qnode
 qnode copied to clipboard
qnode copied to clipboard
Client node of LwM2M-like Lightweight Message Queuing Network (LwMQN).
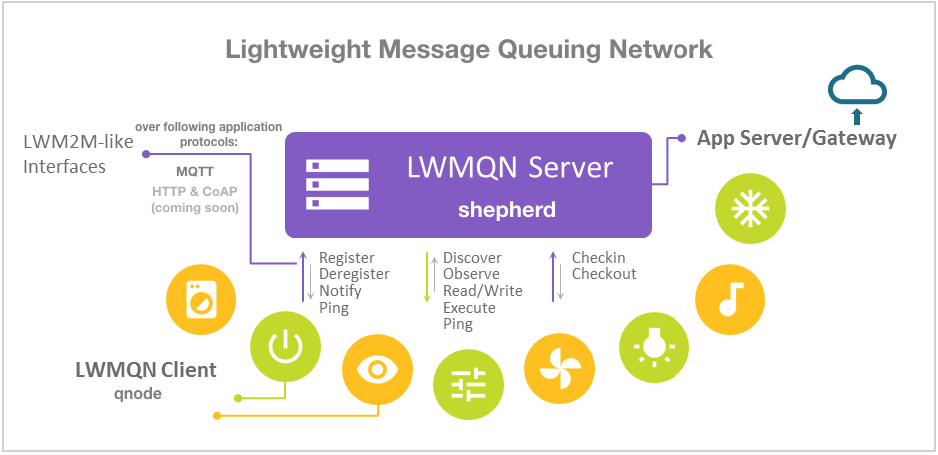
What is LWMQN
Lightweight Message Queuing Network (LwMQN) is an open source project that follows part of OMA LwM2M v1.0 specification to meet the minimum requirements of machine network management.
Server-side and Client-side Libraries:
- LwMQN project provides you with this machine-side @lwmqn/qnode library and a server-side @lwmqn/shepherd library to build your machine network with JavaScript and node.js easily.
- Server-side library: @lwmqn/shepherd
- Client-side library: @lwmqn/qnode (this module)
- A simple demo webapp
Features
- Communication based on MQTT protocol and mqtt.js client.
- Hierarchical Smart Object data model (IPSO), which leads to a comprehensive and consistent way in describing real-world gadgets.
- LWM2M-like interfaces for Client/Server interaction.
- Auto handles many REQ/RSP things for you. All you have to do is to plan your Resources well.
Understanding Smart Objects and the IPSO Model
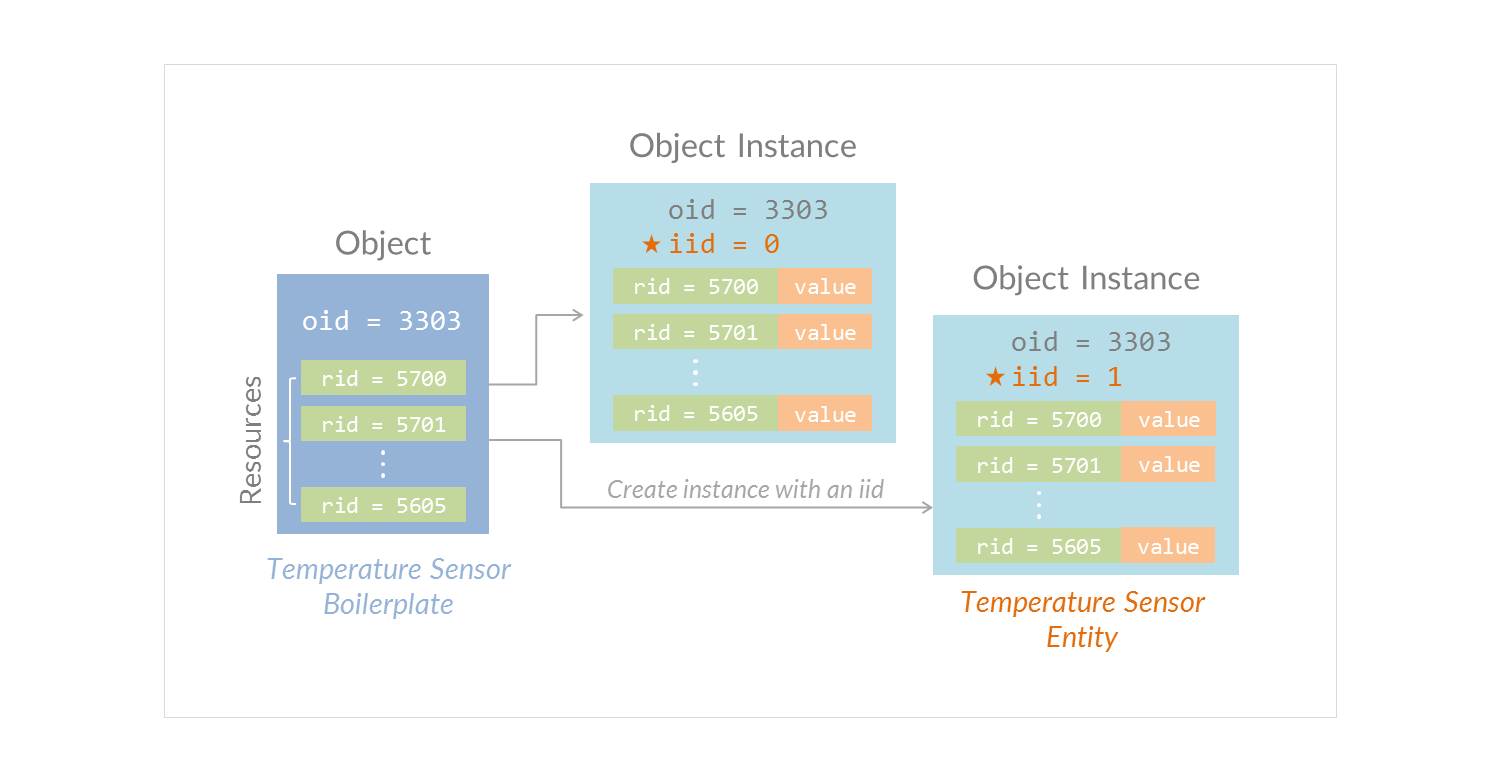
Acronyms and Abbreviations
- Server: LWMQN server
- Client or Client Device: LWMQN client, which is a machine node in the network
-
Qnode: Class exposed by
require('@lwmqn/qnode') -
SmartObject: Class exposed by
require('@lwmqn/smartobject') - qnode: Instance of Qnode class
- so: Instance of SmartObject class
Installation
Currently Node.js 8.x LTS or higher is required.
$ npm install @lwmqn/qnode
$ npm install @lwmqn/smartobject
Compabitility table
| Qnode versions / Node.js versions |
8.x LTS |
10.x LTS |
11.x | 12.x LTS |
13.x |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v0.10.0 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ |
Basic Usage
Here is a quick example, with two humidity sensors and one custom object, which shows how to use @lwmqn/qnode and @lwmqn/smartobject on your client machine.
const Qnode = require('@lwmqn/qnode')
const SmartObject = require('@lwmqn/smartobject')
const so = new SmartObject()
// Humidity sensor - the first instance
so.init('humidity', 0, { // oid = 'humidity', iid = 0
sensorValue: 20,
units: 'percent'
})
// Humidity sensor - the second instance
so.init('humidity', 1, { // oid = 'humidity', iid = 1
sensorValue: 16,
units: 'percent'
})
// A custom Object with two Resources: myResrc1 and myResrc2
so.init('myObject', 0, { // oid = 'myObject', iid = 0
myResrc1: 20,
myResrc2: 'hello world!'
})
// Create a qnode with a client id and your smart object. And attach your 'ready' and 'registered' event listeners
const qnode = new Qnode('my_foo_client_id', so)
qnode.on('ready', function () {
// The ready event fires when the device is ready, but not yet remotely register to a Server.
// You can start to run your local app, such as showing the sensed value on an OLED monitor.
// To interact with your Resources, simply use the handy APIs provided by SmartObject class.
})
qnode.on('registered', function () {
// The event fires when registration procedure completes successfully, which means your device
// has joined the network and managed by the Server. After a success of registration, you can
// take the LWMQN Server as a simple MQTT broker. Your device can subscribe to any topic or
// publish any topic to the network (if authorized).
})
qnode.on('login', function () {
// Your qnode is now ready to accept remote requests from the Server. Don't worry about the
// REQ/RSP things, qnode itself will handle them for you.
})
// Connect and register to a Server, that's it!
qnode.connect('mqtt://192.168.0.2')
The following example shows how to operate upon this qnode at server-side (please go to mqtt-shepherd document for details):
const qnode = qserver.find('my_foo_client_id') // find the registered device by its client id
if (qnode) {
qnode.readReq('humidity/0/sensorValue', function (err, rsp) {
if (!err) console.log(rsp) // { status: 205, data: 20 }
})
qnode.readReq('myObject/0/myResrc2', function (err, rsp) {
if (!err) console.log(rsp) // { status: 205, data: 'hello world!' }
})
}
Documentation
-
Basic APIs -
Networking APIs -
Generic MQTT Interfaces -
Events -
Message Encryption -
Identifying Mode -
Debug messages
License
Licensed under MIT.





