sngan_projection
 sngan_projection copied to clipboard
sngan_projection copied to clipboard
How to combine wgan and spectral norm?
Your spectral normalization normalizes the spectral norm of the weight matrix W so that it satisfies the Lipschitz constraint = 1. So we consider whether to combine the wasserstein gan with spectral normalization or not?
So, we have done some related experiments using wgan with sn normalization(remove gradient penalty). However, The network is very unstable and hard to generate very high-quality samples.
We hope to know how to combine wgan and your sn normalization without gradient penalty?
@takerum
Hi,
We have tried the combination of wgan loss and spectral normalization, but it does not work. We are not sure why that happens, and also happy if you have ideas on that problem!
Recently, I combine wgan loss and spectral norm, and got a better result than before. Some changes in our experiments.
(1) D network, using spectral norm, but remove fully_connect layers (2) Using RMSprop instead of Adam. (3) Add a regu term for D loss(proposed by pg-gan) to keep the output values from drifting too far away from zero:
0.0001 * tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.D_pro_logits))
You can try, these are for reference only.
If necessary, I will public this code. --OO--
Thanks so much! and there perhaps are some people who have the same issue, so I appreciate if you make your implementation public.
@takerum Ask you some questions:
- Table 2 in SN-GAN paper, How do you calculate the FID score of real data? (7.8)
- Table 2 How many generated samples are used for getting FID or Inception scores? 5000 or 50000?
@takerum Your paper used 5000 samples to compute FID and Inception score. But in improved-gan paper, they use 50000 samples to get Inceptions scores.
????
Table 2 in SN-GAN paper, How do you calculate the FID score of real data? (7.8)
We sample 10000 images on test set and 5000 images on training set and calculate FID on the two sets of the images.
Table 2 How many generated samples are used for getting FID or Inception scores? 5000 or 50000?
Your paper used 5000 samples to compute FID and Inception score. But in improved-gan paper, they use 50000 samples to get Inceptions scores.
Both of the original paper and our paper use 50,000 samples for calculating the "mean" and "std" of the inception scores. The original paper and our paper calculate inception score with 5,000 samples and repeated 10 times to estimate the mean and variance of inception scores on each independently generated set of images. For FID, we calculate it with 5,000 samples and report the value, because we found that the variation of FID within independent sets is very small compared to the value of FID.
ok, thanks
I got 7.78 scores of FID for real data.
For FID, we calculate it with 5,000 samples and report the value, because we found that the variation of FID within independent sets is very small compared to the value of FID.
Friendly PSA: don't do this. The FID estimator has very low variance across runs, but very strong bias, especially due to the sample size; the numbers can only be compared with a consistent sample size, and most people use 50,000. Check out section 4 (starting page 7) and appendix D (starting page 30) of our paper Demystifying MMD GANs for more about this.
@takerum Now, I use tensorflow to implement dcgan+sn. The training parameter is
batch_size=16; softplus function for standard loss; learn_rate=0.002; sn=True; not resnet; n_critic=5; beta2=0.9; iterations = 100,000; dataset=cifar10; The architecture is same to Table 3(a)
I got 7.06+-0.08 inception scores, which is lower than 7.42+-0.08 of table 2 in your paper. Can you tell me the reason?
So, I want to ask you some question about the experiments corresponding to inception score of sn-gans in cifar10(7.42+-0.08) ?
(1)What is the number of all iterations? (2)Are you using decay of learning rate? (3)The init methods of weights.
please look at https://github.com/pfnet-research/chainer-gan-lib. This repository includes the reproducing code of SN-GANs on CIFAR-10 dataset.
thank you
@takerum , using the default parameters?
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Train script')
parser.add_argument('--algorithm', '-a', type=str, default="dcgan", help='GAN algorithm')
parser.add_argument('--architecture', type=str, default="dcgan", help='Network architecture')
parser.add_argument('--batchsize', type=int, default=64)
parser.add_argument('--max_iter', type=int, default=100000)
parser.add_argument('--gpu', '-g', type=int, default=0, help='GPU ID (negative value indicates CPU)')
parser.add_argument('--out', '-o', default='result', help='Directory to output the result')
parser.add_argument('--snapshot_interval', type=int, default=10000, help='Interval of snapshot')
parser.add_argument('--evaluation_interval', type=int, default=10000, help='Interval of evaluation')
parser.add_argument('--display_interval', type=int, default=100, help='Interval of displaying log to console')
parser.add_argument('--n_dis', type=int, default=5, help='number of discriminator update per generator update')
parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.5, help='hyperparameter gamma')
parser.add_argument('--lam', type=float, default=10, help='gradient penalty')
parser.add_argument('--adam_alpha', type=float, default=0.0002, help='alpha in Adam optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--adam_beta1', type=float, default=0.0, help='beta1 in Adam optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--adam_beta2', type=float, default=0.9, help='beta2 in Adam optimizer')
parser.add_argument('--output_dim', type=int, default=256, help='output dimension of the discriminator (for cramer GAN)')
yes we used the default parameters other than those we specified here: https://github.com/pfnet-research/chainer-gan-lib/blob/master/example.sh#L8
Thanks!
@zhangqianhui Thanks for the suggestion! Should we include all below? Or which one is the most important for that wgan works with spectral norm?
(1) D network, using spectral norm, but remove fully_connect layers (2) Using RMSprop instead of Adam. (3) Add a regu term for D loss(proposed by pg-gan) to keep the output values from drifting too far away from
Sorry, I am not sure. You can try.
@takerum hello, can you help me to check this implement of spectral norma function below?
def spectral_norm(w, iteration= 1):
w_shape = w.shape.as_list()
w = tf.reshape(w, [-1, w_shape[-1]])
# w = tf.reshape(w, [1, w.shape.as_list()[0] * w.shape.as_list()[1]])
u = tf.get_variable("u", [1, w.shape.as_list()[-1]], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(), trainable=False)
u_hat = u
v_hat = None
for i in range(iteration):
"""
power iteration
Usually iteration = 1 will be enough
"""
v_ = tf.matmul(u_hat, tf.transpose(w))
v_hat = _l2normalize(v_)
u_ = tf.matmul(v_hat, w)
u_hat = _l2normalize(u_)
#real_sn = tf.svd(w, compute_uv=False)[...,0]
sigma = tf.matmul(tf.matmul(v_hat, w), tf.transpose(u_hat))
w_norm = w / sigma
#Get the real spectral norm
#real_sn_after = tf.svd(w_norm, compute_uv=False)[..., 0]
#frobenius norm
#f_norm = tf.norm(w, ord='fro', axis=[0, 1])
#tf.summary.scalar("real_sn", real_sn)
tf.summary.scalar("powder_sigma", tf.reduce_mean(sigma))
#tf.summary.scalar("real_sn_afterln", real_sn_after)
#tf.summary.scalar("f_norm", f_norm)
with tf.control_dependencies([u.assign(u_hat)]):
w_norm = tf.reshape(w_norm, w_shape)
return w_norm
I can not find the problem, but hard to get the same scores using the default hyper-paramters that you mentioned above?
@zhangqianhui I think you should try to add u_hat = tf.stop_gradient(u_hat) and v_hat = tf.stop_gradient(v_hat) to avoid the gradient from v_hat and u_hat to w. Like the code below from @takerum, _v and _u have no gradient to W, but sigma has.

My implementation: https://github.com/LynnHo/GAN-Techniques-Tensorflow/blob/master/tflib/layers/layers.py
@zhangqianhui This is my SN implementation in TF.
def sn(W, collections=None, seed=None, return_norm=False, name='sn'):
shape = W.get_shape().as_list()
if len(shape) == 1:
sigma = tf.reduce_max(tf.abs(W))
else:
if len(shape) == 4:
_W = tf.reshape(W, (-1, shape[3]))
shape = (shape[0] * shape[1] * shape[2], shape[3])
else:
_W = W
u = tf.get_variable(
name=name + "_u",
shape=(FLAGS.num_sn_samples, shape[0]),
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer,
collections=collections,
trainable=False
)
_u = u
for _ in range(FLAGS.Ip_sn):
_v = tf.nn.l2_normalize(tf.matmul(_u, _W), 1)
_u = tf.nn.l2_normalize(tf.matmul(_v, tf.transpose(_W)), 1)
_u = tf.stop_gradient(_u)
_v = tf.stop_gradient(_v)
sigma = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(_u * tf.transpose(tf.matmul(_W, tf.transpose(_v))), 1))
update_u_op = tf.assign(u, _u)
with tf.control_dependencies([update_u_op]):
sigma = tf.identity(sigma)
if return_norm:
return W / sigma, sigma
else:
return W / sigma
@LynnHo @takerum thanks
@zhangqianhui 您好,您是使用WGAN损失函数Ex∼qdata[D(x)]−Ez∼p(z)[D(G(z))] 和在判别器中使用谱归一化?这样进行有效果吗? 之前我试过直接在WGAN-GP加入谱归一化,结果生成器和判别器的loss都是nan。
@IPNUISTlegal It works in my experiments, but could not get the higher inception scores than sn-gan
@zhangqianhui
@takerum
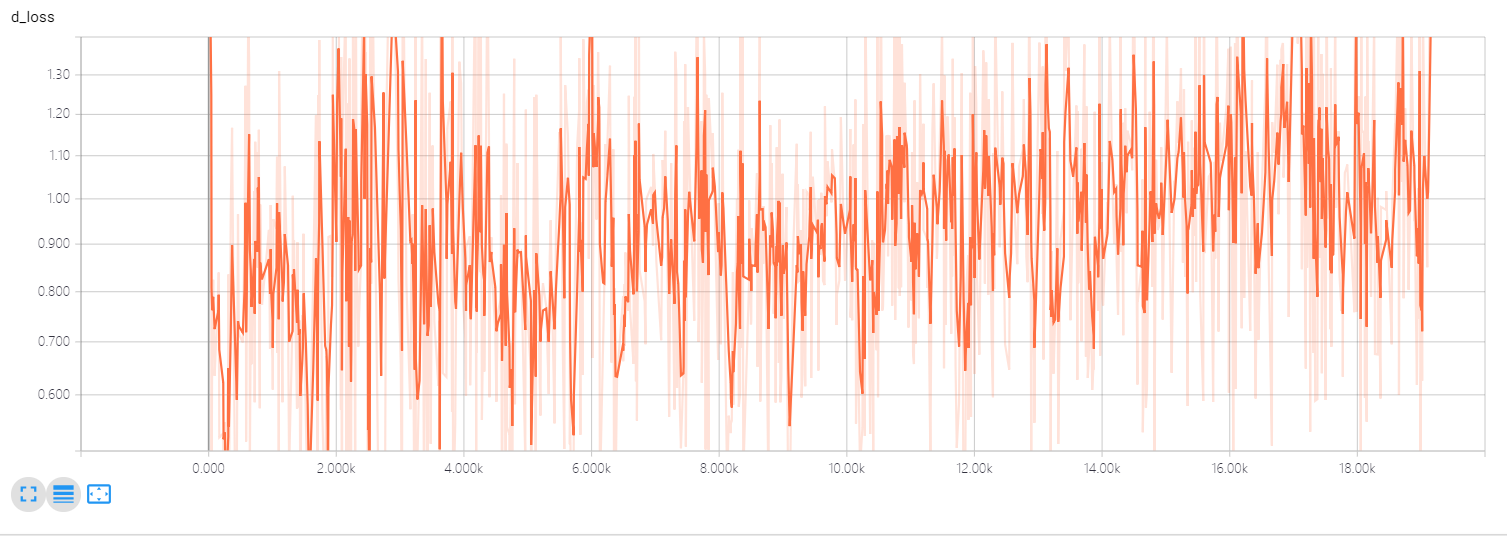 i apply hinge loss and spectral normalization to my experiment ,which actually outperform the WGAN-GP loss function with the same network structure.
a little pity, the discriminator loss does not convergence to a certain value and crazy up and down swing!
why?confused me many days
thx!(#^.^#)
i apply hinge loss and spectral normalization to my experiment ,which actually outperform the WGAN-GP loss function with the same network structure.
a little pity, the discriminator loss does not convergence to a certain value and crazy up and down swing!
why?confused me many days
thx!(#^.^#)
Is it the curve of D loss using hinge loss ?
@zhangqianhui
yeah,it is the D loss using hinge loss and does not convergence to a certain value.
why?
thx