fantasy-land-traditional-chinese
 fantasy-land-traditional-chinese copied to clipboard
fantasy-land-traditional-chinese copied to clipboard
Fantasy Land Specification 繁體中文文件
Fantasy Land Specification
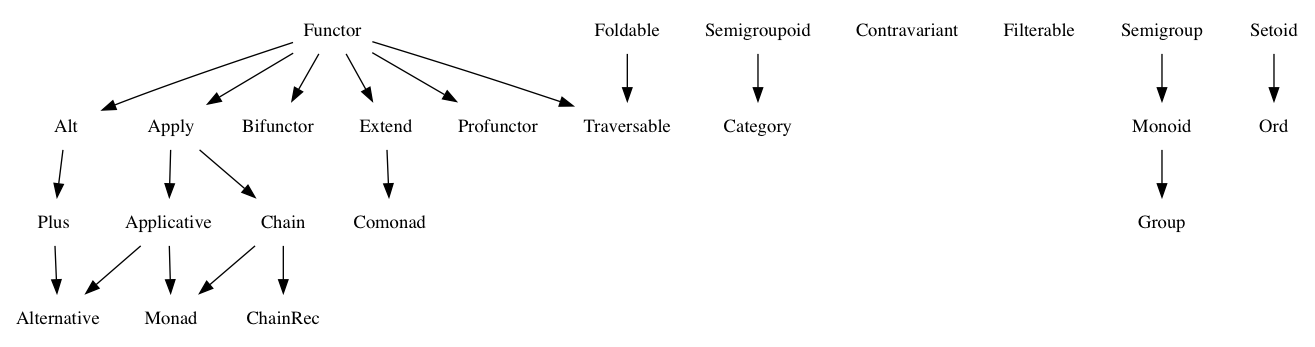
概述
代數是一組值,一組操作,它是封閉的,必須遵守一些規則。
每個 Fantasy Land 代數是一個獨立的規範。一個代數可能依賴於其他必須實現的代數。
術語
- 「value」是任何 JavaScript 的值,包含具有下面定義的的任何結構。
- 「equivalent」對於給定的值有一個等價的定義。這個定義應該確保這兩個值可以在一個尊重抽象的程式中安全的被交換出來。例如:
- 如果兩個 list 所有指數都是相同的,那它們是相同的。
- 兩個被解釋為 dictionary 的 JavaScript 純 Object,當它們有相等的 key 時,它們是等價的。
- 當兩個 Promise 產生相等的值時,它們是等價的。
- 如果兩個函式輸入相同的值,且得到相同的輸出,它們是等價的。
Type Signature 符號
以下介紹文件中使用的 Type Signature 符號:
-
::「is a member of」。-
e :: t可以讀作:「表達式e是類型t的一位成員」。 -
true :: Boolean- 「true是類型Boolean的一位成員」。 -
42 :: Integer, Number- 「42是類型Integer和Number的一位成員」。
-
-
新 type 可以藉由 type constructor 被建立。
- Type constructor 可以接受零個或多個 type 參數。
-
Array是一個 type constructor,它接受一個 type 參數。 -
Array String是一個字串陣列的 type。以下每個 type 都是Array String:[]、['foo', 'bar', 'baz']。 -
Array (Array String)是一個陣列的字串陣列 type。以下每個 type 都是Array (Array String):[]、[ [], [] ]、[ [], ['foo'], ['bar', 'baz'] ]。
-
小寫字母代表 type 變數。
- Type 變數可以接受任何 type,除非已經透過 type constraint 被限制(參考以下 fat arrow)。
-
->(arrow)Function type constructor。-
->是一個 infix type constructor,它接受兩個 type 參數,左邊參數是輸入的 type,右邊的則是輸出 type。 -
->的輸入 type 可以是一組 type 來建立接受零個或多個的函式類型。語法是:(<input-types>) -> <output-type>,其中<input-types>包含零個或多個逗號(,)來分隔 type 表示,對於一元函式可以省略括號。(參考此 Issue 解釋) -
String -> Array String是一個透過函式滿足的 type,接受一個String並回傳一個Array String。 -
String -> Array String -> Array String是一個透過函式滿足的 type,它接受一個String並回傳一個函式接受一個Array String最後回傳一個Array String。 -
(String, Array String) -> Array String是一個透過函式滿足的 type,它接受一個String和一個Array String作為參數,並回傳一個Array String。 -
() -> Number是一個透過函式滿足的 type,它不接受任何的參數,並回傳一個Number。
-
-
~>(squiggly arrow)Method type constructor。- 當函式是一個 Object 的屬性時,它被稱為一個方法。所有的方法有一個隱式的參數 type - 它們是屬性的 type。
-
a ~> a -> a是 typea的 Object 上的方法所滿足的類型,它將 typea作為參數並回傳 typea的值。
-
=>(fat arrow)表示對 type 變數的 constraint。- 在
a ~> a -> a(參考上方的 squiggly arrow),a可以是任何 type。Semigroup a => a ~> a -> a加入了一個 constraint,使得 typea現在必須滿足Semigrouptypeclass。滿足 typeclass 意思是,合法地實現 typeclass 指定的所有函式和方法。
- 在
例如:
traverse :: Applicative f, Traversable t => t a ~> (TypeRep f, a -> f b) -> f (t b)
'------' '--------------------------' '-' '-------------------' '-----'
' ' ' ' '
' ' - type constraints ' ' - argument types ' - return type
' '
'- method name ' - method target type
更多資訊,請參考 Sanctuary 文件的 Type 部分。↩️
前綴方法名稱
為了讓 data type 可以兼容 Fantasy Land,其值必須具有某些屬性。這些所有屬性都由 fantasy-land/ 作為前綴。例如:
// MyType#fantasy-land/map :: MyType a ~> (a -> b) -> MyType b
MyType.prototype['fantasy-land/map'] = ...
此外,在本份文件沒有使用前綴名稱。
為了方便你可以使用 fantasy-land 的 package:
var fl = require('fantasy-land')
// ...
MyType.prototype[fl.map] = ...
// ...
var foo = bar[fl.map](x => x + 1)
Type 代表
某些行為是從一個 type 成員的角度定義的。其他行為不需要一個成員。因此,某些代數要求一個 type 提供一個 value 層級的代表(具有一定的屬性)。例如,可以提供 Id 作為其 type 代表:Id :: TypeRep Identity。
如果一個 type 提供了一個 type 代表,該 type 的每個成員必須有一個 constructor 屬性,該屬性是對 type 代表的引用。
代數
Setoid
-
a.equals(a) === true(反身性) -
a.equals(b) === b.equals(a)(對稱性) - 如果
a.equals(b)而且b.equals(c),因此a.equals(c)(傳遞性)
equals 方法
equals :: Setoid a => a ~> a -> Boolean
具有 Setoid 的值必須提供一個 equals 方法。equals 方法接受一個參數:
a.equals(b)
-
b必須是相同於 Setoid 的值。- i. 如果
b不相同於 Setoid,equals的行為是沒有被指定的(推薦回傳false)。
- i. 如果
-
equals必須回傳一個布林值(true或false)。
Ord
實作 Ord 規範的該值也必須實作 Setoid 規範。
-
a.lte(b)或b.lte(a)(完整性) - 如果
a.lte(b)而且b.lte(a),因此a.equals(b)(反對稱性) - 如果
a.lte(b)而且b.lte(c),因此a.lte(c)(傳遞性)
lte 方法
lte :: Ord a => a ~> a -> Boolean
具有 Ord 的值必須提供一個 lte 方法。lte 方法接受一個參數:
a.lte(b)
-
b必須是相同於 Ord 的值。 i. 如果b不相同於 Ord,lte的行為是沒有被指定的(推薦回傳false)。 -
lte必須回傳一個布林值(true或false)。
Semigroupid
a.compose(b).compose(c) === a.compose(b.compose(c))(關聯性)
compose 方法
compose :: Semigroupoid c => c i j ~> c j k -> c i k
具有 Semigroupoid 的值必須提供一個 compose 方法。compose 方法接受一個參數:
a.compose(b)
-
b必須是相同的 Semigroupoid 的值。 i. 如果b不是相同的 Semigroupoid,compose的行為是沒有被指定的。 -
compose必須回傳一個相同的 Semigroupoid 的值。
Category
實作 Category 規範的該值也必須實作 Semigroupoid 規範。
-
a.compose(C.id())相等於a(Right Identity) -
C.id().compose(a)相等於a(Left Identity)
id 方法
id :: Category c => () -> c a a
具有 Category 的值必須在它的 type 代表上提供一個 id 方法:
C.id()
給定一個 c 值,可以通過 constructor 屬性拜訪其 type 代表:
c.constructor.id()
-
id必須回傳一個相同的 Category 的值。
Semigroup
-
a.concat(b).concat(c)相等於a.concat(b.concat(c))(關聯性)
contact 方法
concat :: Semigroup a => a ~> a -> a
具有 Semigroup 的值必須提供一個 contact 方法。contact 方法接受一個參數:
s.concat(b)
-
b必須是相同的 Semigroup 的值。 i. 如果b不是相同的 Semigroup,contact的行為是沒有被指定的。 -
contact必須回傳一個相同的 Semigroup 的值。
Monoid
實作 Monoid 規範的該值也必須實作 Semigroup 規範。
empty 方法
empty :: Monoid m => () -> m
具有 Monoid 的值必須在它的 type 代表上提供一個 empty 方法:
M.empty()
給定一個 m 值,可以通過 constructor 屬性拜訪其 type 代表:
m.constructor.empty()
-
empty必須回傳一個相同的 Monoid 的值。
Group
實作 Group 規範的該值也必須實作 Monoid 規範。
-
g.concat(g.invert())相等於g.constructor.empty()(Right Inverse) -
g.invert().concat(g)相等於g.constructor.empty()(Left Inverse)
invert 方法
invert :: Group g => g ~> () -> g
具有 Group 的值必須提供一個 invert 方法。invert 方法不接受參數:
g.invert()
-
invert必須回傳相同的 Group 的值。
Functor
-
u.map(a => a)相等於u(identity) -
u.map(x => f(g(x)))相等於u.map(g).map(f)(組合性)
map 方法
map :: Functor f => f a ~> (a -> b) -> f b
具有 Functor 的值必須提供一個 map 方法。map 方法接受一個參數:
u.map(f)
-
f必須是一個函式,- i. 如果
f不是一個函式,map的行為是沒有被指定的。 - ii.
f可以回傳任何值。 - iii. No parts of f's return value should be checked.
- i. 如果
-
map必須回傳一個相同的 Functor 的值。
Contravariant
-
u.contramap(a => a)相等於u(identity) -
u.contramap(x => f(g(x)))相等於u.contramap(f).contramap(g)(composition)
contramap 方法
contramap :: Contravariant f => f a ~> (b -> a) -> f b
具有 Contravariant 的值必須提供一個 contramap 方法。contrampa 方法接受一個參數:
u.contramap(f)
-
f必須是一個函式,- i. 如果
f不是一個函式,contramap的行為是沒有被指定的。 - ii.
f可以回傳任何值。 - iii. No parts of f's return value should be checked.
- i. 如果
-
contramap必須回傳一個相同的 Contravariant 的值。
Apply
實作 Apply 規範的該值也必須實作 Functor 規範。
-
v.ap(u.ap(a.map(f => g => x => f(g(x)))))相等於v.ap(u).ap(a)(composition)
ap 方法
ap :: Apply f => f a ~> f (a -> b) -> f b
具有 Apply 的值必須提供一個 ap 方法。ap 方法接受一個參數:
a.ap(b)
-
b必須是一個 Apply 函式,- i. 如果
b不是代表一個函式,ap的行為是沒有被指定的。 - ii.
b必須相同於 a 是 Apply。
- i. 如果
-
a必須是任何值的一個 Apply。 -
ap必須將 Applyb中的函式應用於 Applya中的值。- i. 該函式沒有回傳值的部分需要被檢查
- 透過
ap被回傳的 Apply 必須與a和b相同。
Applicative
實作 Applicative 規範的該值也必須實作 Apply 規範。
-
v.ap(A.of(x => x))相等於v(identity) -
A.of(x).ap(A.of(f))相等於A.of(f(x))(homomorphism) -
A.of(y).ap(u)相等於u.ap(A.of(f => f(y)))(interchange)
of 方法
of :: Applicative f => a -> f a
具有 Applicative 的值必須在它的 type representative 上提供一個 of 方法。of 方法接受一個參數:
F.of(a)
給定一個 f 值,透過 constructor 屬性訪問它的 type representative:
f.constructor.of(a)
-
of必須提供相同的 Applicative 值- i. 不需要檢查任何部分
Alt
實作 Alt 規範的該值也必須實作 Functor 規範。
-
a.alt(b).alt(c)相等於a.alt(b.alt(c))(associativity) -
a.alt(b).map(f)相等於a.map(f).alt(b.map(f))(distributivity)
alt 方法
alt :: Alt f => f a ~> f a -> f a
具有 Alt 的值必須提供一個 alt 方法。alt 方法接受一個參數:
a.alt(b)
-
b必須是相同 Alt 的值。- i. 如果
b不相同於 Alt,alt的行為是沒有被指定的。 - ii.
a和b可以包涵任何相同 type 的值。 - iii. No parts of
a's andb's containing value should be checked.
- i. 如果
-
alt必須回傳一個相同 Alt 的值。
Plus
實作 Plus 規範的該值也必須實作 Alt 規範。
-
x.alt(A.zero())相等於x(right identity) -
A.zero().alt(x)相等於x(left identity) -
A.zero().map(f)相等於A.zero()(annihilation)
zero 方法
zero :: Plus f => () -> f a
具有 Plus 的值必須在它的 type representative 上提供一個 zero 函式:
A.zero()
給定一個 x 值,可以通過 constructor 屬性拜訪其 type 代表:
x.constructor.zero()
-
zero必須回傳一個相同 Plus 的值。