Blog
 Blog copied to clipboard
Blog copied to clipboard
回顾基本数据结构
线性表
线性表是最简单、最常用的一种数据结构,它是n个数据元素的有限集合。实现线性表一般有数组和链表两种方式,数组用一组连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素,链表用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(存储单元可连续也可不连续)。
- 数组
数组是一种大小固定的数据结构,当数组不能再存储线性表中的新元素时,我们可以创建一个新的大的数组来替换当前数组,这样就可以使用数组实现动态的数据结构。前面基于静态类型的语言,动态类型的语言,如javascript,就不同。二分查找的例子:
// 二分查找数组中的数,适用于不经常变动而查找频繁的有序列表
function binarySearch(data, arr, start, end) {
if (start > end) {
return -1;
}
var mid = Math.floor((end + start) / 2);
if (data == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (data < arr[mid]) {
return binarySearch(data, arr, start, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearch(data, arr, mid + 1, end);
}
}
二分查找的时间复杂度为O(logn),比顺序查找的链表(O(n))更快,但插入、删除效率低。
- 链表
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列节点组成,这些节点不必在内存中相连。每个节点由数据部分Data和链部分Next,Next指向下一个节点,添加或者删除时,只需要改变相关节点的Next的指向,效率很高。
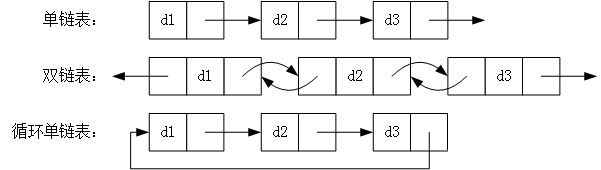
// 删除节点
var deleteNode = function (head, node) {
// 当前节点是不是尾节点
if (node.next) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
// 当前只有一个节点
} else if (node === head) {
node = null;
head = null;
} else {
// 删除的是尾节点
node = head;
while (node.next.next) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = null;
node = null;
}
return node;
};
// 删除重复节点
function deleteDuplication(pHead) {
const map = {};
if (pHead && pHead.next) {
let current = pHead;
// 计数
while (current) {
const val = map[current.val];
map[current.val] = val ? val + 1 : 1;
current = current.next;
}
current = pHead;
while (current) {
const val = map[current.val];
if (val > 1) {
// 删除节点
console.log(val);
if (current.next) {
current.val = current.next.val;
current.next = current.next.next;
} else if (current === pHead) {
current = null;
pHead = null;
} else {
current = pHead;
while (current.next.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = null;
current = null;
}
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
}
return pHead;
}
数组链表的区别:
- 数组在内存中连续存放,每个元素占用的空间相同,能通过下标快速访问,但删除和插入比较困难,需要移动大量元素。
- 链表在内存中不是顺序存储的,访问元素要从第一个开始,直到找到为止,但插入和删除比较高效,只需修改指针。
- 数组长度固定,不能动态增减,当数据增加时,可能超出原先定义的元素个数;当数据减少时,造成内存浪费,它从栈中分配空间,取速度比堆要快,但大小固定,自由度小。
- 链表动态分配,动态增减,方便插入和删除,它在堆中分配,自由度大,管理麻烦。
- javascript中的数组是对象,在堆中进行内存分配,并且是不连续的,类似哈希映射的方式存在。
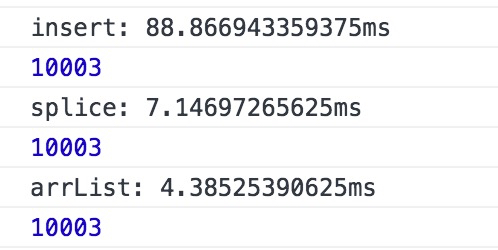
下面是数组与链表插入操作对比:
var arrInsert = [1, 2, 3];
var arrSplice = [1, 2, 3];
var arrList = new LinkedList();
arrList.append(1);
arrList.append(2);
arrList.append(3);
console.time("insert");
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
arrInsert = insert(2, 5, arrInsert);
}
console.timeEnd("insert");
console.log(arrInsert.length);
console.time("splice");
for(var j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
arrSplice.splice(2, 0, 5);
}
console.timeEnd("splice");
console.log(arrInsert.length);
console.time("arrList");
for(var k = 0; k < 10000; k++) {
arrList.insert(2, 5);
}
console.timeEnd("arrList");
console.log(arrList.size());
// 普通插入操作
function insert(index, e, arr) {
var curIndex = arr.length;
while(curIndex > index) {
arr[curIndex--] = arr[curIndex];
}
arr[curIndex] = e;
return arr;
}
function LinkedList() {
var Node = function(element){
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
};
var length = 0;
var head = null;
this.append = function(element){
var node = new Node(element),
current;
if (head === null){
head = node;
} else {
current = head;
while(current.next){
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
length++;
};
// 链表插入操作
this.insert = function(position, element){
if (position >= 0 && position <= length){
var node = new Node(element),
current = head,
previous,
index = 0;
if (position === 0){
node.next = current;
head = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position){
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
length++;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
};
this.getHead = function(){
return head;
};
this.size = function() {
return length;
};
}
运行结果:
栈和队列
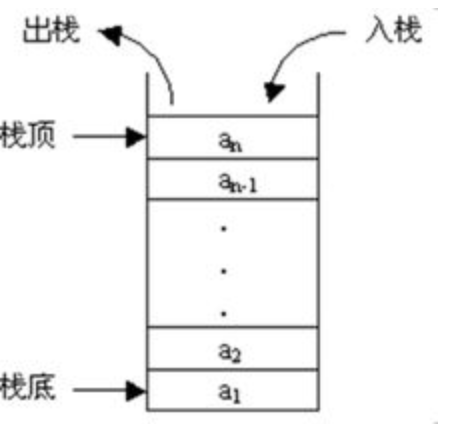
- 栈
栈是一种比较特殊的线性表,访问、插入和删除元素只能在栈顶进行。
如图:
class Stack {
constructor () {
this.items = [];
}
push (element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
pop () {
return this.items.pop();
}
peek () {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
isEmpty () {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
size () {
return this.items.length;
}
clear () {
this.items = [];
}
print () {
console.log(this.items.toString());
}
}
let stack = new Stack();
console.log(stack.isEmpty());
十进制转二进制例子:
let divideBy2 = function (decNumber) {
let remStack = new Stack();
let rem = 0;
let binaryString = '';
while (decNumber > 0) {
rem = decNumber % 2 // 记录当前余数是多少
remStack.push(rem); // 存入栈中
decNumber = parseInt(decNumber / 2); // 与2除取整
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += remStack.pop().toString();
}
return binaryString;
};
- 队列
队列是一种特殊的线性表,先进先出的原则,队列也有顺序队列和链式队列两种实现。数据量已知就使用数组实现队列,未知的话就使用链表实现队列。
如图:

//单链表实现
function LinkedQueue () {
//节点结构定义
var Node = function(element){
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
var length = 0,
front,//队首指针
rear;//队尾指针
//入队操作
this.push = function(element){
var node = new Node(element),
current;
if(length == 0){
front = node;
rear = node;
length++;
return true;
}else{
current = rear;
current.next = node;
rear = node;
length++;
return true;
}
}
//出队操作
this.pop = function(){
if(!front){
return 'Queue is null';
}else{
var current = front;
front = current.next;
current.next = null;
length--;
return current;
}
}
//获取队长
this.size = function(){
return length;
}
//获取队首
this.getFront = function(){
return front;
}
//获取队尾
this.getRear = function(){
return rear;
}
this.toString = function(){
var str = '',
current = front;
while(current){
str += current.element;
current = current.next;
}
return str;
}
//清除队列
this.clear = function(){
front = null;
rear = null;
length = 0;
return true;
}
}
树和二叉树
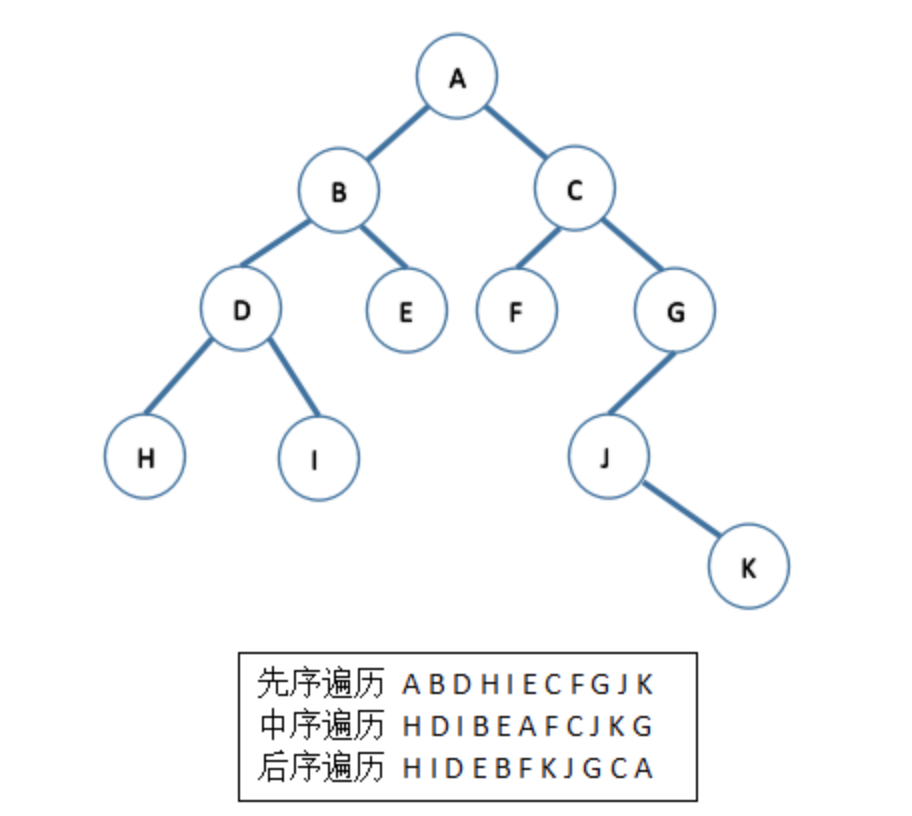
树型结构是一类非常重要的非线性数据结构,二叉树是每个节点最多有两棵子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”和“右子树”。
三种遍历方式:
- 先序遍历:中左右,先找到根节点,再先序遍历左子树,再先序遍历右子树。
- 中序遍历:左中右。
- 后序遍历:左右中。
如图:
二叉搜索树的实现及遍历:
//定义节点
class Node {
constructor(data){
this.root = this;
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null
}
}
//创建二叉搜索树(BST))
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(){
this.root = null
}
//插入节点
insert(data){
const newNode = new Node(data);
const insertNode = (node,newNode) => {
if (newNode.data < node.data){
if(node.left === null){
node.left = newNode
}else {
insertNode(node.left,newNode)
}
}else {
if(node.right === null){
node.right = newNode
}else{
insertNode(node.right,newNode)
}
}
};
if(!this.root){
this.root = newNode
}else {
insertNode(this.root,newNode)
}
}
//删除节点
remove(data){
const removeNode = (node,data) => {
if(node === null) return null;
// 找到节点
if(node.data === data){
// 没有左右子节点
if(node.left === null && node.right === null) return null;
// 没有左子节点,用右子节点覆盖
if(node.left === null) return node.right;
// 没有右子节点,用左子节点覆盖
if(node.right === null) return node.left;
// 有左右子节点,取右子树的最小节点来覆盖删除的节点并删除最小节点,而不改变树的排序
if(node.left !==null && node.right !==null){
let _node = this.getMin(node.right);
node.data = _node.data;
node.right = removeNode(node.right,_node.data);
return node
}
} else if(data < node.data){
// 递归左子树
node.left=removeNode(node.left,data);
return node
} else {
// 递归右子树
node.right=removeNode(node.right,data);
return node
}
};
return removeNode(this.root,data)
}
//中序遍历
inOrder(){
let backs = [];
const inOrderNode = (node,callback) => {
if(node !== null){
inOrderNode(node.left,callback);
backs.push(callback(node.data));
inOrderNode(node.right,callback)
}
};
inOrderNode(this.root,callback);
function callback(v){
return v
}
return backs
}
//前序遍历
preOrder(){
let backs = [];
const preOrderNode = (node,callback) => {
if(node !== null){
backs.push(callback(node.data));
preOrderNode(node.left,callback);
preOrderNode(node.right,callback)
}
};
preOrderNode(this.root,callback);
function callback(v){
return v
}
return backs
}
//后序遍历
postOrder(){
let backs = [];
const postOrderNode = (node,callback) => {
if(node !== null){
postOrderNode(node.left,callback);
postOrderNode(node.right,callback);
backs.push(callback(node.data))
}
};
postOrderNode(this.root,callback);
function callback(v){
return v
}
return backs
}
}
数组、链表和二叉树的比较:
| 操作 | 数组 | 链表 | 二叉树 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 插入、删除 | O(n) | O(1) | O(logn) |
| 查找 | O(1) | O(n) | O(logn) |
堆
堆就是用数组实现的二叉树,所有它没有使用父指针或者子指针,分为最大堆和最小堆。
堆的特点:
- 设父节点的编号为 i, 则其左孩子节点的编号为2i+1, 右孩子节点的编号为2i+2。
- 设孩子节点的编号为i, 则其父节点的编号为(i-1)/2。
堆与树的区别:
- 节点顺序不同。
- 内存占用不同,堆只需要一个数组来存储数据,树还需要为左右子节点分配内存。
- 平衡,二叉搜索树必须是“平衡”的情况下,复杂度为O(logn);
- 堆中搜索会很慢。
例子:
例如数组[10, 7, 2, 5, 1]
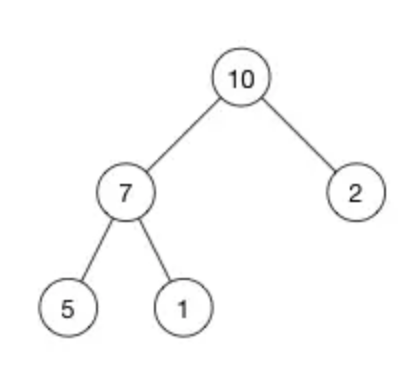
堆的实现:
function MaxHeap(initDataArray, maxSize = 9999) {
let arr=initDataArray || [];
let currSize=arr.length;
// 填充heap,目前还不是一个堆
let heap=new Array(arr.length);
function init() {
for(let i=0; i<currSize;i++){
heap[i]=arr[i];
}
// 最后一个分支节点的父节点
le currPos=Math.floor((currSize-2)/2);
while (currPos>=0){
// 局部自上向下下滑调整
shif_down(currPos, currSize-1);
// 调整下一个分支节点
currPos--;
}
}
function shif_down(start,m) {
// 父节点
let parentIndex=start,
// 左子节点
maxChildIndex=parentIndex*2+1;
while (maxChildIndex<=m){
if(maxChildIndex<m && heap[maxChildIndex]<heap[maxChildIndex+1]){
// 一直指向最大关键码最大的那个子节点
maxChildIndex=maxChildIndex+1;
}
if(heap[parentIndex]>=heap[maxChildIndex]){
break;
}else {
// 交换
let temp=heap[parentIndex];
heap[parentIndex]=heap[maxChildIndex];
heap[maxChildIndex]=temp;
// 调整它的子节点
parentIndex=maxChildIndex;
maxChildIndex=maxChildIndex*2+1
}
}
}
/**
* 插入一个数据
*
* @param {*} data 数据值
* @returns {boolean} isSuccess 返回插入是否成功
*/
this.insert = function (data) {
// 如果当前大小等于最大容量
if(currSize===maxSize){
return false
}
heap[currSize]=data;
shif_up(currSize);
currSize++;
return true;
};
function shif_up(start) {
let childIndex=start; //当前叶节点
let parentIndex=Math.floor((childIndex-1)/2); //父节点
while (childIndex>0){
// 如果大就不交换
if(heap[parentIndex]>=heap[childIndex]){
break;
}else {
let temp=heap[parentIndex];
heap[parentIndex]=heap[childIndex];
heap[childIndex]=temp;
// 调整它的父节点
childIndex=parentIndex;
parentIndex=Math.floor((parentIndex-1)/2);
}
}
}
}
堆的应用:
- 实现优先队列。
- 在海量数据中找到topk数据,在海量的n个数据中,使用k个数据构建一个小顶堆,遍历剩下的数据,如果元素比堆顶元素大,就删除替换堆顶元素,在调整堆。
图
图由边的集合及顶点的集合组成。边是有方向的是有序图(有向图),否则就是无序图(无向图)。可以用邻接表和邻接矩阵来表示边,邻接表是一个二维数组。
如图邻接表:
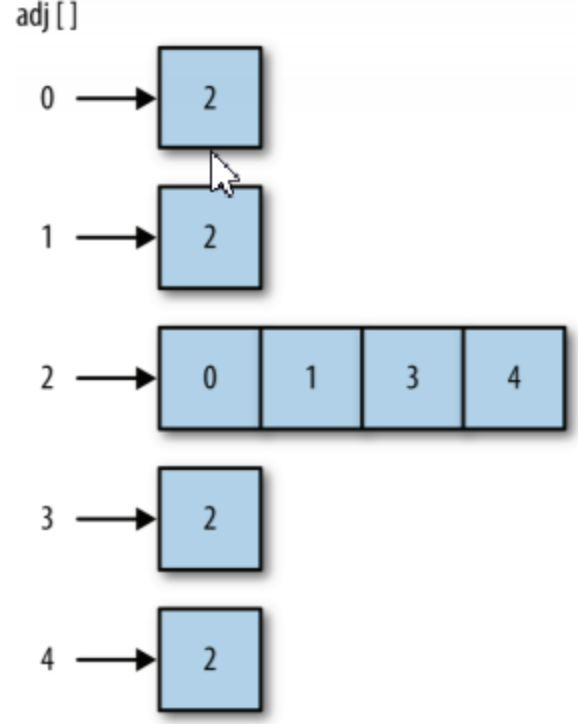
定义:
// 构造图类
function Graph(v) {
this.vertices = v; //顶点的数量
this.edges = 0;
this.adj = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.adj[i] = []; //保存与顶点 i 相邻的顶点列表
}
this.addEdge = addEdge;
this.showGraph = showGraph;
this.dfs = dfs;
this.bfs = bfs;
this.marked = []; //保存未访问过的顶点
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
this.marked[i] = false;
}
}
// 添加边
function addEdge(v, w) {
this.adj[v].push(w);
this.adj[w].push(v);
this.edges++;
}
// 展示图
function showGraph() {
for (var i = 0; i < this.vertices; i++) {
var str = '';
str += i + " -> ";
for (var j = 0; j < this.vertices; j++) {
if (this.adj[i][j] != undefined) {
str += this.adj[i][j] + ' ';
}
}
console.log(str);
}
}
// 深度优先算法
function dfs(v) {
this.marked[v] = true;
if (this.adj[v] != undefined) {
console.log("Visited vertex: " + v);
}
for(var w of this.adj[v]) {
if (!this.marked[w]) {
this.dfs(w);
}
}
}
// 广度优先算法
function bfs(s) {
var queue = [];
this.marked[s] = true;
queue.push(s); // 添加到队尾
while (queue.length > 0) {
var v = queue.shift(); // 从队首移除
if (v != undefined) {
console.log("Visisted vertex: " + v);
}
for(var w of this.adj[v]) {
if (!this.marked[w]) {this.marked[w] = true;
queue.push(w);
}
}
}
}
// 调用
g = new Graph(5);
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 3);
g.addEdge(1, 4);
g.addEdge(2, 4);
g.showGraph();
g.dfs(0);