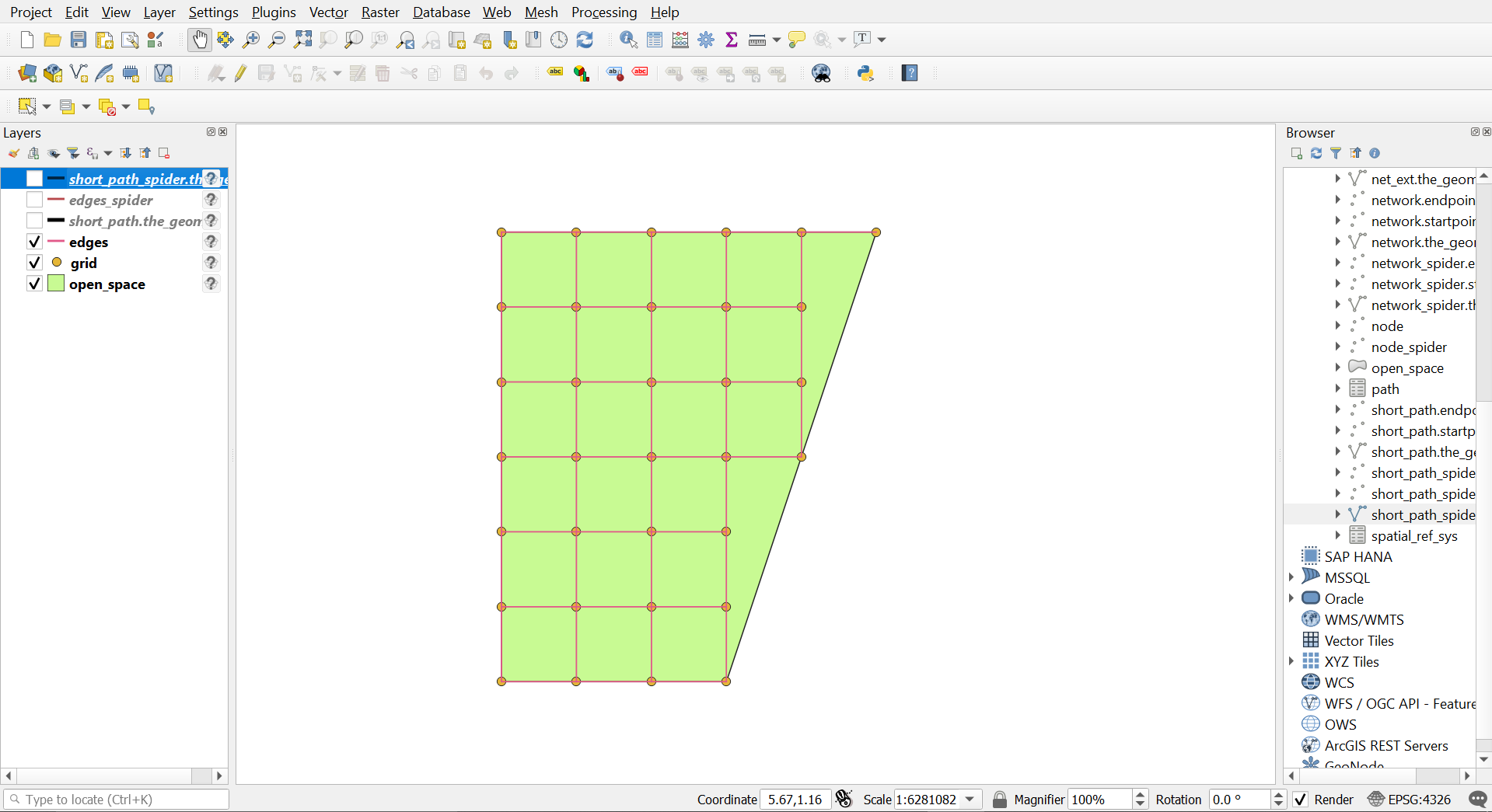
Spider 10 meter
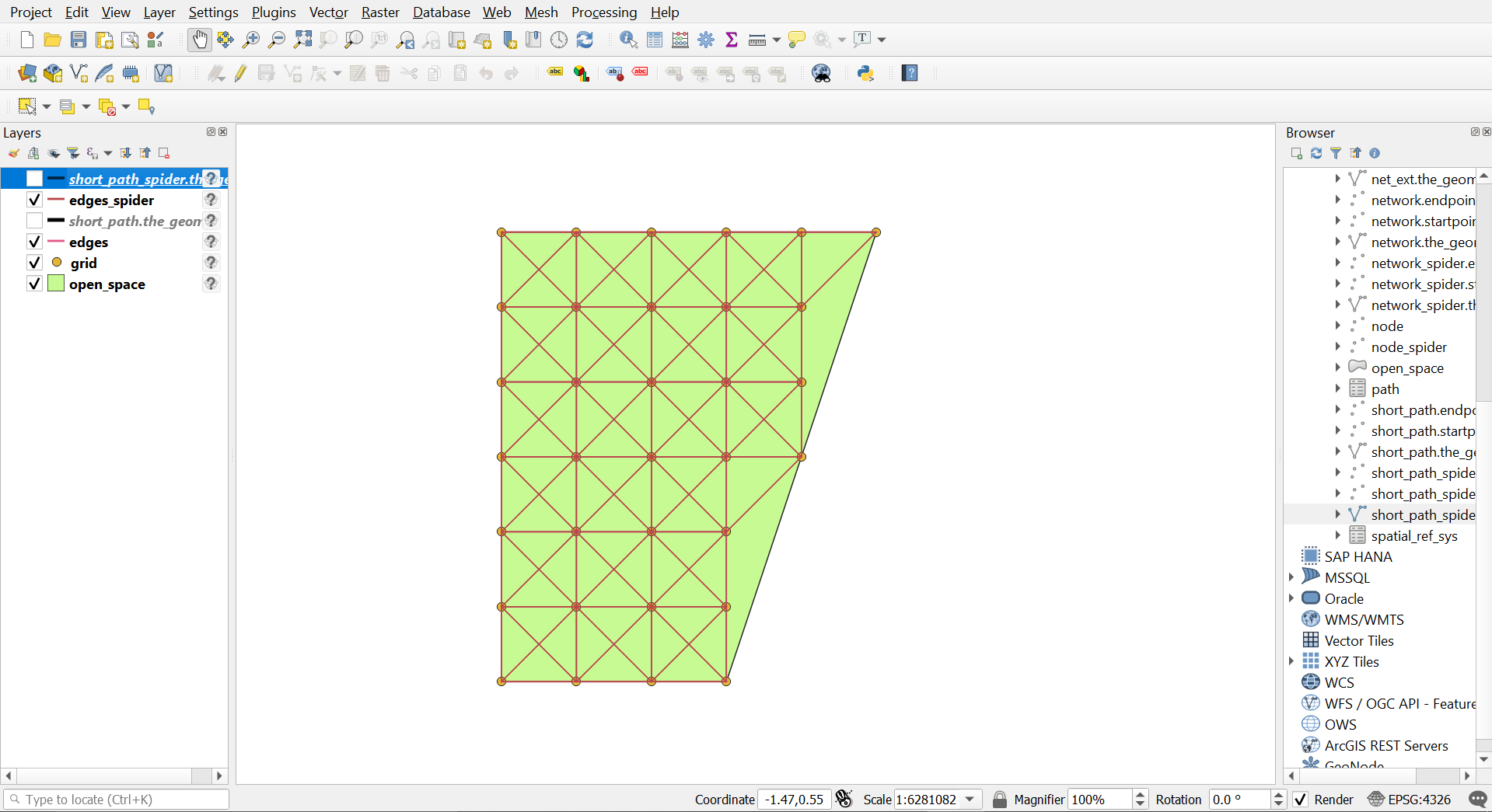
pgRouting Query
Since we have a routable node network now, we can pass it to the pgr_dijkstra() and get the required path. The final output will be a normal output with the sequence IDs of each node and its geometry (if needed).
Grid 10 meter output
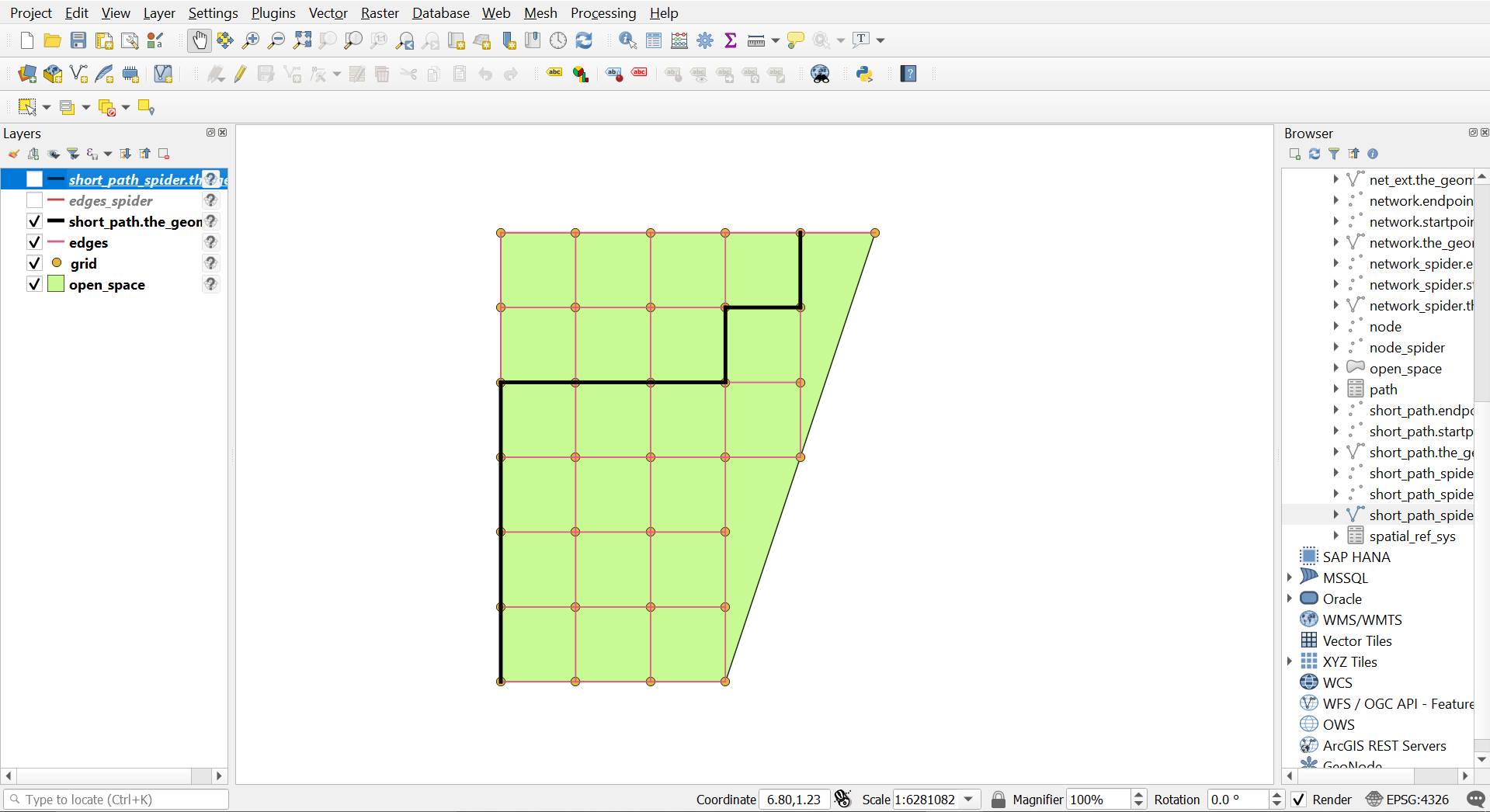
The total distance from Start Point to End Point is 100 meters (considering each edge is 10 meters which is the grid node distance).
Spider 10 meter output
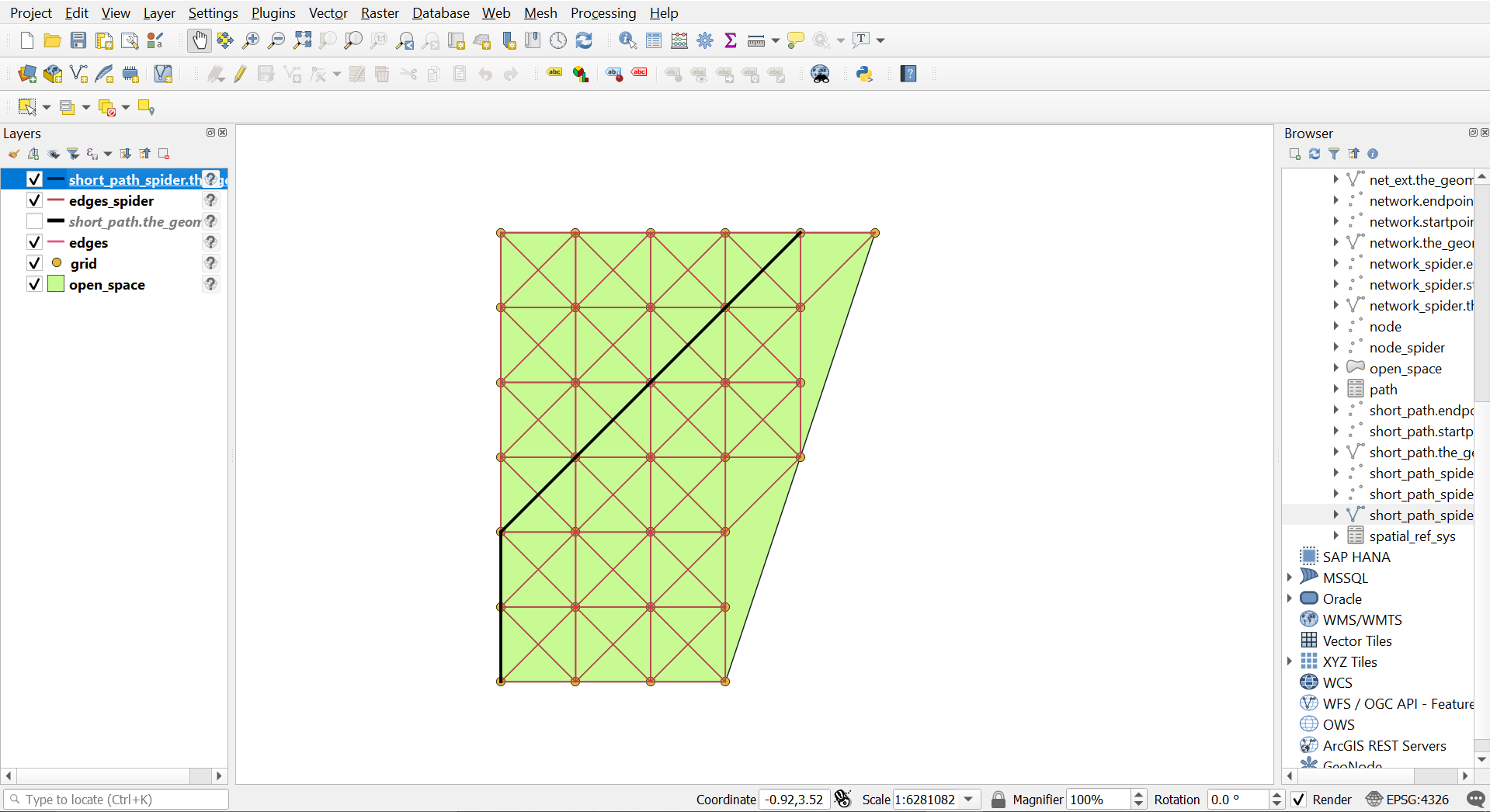
The total distance from Start Point to End Point is around 76.57 meters (considering each edge is 10 meters which is the grid node distance).
Here is a paper that has a comparative study of various algorithms for open space routing - https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/10095020.2017.1399675?needAccess=true
As for theta* in particular, I am not aware of any library which will have it implemented. Would like to know your thoughts on this.
Hi @sauravUppoor I see this as a handy preprocessing function. Once you call createTopology it will consume this open space network and enrich the graph.
Yes, this would be something similar to createTopology and part of preparing a network.
It shouldn't be too difficult to develop, and once there is a graph network pgRouting functions would work as usual.
If someone needs this or wants to contribute this functionality, that's always appreciated. There should be plenty of resources how to contribute, and it's always possible to ask on the mailing list or in chat https://gitter.im/pgRouting/pgrouting
Remember that routing graphs do not use geometries, How would this function work when the data does not have geometries?
Example: From the graph in wiki The following creates the route from 1 to 5.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS table1;
CREATE TABLE table1 (
id SERIAL,
source INTEGER,
target INTEGER,
cost FLOAT
);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (1, 2, 7);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (1, 3, 9);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (1, 6, 14);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (2, 3, 10);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (2, 4, 15);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (3, 6, 2);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (3, 4, 11);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (4, 5, 6);
INSERT INTO table1 (source, target, cost) VALUES (5, 6, 9);
SELECT * FROM pgr_dijkstra(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost FROM table1',
1, 5, false);
What are the "open spaces" in that graph? The graph can be drawn with lines crossing (like if they were bridges or tunnels on a street) That grid generation, wouldn't that be more of a PostGIS function instead of a pgRouting function? like for example: https://postgis.net/docs/manual-dev/ST_SquareGrid.html Is it pgRouting's job prepare all possible ways a geometry of a graph a front end can have?
I still added the Functionality request, just in case
Note that the "network model" does not imply geometry
Hello @cvvergara Regarding "open space" I see it as some randomly shaped region with no nodes/edges within it; thus routing through it could be areal (like in a sea, park, beach) and not linear (like roads). We would need to construct some edges within it to route through it.
I wasn't aware of the function ST_SquareGrid. I think some modifications might be needed in its results (to convert it to edge table since it returns a set of Polygon geometry) but I guess it is what we intend to do.
So few approaches for the above task could be:
- Use PostGIS' function to make grids and convert them to some edge table.
- Perhaps have a new function in pgRouting or extend
createTopologyto handle the making of grids (Grid, Spider, Skeleton, Visibility) and routing network both since it somewhat aligns with pgRouting's Topology family of functions?
@sauravUppoor In pgRouting you can create a graph that represents relationships. you can find the shortest path in the relation with people. How do you define an empty space in such a graph? A graph is an ordered pair G = ( V , E ) G=(V,E) comprising: V, a set of vertices (also called nodes or points); E ⊆ { { x , y } ∣ x , y ∈ V and x ≠ y }
Please find in graph theory what is "open space" of a graph.
@sauravUppoor FYI the majority of the topology functions existed before I arrived to pgRouting. That is the connection with PostGIS when you have a geometry topology and want to convert it to a graph topology to be able to use pgRouting's functions. pgRouting is a graph algorithms library, if you find a graph algorithm that deal with "open areas" on graphs then it is for pgRouting, but if the algorithm involves geometries the it is for PostGIS.
The more I write, the more I see this is not for pgRouting, so I removed the functionality request
I agree with what @cvvergara is saying. This is a preprocessing step before pgRouting kicks in. If the geometries are provided via whatever algorithm (i.e. ST_SquareGrid) to subdivide a closed polygon one can call createTopology() which will add these as vertices & edges to the graph.