MultiButtons
 MultiButtons copied to clipboard
MultiButtons copied to clipboard
Handle multiple buttons using single analog pin for ESP32
Multiple Buttons Library
A totally rebuilt library ButtonFever has been released. It provide much powerful tools for handling various button press event such as double press and long press. It also support both standalone digital button or button array. Please try it!
This is a library for handling multiple buttons with single analog pin for ESP32. It will trigger callback function upon button pressed.
The library handled button debouncing, and you may decide the trigger edge for button event - on press (default) or on release.
It also provide printReading() method for you to check the analog pin reading.
In theory you may add more buttons in the circuit.
Reference Circuit
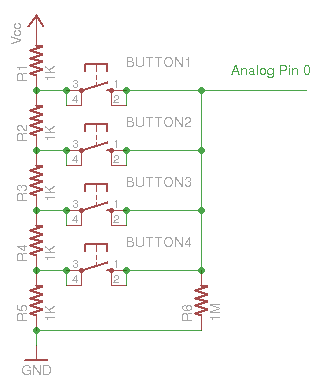
Installation
- Arduino Library Manager (Recommended)
- Download or clone this repository into your arduino libraries directory
Determin Voltage Readings for Each Button
To provide voltage range for each button, you may check the actual readings with printReading() method.
The following sketch can calculate the avarage reading of a button from 5 readings:
#include <MultiButtons.h>
int buffer[5];
int reading, sum, avg;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
static int i = 0;
reading = MultiButtons::printReading(14);
if (reading > 0) {
buffer[i] = reading;
if (i == 4) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
sum += buffer[j];
}
avg = sum / 5;
Serial.print("Avarage Reading: ");
Serial.println(avg);
}
i++;
if (i > 4) {
i = 0;
sum = 0;
}
}
delay(200);
}
NOTE: Readings of analog pin may vary upon other connected devices. Voltage ranges for each button should decide based on measurement of the final circuit with all required devices initialized.
Usage
-
Include the module
#include <MultiButtons.h> -
Declare voltage range for each button
int voltageRanges[][2] = { {3000,3260}, {2200,2450}, {1400,1620}, {600,810} }; int btnCount = sizeof(voltageRanges)/sizeof(voltageRanges[0]); -
Declare callback function
This must be declare before MultiButtons object construction.
Callback function must contain 2 parameters:
Parameter Description MultiButton *mb MultiButtons object itself int btnIndex Button index detected by MultiButtons object, beginning from 0. NOTE: you may call methods of MultiButtons object within callback function by
mb->theMethod();void buttonHandler (MultiButtons *mb, int btnIndex) { int btnID = btnIndex + 1; Serial.print("Button pressed: "); Serial.println(btnID); } -
Create MultiButtons object
MultiButtons mb(btnPin, btnCount, voltageRanges, buttonHandler, 4095, BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_PRESS);Parameters:
Parameter Description int pin GPIO for button array int buttonCount Number of buttons connected int voltageRanges[][2] Upper bound and Lower bound of voltage for each button (see above step 2.) callback_t callback Callback function of actions according to pressed button (see above step 3.) int adcMax The maxmium value of ADC. Default is 4095 (12bit ADC) int triggerEdge Which edge trigger button press event.
On press (0, default) or on release (1) -
Setup MultiButtons object for reading analog pin
void setup() { mb.begin(); } -
Read button state from analog pin
void loop() { mb.loop(); }
Inline manner
MultiButtons mb(btnPin, btnCount, new int[btnCount][2]{
{3000,3260},
{2200,2450},
{1400,1620},
{600,810}
}, [](MultiButtons *mb, int btnIndex) {
int btnID = btnIndex + 1;
Serial.print("Button pressed: ");
Serial.println(btnID);
}, 4095, BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_PRESS);
Example
#include <MultiButtons.h>
const int btnPin = 14;
// Declare voltage ranges for each button
int voltageRanges[][2] = {
{3000,3260},
{2200,2450},
{1400,1620},
{600,810}
};
int btnCount = sizeof(voltageRanges)/sizeof(voltageRanges[0]);
// Must declare buttonHandler callback function and used variables
// before generate MultiButtons object
void buttonHandler (MultiButtons *mb, int btnIndex) {
/*
* NOTE: you may call method in MultiButtons object by 'mb->theMethod();'
*/
int btnID = btnIndex + 1;
Serial.print("Button pressed: ");
Serial.println(btnID);
}
MultiButtons mb(btnPin, btnCount, voltageRanges, buttonHandler, 4095, BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_PRESS);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
mb.begin(); // Prepare reading button state
Serial.println("Ready.");
}
void loop() {
mb.loop(); // Read button state with debouncing
}
Other methods
-
static int printReading ( int pin )
Print analog pin reading through Serial port and return the reading.
int reading = MultiButtons::printReading(14); -
static bool isPressingAny ( int pin )
Class method for checking if any button in the button array pressed.
bool result = MultiButtons::isPressingAny(14); -
bool isPressing ()
Object method version of
isPressingAny().bool result = mb.isPressing(); -
bool isPressing ( int btnIndex )
Check designated button is pressing. Button index begin from 0.
bool result = mb.isPressing(0); -
int getTriggerEdge ()
Retrieve trigger edge value.
int edge = mb.getTriggerEdge();Possible value:
Edge Value Description BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_PRESS 0 Trigger button event on press BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_RELEASE 1 Trigger button event on release -
bool setTriggerEdge ( int edge )
Set trigger edge. Return
truewhen success,falseif provide invalid value.bool result = mb.setTriggerEdge(BTN_TRIGGER_EDGE_PRESS);
Reference
- Multiple button inputs using Arduino analog pin
- How to Debouce Six Buttons on One Analog Pin With Arduino (tcrosley)
In Theory
Voltage Divider Rule
Vout = Vin(R2/R1+R2)
Vin = 3.3V # ESP32
R1+R2 = 5KΩ = 5000Ω
Voltage of each button
- Button 1 Vout = 3.3(4000/5000) = 2.64V
- Button 2 Vout = 3.3(3000/5000) = 1.98V
- Button 3 Vout = 3.3(2000/5000) = 1.32V
- Button 4 Vout = 3.3(1000/5000) = 0.66V
ADC convertion (12bit)
0 ~ 3.3V = 0 ~ 4095
3.3V/4095 = 0.81mV
| Button | MultiMeter Measurement | Expected Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.62V | 3259 |
| 2 | 1.96V~1.97V | 2420~2432 |
| 3 | 1.30V~1.31V | 1605~1617 |
| 4 | 0.65V | 802 |
It is required an adjustment for ESP32 ADC with the following equation:
Vout = e / 4095.0 * 3.3 + 0.1132
| Button | Circuit Measurement | Serial Debug Data | Calculated Voltage w' Adjustment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.61V | 3070~3103 | 2.59V~2.61V |
| 2 | 1.95V~1.96V | 2237~2255 | 1.92V~1.93V |
| 3 | 1.30V | 1456~1461 | ~1.29V |
| 4 | 0.64V~0.65V | 658~664 | 0.64V~0.65V |