Flink-Reinforcement-Learning
 Flink-Reinforcement-Learning copied to clipboard
Flink-Reinforcement-Learning copied to clipboard
Recommender system based on Flink and Reinforcement Learning
Flink-Reinforcement-Learning
English 简体中文 blog post
FlinkRL is a realtime recommender system based upon Flink and Reinforcement Learning. Specifically, Flink is famous for its high-performance stateful streaming processing, which can provide fast and accurate response to the user request in this system. And reinforcement learning is good at planning long-term reward and adjust recommendation results quickly according to realtime user feedback. The combination of these two components makes the system capture the dynamic change pattern of user interests and provide insightful recommendations.
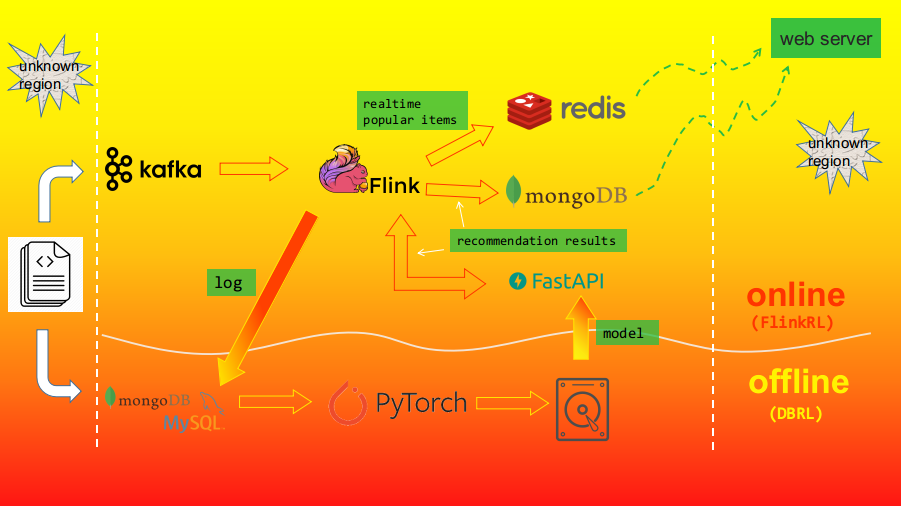
FlinkRL is mainly used for online inference, and the offline model training part is implemented in another repo, i.e. DBRL. The full system architecture is as follows:
Main Workflow
To simulate an online environment, a dataset is used as a producer in order to send data to Kafka, then Flink consumes data from Kafka. Afterwards, Flink will execute three tasks:
- Save user behavior log to MongoDB and MySQL, and the log can be used for offline model training.
- Compute realtime top-N popular items and save them to Redis.
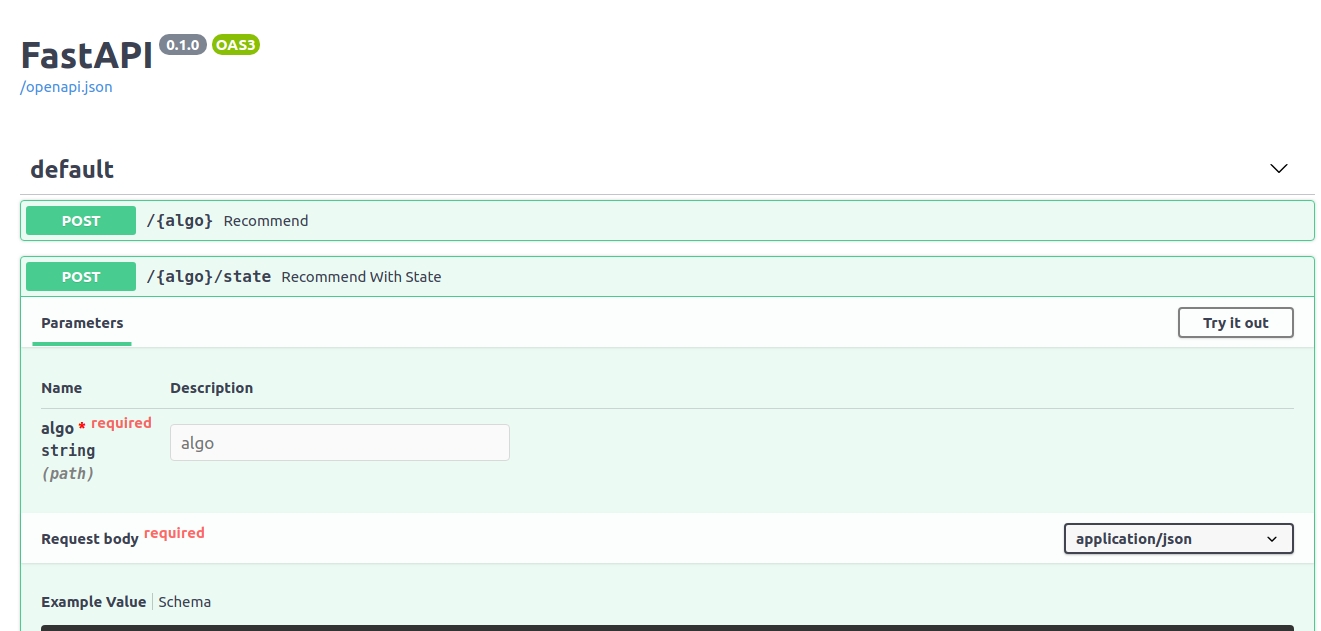
- Collect user's recent consumed items and post data to a web service created through FastAPI to get recommendation results, then save the recommendation to MongoDB.
Thus an online web server can directly take recommendation results and popular items from the databases and send them to the client. Yet another consideration is why using FastAPI to build another web service ? Because the model is trained through PyTorch, and there is seemingly no unified way to deploy a PyTorch model. So FastAPI is used to load the trained model, do some processing and make final recommendation.
Data
The dataset comes from a competition held by Tianchi, a Chinese competition platform. Please refer to the original website for full description. Note that here we only use the round2 data.
You can also download the data from Google Drive.
Usage
Python dependencies: python>=3.6, numpy, pandas, torch>=1.3, tqdm, FastAPI.
You'll need to clone both FlinkRL and DBRL:
$ git clone https://github.com/massquantity/Flink-Reinforcement-Learning.git
$ git clone https://github.com/massquantity/DBRL.git
We'll first use the DBRL repo to do offline training. After downloading the data, unzip and put them into the DBRL/dbrl/resources folder. The original dataset consists of three tables: user.csv, item.csv, user_behavior.csv . We'll first need to filter some users with too few interactions and merge all features together, and this is accomplished by run_prepare_data.py. Then we'll pretrain embeddings for every user and item by running run_pretrain_embeddings.py :
$ cd DBRL/dbrl
$ python run_prepare_data.py
$ python run_pretrain_embeddings.py --lr 0.001 --n_epochs 4
You can tune the lr and n_epochs hyper-parameters to get better evaluate loss. Then we begin to train the model. Currently there are three algorithms in DBRL, so we can choose one of them:
$ python run_reinforce.py --n_epochs 5 --lr 1e-5
$ python run_ddpg.py --n_epochs 5 --lr 1e-5
$ python run_bcq.py --n_epochs 5 --lr 1e-5
At this point, the DBRL/resources should contains at least 6 files:
-
model_xxx.pt, the trained pytorch model. -
tianchi.csv, the transformed dataset. -
tianchi_user_embeddings.npy, the pretrained user embeddings in numpynpyformat. -
tianchi_item_embeddings.npy, the pretrained item embeddings in numpynpyformat. -
user_map.json, a json file that maps original user ids to ids used in the model. -
item_map.json, a json file that maps original item ids to ids used in the model.
After the offline training, we then turn to FlinkRL . First put three files: model_xxx.pt, tianchi_user_embeddings.npy, tianchi_item_embeddings.npy into the Flink-Reinforcement-Learning/python_api folder. Make sure you have already installed FastAPI, then start the service:
$ gunicorn reinforce:app -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker # if the model is reinforce
$ gunicorn ddpg:app -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker # if the model is ddpg
$ gunicorn bcq:app -w 4 -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker # if the model is bcq
The other three files : tianchi.csv, user_map.json, item_map.json are used in Flink, and in principle they can be put in anywhere, so long as you specify the absolute path in the Flink-Reinforcement-Learning/FlinkRL/src/main/resources/config.properties file.
For quick running, you can directly import FlinkRL into an IDE, i.e. IntelliJ IDEA. To run on a cluster, we use Maven to package into a jar file:
$ cd FlinkRL
$ mvn clean package
Put the generated FlinkRL-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar into the Flink installation directory. For now, assume Kafka, MongoDB and Redis have all been started, then we can start the Flink cluster and run tasks:
$ kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic flink-rl # cereate a topic called flink-rl in Kafka
$ use flink-rl # cereate a database called flink-rl in MongoDB
$ # first cd into the Flink installation folder
$ ./bin/start-cluster.sh # start the cluster
$ ./bin/flink run --class com.mass.task.FileToKafka FlinkRL-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar # import data into Kafka
$ ./bin/flink run --class com.mass.task.RecordToMongoDB FlinkRL-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar # save log to MongoDB
$ ./bin/flink run --class com.mass.task.IntervalPopularItems FlinkRL-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar # compute realtime popular items
$ ./bin/flink run --class com.mass.task.SeqRecommend FlinkRL-1.0-SNAPSHOT-jar-with-dependencies.jar # recommend items using reinforcement learning model
$ ./bin/stop-cluster.sh # stop the cluster
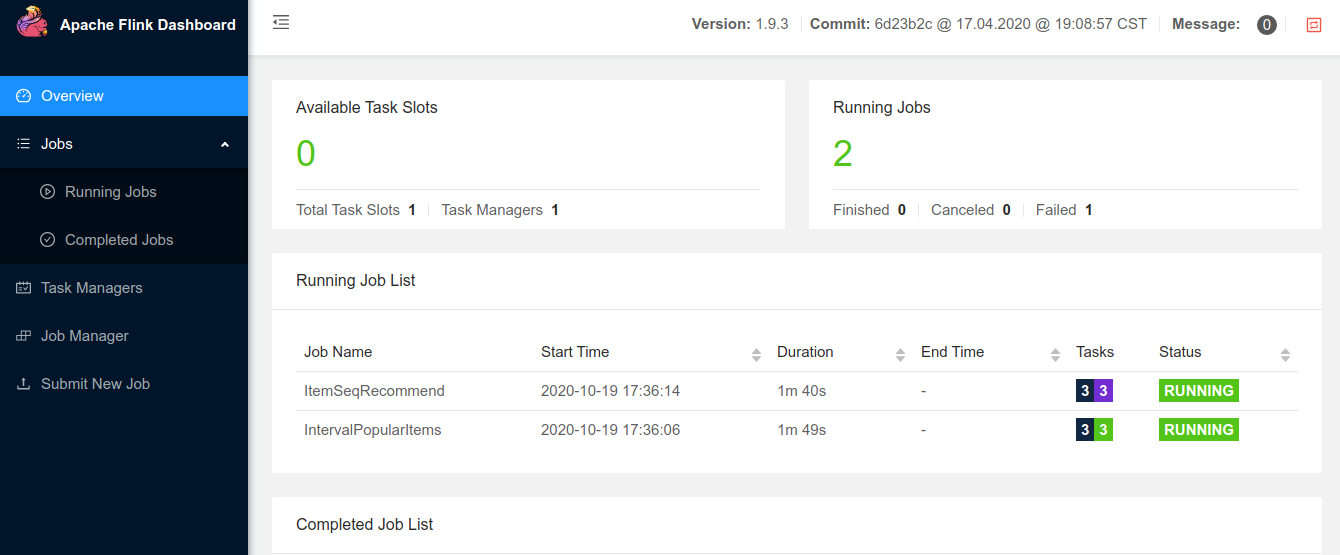
Open http://localhost:8081 to use Flink WebUI :
FastAPI also comes with an interactive WebUI, you can access it through http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs :