gh-trusted-builds-app
 gh-trusted-builds-app copied to clipboard
gh-trusted-builds-app copied to clipboard
gh-trusted-builds-app
An example of using GitHub Actions reusable workflows to create and deploy a trusted software artifact.
Background
These days, companies of all sizes and industries create software, from small scripts to complicated back-of-house inventory forecasting systems. For both security and compliance reasons, companies want to be able to demonstrate that the software they're using is secure. One way to achieve this goal is to have a trusted build system that can produce signed statements about the software artifacts it produces. An authenticated statement like this is called an attestation. Throughout the lifecycle of the artifact, the build system can produce attestations of different types in order to demonstrate that certain events occurred. For example:
- multiple reviewers approved a particular code change
- this container image was built from this code commit
- a container image was scanned for vulnerabilities
Later on, when the software is deployed, the deployment system can check for these attestations and verify that they meet the company's policy for software. Any attempted deployments that fail to meet the policy can be rejected, thereby preventing low quality or malicious software from entering the production environment.
This repository is a demonstration of using GitHub Actions as that trusted build system. It's part of a number of repositories that you can find using the automated-governance topic:
liatrio/github-trusted-builds-app: a very simple Go applicationliatrio/github-trusted-builds-workflows: reusable workflows designed to be used by application teamsliatrio/github-trusted-builds-attestations: a tool for creating attestations of different typesliatrio/github-trusted-builds-policy: Rego policy used to evaluate attestations
Scenario
In this demonstration, multiple teams must approve a software artifact for deployment to production. As a shorthand, we'll call these teams the "central" teams for their particular domain; as opposed to "application" teams, who are responsible for the development and maintenance of one or more applications.
First up is the platform team, which is responsible for providing a Kubernetes cluster and deployment tooling. To facilitate automatic approvals, the platform team maintains a reusable GitHub Actions workflow that builds container images from source and pushes them to GitHub Container Registry. The images are annotated and signed by the workflow; in addition, a record of the signature is also uploaded to Rekor, which is a transparency log for supply chain security. In order to use the workflow, application teams only have to specify the reference to it in a job:
jobs:
build-and-push:
uses: liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@main
The security team also needs to approve which artifacts are deployed to production. Like the platform team, they provide a reusable workflow that scans container images for vulnerabilities and another workflow that evaluates if an artifact meets enterprise policy. This latter workflow produces a verification summary attestation (VSA) which indicates if the artifact passed or failed policy. Later on, the platform team can check for the existence of this VSA and approve or deny deployment accordingly.
Technologies
Before diving into the workflows, it may be helpful to briefly review the core technologies used by the demo.
in-toto Attestations
Much of this demo is involved with producing attestations, or signed statements about a software artifact. A popular format for attestations comes from the in-toto project, which is focused on software supply-chain security. While this demonstration does not use in-toto directly, many open source projects outside in-toto use the in-toto attestation format; this includes all the attestations created in this demo.
The in-toto format consists of several pieces:
- predicate: structured information about a software artifact. The predicate type determines the structure and type of data available.
- statement: contains the predicate and provides a list of subjects (software artifacts) described by the predicate.
- envelope: the wrapper for the statement and any signatures.
Here's an example of an in-toto attestation:
{
"payloadType": "application/vnd.in-toto+json",
"payload": "eyJfdHlwZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vaW4tdG90by5pby9TdGF0ZW1lbnQvdjEiLCJzdWJqZWN0IjpbeyJuYW1lIjoiZ2hjci5pby9saWF0cmlvL2doLXRydXN0ZWQtYnVpbGRzLWFwcCIsImRpZ2VzdCI6eyJzaGEyNTYiOiI0ZDllNzdmZWRjYTI5MzkzZGZmOWEzOWIwNjVkMTU4YWFhOTY0NGMxOGIyYzUxZjc1ZmNhZjg0YjhjOTQxYWJmIn19XSwicHJlZGljYXRlVHlwZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vc2xzYS5kZXYvdmVyaWZpY2F0aW9uX3N1bW1hcnkvdjAuMiIsInByZWRpY2F0ZSI6eyJpbnB1dF9hdHRlc3RhdGlvbnMiOlt7ImRpZ2VzdCI6eyJzaGEyNTYiOiJmMTQwZjg4NjA5NzQ5YWQ5OWUwNTgzYzUyZWNkNWNmMTZjMmU1ZTJjNTBjZDYxNDAzNjRhOTkxY2MxYWYyMmRhIn0sInVyaSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vcmVrb3Iuc2lnc3RvcmUuZGV2L2FwaS92MS9sb2cvZW50cmllcz9sb2dJbmRleD0yMTQ0OTgzMSJ9LHsiZGlnZXN0Ijp7InNoYTI1NiI6ImU3Y2M5ODk2OGU5MDJmMDA2M2I5YWQ0OTJiMjJlYzJkMGE2NDdmMzQzZWQxNjg5YzBhMzdjYjNlZjc2ZjljMzEifSwidXJpIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9yZWtvci5zaWdzdG9yZS5kZXYvYXBpL3YxL2xvZy9lbnRyaWVzP2xvZ0luZGV4PTIxNDQ5ODM0In0seyJkaWdlc3QiOnsic2hhMjU2IjoiOTk1ZWY1ZjYwODkzOGYwM2JmNzQxNWI2NTIzYTVlYzFjYTIwZDFmMWNkMzdkNjUwYzIzM2FlYjM2NThmYjFmYSJ9LCJ1cmkiOiJodHRwczovL3Jla29yLnNpZ3N0b3JlLmRldi9hcGkvdjEvbG9nL2VudHJpZXM/bG9nSW5kZXg9MjE0NDk4NjEifV0sInBvbGljeSI6eyJ1cmkiOiJodHRwczovL2dpdGh1Yi5jb20vbGlhdHJpby9naC10cnVzdGVkLWJ1aWxkcy1wb2xpY3kvcmVsZWFzZXMvZG93bmxvYWQvdjEuMS4xL2J1bmRsZS50YXIuZ3oifSwicG9saWN5X2xldmVsIjoiU0xTQV9MRVZFTF8zIiwicmVzb3VyY2VfdXJpIjoiZ2hjci5pby9saWF0cmlvL2doLXRydXN0ZWQtYnVpbGRzLWFwcCIsInRpbWVfdmVyaWZpZWQiOiIyMDIzLTA1LTIzVDE3OjUyOjE0LjE4NjE2MTE2NVoiLCJ2ZXJpZmljYXRpb25fcmVzdWx0IjoiUEFTU0VEIiwidmVyaWZpZXIiOnsiaWQiOiJodHRwczovL2dpdGh1Yi5jb20vbGlhdHJpby9naC10cnVzdGVkLWJ1aWxkcy13b3JrZmxvd3MvLmdpdGh1Yi93b3JrZmxvd3MvcG9saWN5LXZlcmlmaWNhdGlvbi55YW1sQHJlZnMvaGVhZHMvbWFpbiJ9fX0=",
"signatures": [
{
"keyid": "",
"sig": "MEUCICYn68n2eOij6SLpgnzz1lyrW5dSixGRambvA/625DwiAiEAktVa8wx6mqSYpzzsVWUzcaAZcLsQYs/paYFRJGpSx2o="
}
]
}
This is the envelope, which contains the in-toto statement in the payload field. Decoding the payload field shows the statement:
example in-toto statement (click to expand)
{
"_type": "https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1",
"subject": [
{
"name": "ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app",
"digest": {
"sha256": "4d9e77fedca29393dff9a39b065d158aaa9644c18b2c51f75fcaf84b8c941abf"
}
}
],
"predicateType": "https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2",
"predicate": {
"input_attestations": [
{
"digest": {
"sha256": "f140f88609749ad99e0583c52ecd5cf16c2e5e2c50cd6140364a991cc1af22da"
},
"uri": "https://rekor.sigstore.dev/api/v1/log/entries?logIndex=21449831"
},
{
"digest": {
"sha256": "e7cc98968e902f0063b9ad492b22ec2d0a647f343ed1689c0a37cb3ef76f9c31"
},
"uri": "https://rekor.sigstore.dev/api/v1/log/entries?logIndex=21449834"
},
{
"digest": {
"sha256": "995ef5f608938f03bf7415b6523a5ec1ca20d1f1cd37d650c233aeb3658fb1fa"
},
"uri": "https://rekor.sigstore.dev/api/v1/log/entries?logIndex=21449861"
}
],
"policy": {
"uri": "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-policy/releases/download/v1.1.1/bundle.tar.gz"
},
"policy_level": "SLSA_LEVEL_3",
"resource_uri": "ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app",
"time_verified": "2023-05-23T17:52:14.186161165Z",
"verification_result": "PASSED",
"verifier": {
"id": "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main"
}
}
}
This statement links a particular container image (ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:4d9e77fedca29393dff9a39b065d158aaa9644c18b2c51f75fcaf84b8c941abf) to a predicate (https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2).
We'll see more on this predicate type later. For more information about in-toto attestations, the official specification is a good place to start.
SLSA
Software supply-chain security has been a growing concern in the past few years. SLSA (supply-chain levels for software artifacts) is an attempt to codify best practices around producing software artifacts by describing a series of standards and levels that a software artifact can obtain. A higher level indicates a more secure and robust software delivery process. The SLSA website gives a more comprehensive overview of the levels.
The initial focus of SLSA is around how software is built, and the framework describes a provenance attestation. Provenance links a software artifact to the source code from which it was created, as well as the method and environment in which the build ran.
The project also provides some tools for creating provenance, like the slsa-github-generator, which provides ways to create provenance attestations for different artifact types built in GitHub Actions.
This demonstration uses the SLSA container generator to create a provenance attestation.
Open Policy Agent
Open Policy Agent (OPA) is a set of tools for writing and executing policies in a language called Rego. The policies are used to authorize some request or event, given input data. For example, this is part of a larger policy used in this demo to check that a pull request had at least one reviewer:
package security.pullrequest
default allow = false
allow {
count(violation) == 0
}
violation[msg] {
count(input.predicate.reviewers) < 1
msg := "pull request reviewers is less than 1"
}
This demonstration uses Rego in multiple places: first liatrio/github-trusted-builds-attestations uses policy on
the attestations generated by the workflow in order to produce a verification summary attestation (VSA). Later on, when the workflow attempts to deploy to a local Kubernetes cluster, the Sigstore policy controller
is configured with a Rego policy that checks the attributes of the VSA produced earlier.
GitHub Actions: Reusable Workflows
GitHub Actions has multiple ways to minimize duplication in a workflow -- one method is to create a custom action. With composite actions, it's even possible to use wrap multiple external actions in a single reusable unit.
However, for this demonstration, we're relying on a larger unit -- the reusable workflow. A reusable workflow functions similarly to a composite action, in that it allows you to bundle multiple actions together and pass inputs/outputs between them. Instead of wrapping individual actions, the workflow can include one or more complete jobs, so we can perform separate tasks in parallel. In addition, a reusable workflow has different security features that make it desirable over other ways to reduce duplication in GitHub Actions.
First and foremost is the fact that a reusable workflow runs in a separate virtual machine than other jobs in the caller's workflow. This is in contrast to an individual action, which always runs in the larger context of a job. Running on the same virtual machine as the workflow caller makes it difficult to access secrets in a way that doesn't also allow the caller to use them. It also means that a caller can manipulate the environment in order to do things like capture environment variables or snoop on network traffic. With reusable workflows, we can eliminate these concerns which would otherwise make it difficult for us to trust the attestations produced by the workflows.
This demonstration also shows the use of least-privilege access with reusable workflows. Each reusable workflow is specifically granted the token permissions the caller will allow. This enables the caller repository to have a safer, read-only default to GitHub token permissions.
GitHub Actions: OpenID Connect
A GitHub Actions feature that complements reusable workflows is the OpenID Connect (OIDC) integration, which allows a job to acquire an OIDC id token, which is a JSON web token (JWT) signed by GitHub Actions.
A JWT is a popular token format that contains three sections: a header, claims, and signature. The header contains metadata about the token, while the claims typically contain information about the entity described by the token, as well as details needed to validate the token, such as the token issuer and expiry. Finally, the signature encompasses the header and claims, so that by verifying the signature, we know that we can trust the information in the other two sections.
In the case of GitHub Actions, the claims in the token describe the running workflow:
{
"jti": "79ba45c1-a46f-4605-b68d-8207b5a5287f",
"sub": "repo:liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app:ref:refs/heads/main",
"aud": "https://github.com/liatrio",
"ref": "refs/heads/main",
"sha": "0c960da8e1b1844d14ac4048b60f2ec892ed21a3",
"repository": "liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app",
"repository_owner": "liatrio",
"repository_owner_id": "5726618",
"run_id": "4724225373",
"run_number": "22",
"run_attempt": "1",
"repository_visibility": "public",
"repository_id": "627556067",
"actor_id": "9082799",
"actor": "alexashley",
"workflow": "app",
"head_ref": "",
"base_ref": "",
"event_name": "workflow_dispatch",
"ref_type": "branch",
"workflow_ref": "liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/.github/workflows/app.yaml@refs/heads/main",
"workflow_sha": "0c960da8e1b1844d14ac4048b60f2ec892ed21a3",
"job_workflow_ref": "liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main",
"job_workflow_sha": "f1e5fbbfa4f750e221038adca773bca75ec38c3d",
"runner_environment": "github-hosted",
"iss": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com",
"nbf": 1681753278,
"exp": 1681754178,
"iat": 1681753878
}
One claim in particular, job_workflow_ref, is instrumental to the security properties of this demonstration; it indicates the workflow path and Git reference that were used in this job. You may also notice the similarly-named workflow_ref claim, which is the path to the running workflow definition.
When using a normal workflow, the values of these two claims is the same, but when a reusable workflow is called by another workflow, the value of job_workflow_ref will be the path and Git ref of the reusable workflow.
Because the token is signed by GitHub Actions, as long as we validate the token signature and claims, we can trust that only a running instance of the workflow is in possession of the token.
This property allows us to create federated trust in order to access cloud provider resources or even request code-signing certificates.
In order to validate tokens, we need to know what keys were used to sign the tokens. GitHub Actions hosts an OpenID Connect provider at https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com, which includes an OIDC discovery document at the /.well-known/openid-configuration endpoint:
{
"issuer": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com",
"jwks_uri": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com/.well-known/jwks",
"subject_types_supported": [
"public",
"pairwise"
],
"response_types_supported": [
"id_token"
],
"claims_supported": [
"sub",
"aud",
"exp",
"iat",
"iss",
"jti",
"nbf",
"ref",
"repository",
"repository_id",
"repository_owner",
"repository_owner_id",
"run_id",
"run_number",
"run_attempt",
"actor",
"actor_id",
"workflow",
"workflow_ref",
"workflow_sha",
"head_ref",
"base_ref",
"event_name",
"ref_type",
"environment",
"environment_node_id",
"job_workflow_ref",
"job_workflow_sha",
"repository_visibility",
"runner_environment"
],
"id_token_signing_alg_values_supported": [
"RS256"
],
"scopes_supported": [
"openid"
]
}
The jwks_uri field (JSON web key set) contains a URL that can be used to grab the public keys which are needed to verify the signature on the JWTs issued
by GitHub Actions.
Finally, it's worth mentioning how a job receives an id token, as it's not one of the standard OAuth2 grants.
In order to acquire an id token, a job must first be configured with the id-token permission:
jobs:
demo:
permissions:
id-token: write
Later on, once the job is running, it will have access to the following environment variables:
ACTIONS_ID_TOKEN_REQUEST_URLACTIONS_RUNTIME_TOKEN
The job can then make an HTTP POST request to $ACTIONS_ID_TOKEN_REQUEST_URL with $ACTIONS_RUNTIME_TOKEN in the authorization header (using the bearer token scheme), and the job will receive an
id token in the value field of the JSON response.
For a more in-depth overview of using GitHub Actions' OIDC feature with reusable workflows, the SLSA GitHub Generator specifications go into additional detail.
Sigstore: Cosign
Cosign is a tool from the Sigstore project for signing and verifying container images, blobs, and attestations. It also supports running OPA or CUE policies against those attestations. In this demonstration, we'll use cosign to sign both a container image and a number of attestations about the image.
Sigstore: Policy Controller
Another Sigstore project, the policy controller, is used to gate Kubernetes deployments with OPA or CUE policy. It can verify that images are signed and check the attestations against a supplied policy. We'll use it in this demo to check that our container image has an attestation signed by the right identity.
Sigstore: Rekor Transparency Log
Rekor is an open-source software supply chain tool that’s part of the larger Sigstore project. It consists of a transparency log server and a command line tool to interact with the server. While there is a public instance, enterprises can also deploy and run Rekor on their own infrastructure.
Rekor has a number of properties that make it useful as an attestation store; first, its underlying storage is a robust, append-only log – new entries can be added, but old entries cannot be updated or deleted. Rekor’s implementation also provides the ability to demonstrate that an entry is actually included in the log, which users can verify through what’s called an inclusion proof. Similarly, by recording certain metadata about the log, users can also verify over time that the log hasn’t been tampered with and that only new entries have been created (through a consistency proof).
Rekor is used to store container image signatures, along with the public key or certificate that's needed to verify the signature. It can also store in-toto attestations, along with a few other built-in record types.
Sigstore: Fulcio Certificate Authority
Fulcio is a certificate authority for code-signing -- it issues short-lived (10 minute) certificates that anyone can use to sign images or attestations. The official documentation goes into more detail, but at a high level this is the flow for acquiring a code-signing certificate:
- Acquire an id token from an issuer that Fulcio is configured to trust. This demo uses the GitHub Actions id token
- Generate a temporary public/private key pair -
cosignwill do this automatically - Prove that you control the key pair by doing one of the following:
- Create a certificate signing request (CSR)
- Grab the
subclaim from the id token and sign it
- Make a request to Fulcio with the id token and the proof from the previous step
- Fulcio will validate the id token and check the provided proof
- If the request is valid, Fulcio will issue a code-signing certificate and populate the certificate fields with information from the id token
- When using a GitHub Actions OIDC token, the issuer will be
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.comand the subject will be the value of thejob_workflow_refclaim
- When using a GitHub Actions OIDC token, the issuer will be
- Depending on the deployment type, Fulcio will also submit a request to a certificate transparency log to include the certificate in the logs. The response from the certificate transparency log will include a signed timestamp that will be added to the certificate.
After receiving the certificate, cosign or other tools can sign images or attestations with the private key generated earlier, and then upload the signature and certificate to Rekor.
Once the signing is finished, the key pair can be discarded, as the certificate will be in Rekor for validation later.
For a more concrete example, this is a sequence diagram that shows how a GitHub Actions workflow might build & sign a container image:
Later, when someone tries to validate the signature, they can check that the certificate chains up to the Fulcio root, that the signature happened during the window when the certificate was valid, and, most importantly, verify that the certificate identity matches the expected signer. Anyone can use the Sigstore public good Fulcio instance to get a certificate, so it's important that you only trust signatures from identities that you trust.
Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)
A software bill of materials describes the components that make up a software artifact. The SBOM includes the dependencies of an artifact and may include licensing information about the artifact and its dependencies. While an SBOM can be useful to enforce internal licensing standards, it's also valuable for vulnerability analysis; this is especially true when there's a need to retroactively look at software running in production and determine if it's vulnerable to a new attack. If an organization already has SBOMs for the software it's running, it becomes much easier to tell if there's an impact from a new vulnerability.
There are several standard formats, like SPDX from the Linux Foundation and CycloneDX from OWASP. Fortunately, there are a number of tools for generating and working with SBOMs and most tools understand multiple standards. In this demonstration, we're using SPDX as the format and Syft as the tool to generate SBOMs.
Workflows
The demo makes use of several reusable workflows defined in liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows.
Each workflow is owned by either the platform or security teams.
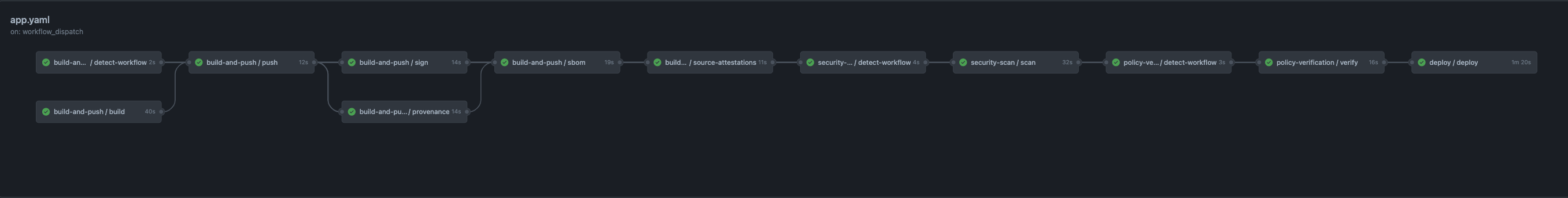
Platform: Build & Push
The platform team's build-and-push workflow is split into several jobs:
detect-workflowbuildpushsignsource-attestationsprovenancesbom
The build job uses Docker to build a container image, but doesn't push it to a container registry.
Instead, the job outputs a tar file that will be pushed by the next job.
The reason to split build and push is that the build step is executing untrusted code from the application team; consequently, we don't want that job to be able to request the id token that's used for signing or to try to push a malicious image.
It's also often the case that organizations will use a central registry for all teams, and the authenticated machine identity is likely to have access to more repositories than the one used by the application image.
In that case, the build job could even push images to other repositories; while the authentication in this demo is scoped to the liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app repository, it's still important to separate these steps for those reasons.
So the build job only has the permissions it needs in order to checkout the repo:
jobs:
build:
permissions:
contents: read
Next up is the push job, which loads the tar file from the build job and pushes it to GitHub Container Registry (GHCR). Like the build job, it only has the permissions it needs to write to the registry:
jobs:
push:
permissions:
packages: write
With the image built and stored in GHCR, we can now sign the image in the sign job.
This job has access to the workflow id token so that it can request a signing certificate from Fulcio; the job also needs permission to push the signature to the registry, so it has that access as well:
jobs:
sign:
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: read
packages: write
The sign job uses cosign to sign the image and annotate it with the workflow run:
- name: Sign
run: |
cosign sign \
--annotations liatr.io/github-actions-run-link='${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}' \
--annotations liatr.io/signed-off-by=platform-team \
--rekor-url ${{ inputs.rekorUrl }} \
--fulcio-url ${{ inputs.fulcioUrl }} \
--yes ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}@${{ needs.push.outputs.digest }}
Next, the provenance and source-attestations job both produce attestations that are signed by the workflow.
The provenance job uses the container generator from slsa-framework/slsa-github-generator to produce a provenance attestation that links the container image and source code, along with some metadata about how the artifact was produced.
Because the workflow is only using the generator, it doesn't have the full context necessary to populate the entire provenance, so some fields aren't present.
Here's an example of the provenance generated by this job (Rekor entry):
SLSA Provenance attestation (click to expand)
_type: https://in-toto.io/Statement/v0.1
predicateType: https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2
subject:
- name: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
digest:
sha256: 6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
predicate:
builder:
id: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main
buildType: https://github.com/slsa-framework/slsa-github-generator/container@v1
invocation:
configSource:
uri: git+https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@refs/heads/main
digest:
sha1: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
entryPoint: .github/workflows/app.yaml
parameters: {}
environment:
github_actor: rcoy-v
github_actor_id: '9846738'
github_base_ref: ''
github_event_name: push
github_event_payload:
after: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
base_ref: null
before: c4df379485ab80b62ae0cc57c611348a3015f944
commits:
- author:
email: [email protected]
name: Ryan Vance
username: rcoy-v
committer:
email: [email protected]
name: GitHub
username: web-flow
distinct: true
id: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
message: 'docs: remove extra newline (#1)'
timestamp: '2023-05-22T10:27:27-05:00'
tree_id: e5dc0b7046c70012c4b84bc7ede6f969efe79edf
url: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/commit/e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
compare: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/compare/c4df379485ab...e1f1d4396181
created: false
deleted: false
forced: false
head_commit:
author:
email: [email protected]
name: Ryan Vance
username: rcoy-v
committer:
email: [email protected]
name: GitHub
username: web-flow
distinct: true
id: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
message: 'docs: remove extra newline (#1)'
timestamp: '2023-05-22T10:27:27-05:00'
tree_id: e5dc0b7046c70012c4b84bc7ede6f969efe79edf
url: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/commit/e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
organization:
avatar_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/5726618?v=4
description: Enterprise Delivery Transformation, DevOps, Cloud Native Automation
events_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/events
hooks_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/hooks
id: 5726618
issues_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/issues
login: liatrio
members_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/members{/member}
node_id: MDEyOk9yZ2FuaXphdGlvbjU3MjY2MTg=
public_members_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/public_members{/member}
repos_url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio/repos
url: https://api.github.com/orgs/liatrio
pusher:
email: [email protected]
name: rcoy-v
ref: refs/heads/main
repository:
allow_forking: true
archive_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/{archive_format}{/ref}
archived: false
assignees_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/assignees{/user}
blobs_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/git/blobs{/sha}
branches_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/branches{/branch}
clone_url: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app.git
collaborators_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/collaborators{/collaborator}
comments_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/comments{/number}
commits_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/commits{/sha}
compare_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/compare/{base}...{head}
contents_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/contents/{+path}
contributors_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/contributors
created_at: 1684768749
default_branch: main
deployments_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/deployments
description: null
disabled: false
downloads_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/downloads
events_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/events
fork: false
forks: 0
forks_count: 0
forks_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/forks
full_name: liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
git_commits_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/git/commits{/sha}
git_refs_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/git/refs{/sha}
git_tags_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/git/tags{/sha}
git_url: git://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app.git
has_discussions: false
has_downloads: true
has_issues: true
has_pages: false
has_projects: true
has_wiki: true
homepage: null
hooks_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/hooks
html_url: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
id: 643991426
is_template: false
issue_comment_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/issues/comments{/number}
issue_events_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/issues/events{/number}
issues_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/issues{/number}
keys_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/keys{/key_id}
labels_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/labels{/name}
language: Go
languages_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/languages
license: null
master_branch: main
merges_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/merges
milestones_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/milestones{/number}
mirror_url: null
name: gh-trusted-builds-app
node_id: R_kgDOJmKHgg
notifications_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/notifications{?since,all,participating}
open_issues: 0
open_issues_count: 0
organization: liatrio
owner:
avatar_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/5726618?v=4
email: [email protected]
events_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/events{/privacy}
followers_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/followers
following_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/following{/other_user}
gists_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/gists{/gist_id}
gravatar_id: ''
html_url: https://github.com/liatrio
id: 5726618
login: liatrio
name: liatrio
node_id: MDEyOk9yZ2FuaXphdGlvbjU3MjY2MTg=
organizations_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/orgs
received_events_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/received_events
repos_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/repos
site_admin: false
starred_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/starred{/owner}{/repo}
subscriptions_url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio/subscriptions
type: Organization
url: https://api.github.com/users/liatrio
private: false
pulls_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/pulls{/number}
pushed_at: 1684769247
releases_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/releases{/id}
size: 0
ssh_url: [email protected]:liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app.git
stargazers: 0
stargazers_count: 0
stargazers_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/stargazers
statuses_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/statuses/{sha}
subscribers_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/subscribers
subscription_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/subscription
svn_url: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
tags_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/tags
teams_url: https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/teams
topics: []
trees_url: >-
https://api.github.com/repos/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/git/trees{/sha}
updated_at: '2023-05-22T15:19:19Z'
url: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
visibility: public
watchers: 0
watchers_count: 0
web_commit_signoff_required: false
sender:
avatar_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/9846738?v=4
events_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/events{/privacy}
followers_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/followers
following_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/following{/other_user}
gists_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/gists{/gist_id}
gravatar_id: ''
html_url: https://github.com/rcoy-v
id: 9846738
login: rcoy-v
node_id: MDQ6VXNlcjk4NDY3Mzg=
organizations_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/orgs
received_events_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/received_events
repos_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/repos
site_admin: false
starred_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/starred{/owner}{/repo}
subscriptions_url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v/subscriptions
type: User
url: https://api.github.com/users/rcoy-v
github_head_ref: ''
github_ref: refs/heads/main
github_ref_type: branch
github_repository_id: '643991426'
github_repository_owner: liatrio
github_repository_owner_id: '5726618'
github_run_attempt: '1'
github_run_id: '5047631192'
github_run_number: '4'
github_sha1: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
metadata:
buildInvocationID: 5047631192-1
completeness:
parameters: true
environment: false
materials: false
reproducible: false
materials:
- uri: git+https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@refs/heads/main
digest:
sha1: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
In addition to the provenance, the build-and-push workflow's source-attestation job produces a custom pull request attestation using liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-attestations.
This attestation ties the commit to the pull request and includes information about whether the pull request was approved and which individuals reviewed it.
Many enterprises have policies that require a minimum number of reviewers, so this attestation can be used to require that artifacts were built only from approved source code changes.
Here's an example of a pull request attestation produced by the workflow (Rekor entry):
_type: https://in-toto.io/Statement/v0.1
predicateType: https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1
subject:
- name: git+https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app.git
digest:
sha1: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
- name: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
digest:
sha256: 6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
predicate:
link: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/pull/1
title: 'docs: remove extra newline'
author: rcoy-v
mergedBy: rcoy-v
createdAt: '2023-05-22T15:27:05Z'
mergedAt: '2023-05-22T15:27:27Z'
base: main
head: rcoy-v-patch-1
approved: true
reviewers:
- name: alexashley
approved: true
reviewLink: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/pull/1#pullrequestreview-1436887240
timestamp: '2023-05-22T15:27:18Z'
contributors:
- name: rcoy-v
predicateCreatedAt: '2023-05-22T15:28:48.369418041Z'
Finally, the last job in this workflow, called sbom, produces a software bill of materials using Syft.
The workflow runs Syft against the pushed image and produces an SBOM in the SPDX format.
Then the job runs cosign attest in order to sign and upload the SBOM as an attestation.
While there's support in Syft for attesting the SBOM through sfyt attest, we're using cosign directly for more fine-grained configuration:
$ syft -o spdx-json --file sbom.spdx.json ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}@${{ needs.push.outputs.digest }}
$ cosign attest --predicate="sbom.spdx.json" \
--rekor-url ${{ inputs.rekorUrl }} \
--type spdxjson \
--fulcio-url ${{ inputs.fulcioUrl }} \
--yes \
ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}@${{ needs.push.outputs.digest }}
For an example of an SBOM, here's an attestation from one of the workflow runs (Rekor log entry):
SPDX bill of materials (click to expand)
_type: https://in-toto.io/Statement/v0.1
predicateType: https://spdx.dev/Document
subject:
- name: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
digest:
sha256: 294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
predicate:
SPDXID: SPDXRef-DOCUMENT
creationInfo:
created: '2023-05-26T22:02:06Z'
creators:
- 'Organization: Anchore, Inc'
- 'Tool: syft-0.82.0'
licenseListVersion: '3.20'
dataLicense: CC0-1.0
documentNamespace: >-
https://anchore.com/syft/image/ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256-294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc-5b3e747f-d8dc-4a0b-a01f-60d9ed082d68
files:
- SPDXID: SPDXRef-File-app-d20c3eddd3b3b879
checksums:
- algorithm: SHA1
checksumValue: '0000000000000000000000000000000000000000'
comment: >-
layerID:
sha256:53ea96ed00f53fed01d48a16b049a99938902ed5ee4517e57f464d7fabacb33f
copyrightText: ''
fileName: /app
fileTypes:
- OTHER
licenseConcluded: NOASSERTION
- SPDXID: SPDXRef-File-app-server-50b4875c6ae53f25
checksums:
- algorithm: SHA256
checksumValue: a947dcd63d19e76e860f32f8bdd33ca47297d10d8e6f1a2eb913224d93fe9fe4
comment: >-
layerID:
sha256:53ea96ed00f53fed01d48a16b049a99938902ed5ee4517e57f464d7fabacb33f
copyrightText: ''
fileName: /app/server
fileTypes:
- APPLICATION
- BINARY
licenseConcluded: NOASSERTION
name: >-
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
packages:
- SPDXID: >-
SPDXRef-Package-go-module-github.com-liatrio-gh-trusted-builds-app-1808e23a377c2b90
copyrightText: NOASSERTION
downloadLocation: NOASSERTION
externalRefs:
- referenceCategory: SECURITY
referenceLocator: cpe:2.3:a:liatrio:gh-trusted-builds-app:\(devel\):*:*:*:*:*:*:*
referenceType: cpe23Type
- referenceCategory: SECURITY
referenceLocator: cpe:2.3:a:liatrio:gh_trusted_builds_app:\(devel\):*:*:*:*:*:*:*
referenceType: cpe23Type
- referenceCategory: PACKAGE-MANAGER
referenceLocator: pkg:golang/github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@(devel)
referenceType: purl
licenseConcluded: NOASSERTION
licenseDeclared: NOASSERTION
name: github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
sourceInfo: 'acquired package info from go module information: /app/server'
versionInfo: (devel)
relationships:
- comment: >-
evident-by: indicates the package's existence is evident by the given
file
relatedSpdxElement: SPDXRef-File-app-server-50b4875c6ae53f25
relationshipType: OTHER
spdxElementId: >-
SPDXRef-Package-go-module-github.com-liatrio-gh-trusted-builds-app-1808e23a377c2b90
- relatedSpdxElement: SPDXRef-DOCUMENT
relationshipType: DESCRIBES
spdxElementId: SPDXRef-DOCUMENT
spdxVersion: SPDX-2.3
Security: Image Scan
Now that the image is built, it needs to be scanned for vulnerabilities by an approved image scanner.
The security team uses Trivy for this, because it supports outputting the scan results in a format that cosign can use to create an attestation:
steps:
- name: Trivy Scan
uses: aquasecurity/[email protected]
with:
image-ref: ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }}@${{ inputs.digest }}
format: 'cosign-vuln'
output: trivy.report.json
env:
TRIVY_USERNAME: ${{ github.actor }}
TRIVY_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
The scan-image workflow only contains a single job called scan, which takes as an input the digest of the image created in the build-and-push workflow.
It invokes the Trivy GitHub Action and then uses cosign attest to upload the vulnerability results as an attestation to Rekor.
This is an example of what the vulnerability attestation looks like (Rekor entry):
Vulnerability attestation (click to expand)
_type: https://in-toto.io/Statement/v0.1
predicateType: https://cosign.sigstore.dev/attestation/vuln/v1
subject:
- name: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
digest:
sha256: 6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
predicate:
invocation:
parameters: null
uri: ''
event_id: ''
builder.id: ''
scanner:
uri: pkg:github/aquasecurity/[email protected]
version: 0.38.1
db:
uri: ''
version: ''
result:
ArtifactName: >-
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
ArtifactType: container_image
Metadata:
DiffIDs:
- >-
sha256:0c2717ceeb1e6dec4b2a748974b77fd8f13ac5c3d9d434f80f2c1b58c83f31ae
- >-
sha256:8a90007133baa3918410eca530757f8e7c65aff8421ac010a185ff51c2f88e80
ImageConfig:
architecture: amd64
config:
Entrypoint:
- /app/server
Env:
- >-
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
Labels:
org.opencontainers.image.created: '2023-05-22T15:27:46.155Z'
org.opencontainers.image.description: ''
org.opencontainers.image.licenses: ''
org.opencontainers.image.revision: e1f1d4396181766e12fca22f2ba856e8154b4304
org.opencontainers.image.source: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
org.opencontainers.image.title: gh-trusted-builds-app
org.opencontainers.image.url: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
org.opencontainers.image.version: main
WorkingDir: /app
created: '2023-05-22T15:28:09.391753905Z'
history:
- comment: buildkit.dockerfile.v0
created: '2023-05-22T15:27:48.389191081Z'
created_by: WORKDIR /app
- comment: buildkit.dockerfile.v0
created: '2023-05-22T15:28:09.391753905Z'
created_by: 'COPY /app/server . # buildkit'
- comment: buildkit.dockerfile.v0
created: '2023-05-22T15:28:09.391753905Z'
created_by: ENTRYPOINT ["/app/server"]
empty_layer: true
os: linux
rootfs:
diff_ids:
- >-
sha256:0c2717ceeb1e6dec4b2a748974b77fd8f13ac5c3d9d434f80f2c1b58c83f31ae
- >-
sha256:8a90007133baa3918410eca530757f8e7c65aff8421ac010a185ff51c2f88e80
type: layers
ImageID: >-
sha256:dfde59c7ffd4a99f202c45669cc6311dadc906d82f7e40f445ebc7a226bd8781
RepoDigests:
- >-
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
SchemaVersion: 2
metadata:
scanStartedOn: '2023-05-22T15:29:20.193667225Z'
scanFinishedOn: '2023-05-22T15:29:20.193667225Z'
The image produced by the demo is very simple, and as of this writing doesn't contain any vulnerabilities. However, if there were vulnerabilities in the image, they would appear in the attestation and policy could be used to reject artifacts that either had too many vulnerabilities or had certain high-risk CVEs.
Security: Policy Verification
Now that we've attested to the number of code reviewers, built and signed an image, attested to image provenance and vulnerabilities, it's time to evaluate those attestations. While it would be possible to use a workflow or Kubernetes validating admission webhook to evaluate all the attestations, it would be cumbersome to have that controller know everything that needs to be validated about the image. Especially considering that enterprises will refine their internal policies over time and need to make adjustments to every deployment gate.
Instead, we can evaluate all the attestations up to this point and produce a verification summary attestation, which will attest that the container image either passed or failed a particular policy.
In order to do this, we use liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-attestations to pull the attestations for an image, verify that the attestations were signed by the expected workflows, and
then run policy against those attestations in order to check if the image meets the standards enforced by the policy.
Either way, the attestations tool will produce a VSA that can be used later to prevent low quality or malicious images from being deployed. Here's an example of what the VSA produced by the workflow looks like (Rekor entry):
_type: https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1
subject:
- name: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
digest:
sha256: 6c3bf887638f7c0d86731e6208befa1b439e465cb435465d982c50609553b514
predicateType: https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2
predicate:
input_attestations:
- digest:
sha256: 1c735dab58c44079863b1a5e209617f8357409d63203e2309894e0b0d1e0ffaa
uri: https://rekor.sigstore.dev/api/v1/log/entries?logIndex=21341724
- digest:
sha256: cdcf6759b454b26b6f151b2913c2949d4b1bef8c97d78085553f55ededc79f15
uri: https://rekor.sigstore.dev/api/v1/log/entries?logIndex=21341756
policy:
uri: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-policy/releases/download/v1.1.1/bundle.tar.gz
policy_level: SLSA_LEVEL_3
resource_uri: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
time_verified: '2023-05-22T15:29:58.061215474Z'
verification_result: PASSED
verifier:
id: >-
https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main
Internally, the policy-verification workflow has two jobs:
detect-workflowverify
The detect-workflow job determines the reusable workflow ref by requesting an id token and grabbing the job_workflow_ref claim, which is used later by the verify job to populate the verifier.id field in the SLSA VSA.
This job may be removed in the future if GitHub enhances the github context by making the job_workflow_ref information available directly.
Next, the verify job invokes liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-attestations with the vsa subcommand:
- name: Create Verification Summary Attestation
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: |
attestation vsa \
--artifact-uri ghcr.io/${{ github.repository }} \
--artifact-digest ${{ inputs.digest }} \
--policy-url "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-policy/releases/download/v1.1.1/bundle.tar.gz" \
--verifier-id ${{ github.server_url }}/${{ needs.metadata.outputs.jobWorkflowRef }} \
--fulcio-url ${{ inputs.fulcioUrl }} \
--rekor-url ${{ inputs.rekorUrl }}
The GITHUB_TOKEN environment variable is used to query GHCR for attestations and also to push the VSA to the registry after verification is finished.
Like the other jobs that produce attestations, it also needs the ability to request an id token:
jobs:
verify:
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: read
packages: write
Platform: Deployment
Finally, we'd like to actually deploy the artifact that the workflow built. In an enterprise setting, this may not be part of the same workflow that built the image, but the deployment is included here to show an end-to-end picture.
In this workflow, we first download k3d, which is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution that runs in Docker.
It'll serve as our deployment target for the demo, as we can use it to spin up a temporary Kubernetes cluster in the GitHub Actions runner.
Once it's installed, we can create a simple cluster called demo:
$ k3d cluster create --agents 1 --no-lb --wait demo
Now we can install and configure the Sigstore policy-controller, which is what we'll use to verify the VSA produced by the policy-verification workflow.
The policy-controller has a custom ClusterImagePolicy Kubernetes resource that we need to create in order to tell the controller what attestations to verify.
For the ease of development, this policy is hard-coded in the workflow:
apiVersion: policy.sigstore.dev/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterImagePolicy
metadata:
name: demo
spec:
images:
- glob: "ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app**"
authorities:
- name: attestation
keyless:
url: https://fulcio.sigstore.dev
trustRootRef:
identities:
- issuer: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main
ctlog:
url: https://rekor.sigstore.dev
trustRootRef:
attestations:
- name: has-passing-vsa
predicateType: "https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2"
policy:
type: rego
data: |
package sigstore
default isCompliant = false
isCompliant {
input.predicate.verifier.id == "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main"
input.predicate.verification_result == "PASSED"
}
This ClusterImagePolicy says we're expecting an attestation of type https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2 that was signed with a certificate issued from the GitHub Actions issuer via Fulcio, and that the certificate was issued to the policy-verification workflow.
In the attestation policy, we also check that the VSA result was PASSED and that the verifier was the one we expect.
If the policy controller allows the deployment, then the end result won't look any different from a normal Kubernetes deployment. However, if image fails to meet policy, the deployment will be blocked and this message will be returned from the Kubernetes API server:
error: failed to create deployment: admission webhook "policy.sigstore.dev" denied the request: validation failed: failed policy: demo: spec.template.spec.containers[0].image
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:4c2a8a95f7ecc73abc62abd699dfb33579dd29ecde4f44f009dbbca6305609e4 failed evaluating rego policy for type has-passing-vsa: policy is not compliant for query 'isCompliant = data.sigstore.isCompliant'
Unfortunately, it doesn't appear that there's much feedback on what aspect of the policy failed. In this case, it's a very simple policy, which would make it easier to understand what failed. However, there's more that could be done to make the error understandable for end-users.
Verification
While the image attestations are validated by liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-attestations and the policy-controller, it's also possible to validate the steps that were done in
this demo by using cosign directly.
To demonstrate, we'll use this workflow run which produced the image ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc.
To get an overview of the images' attestations and signatures, we can use cosign tree:
$ 📦 Supply Chain Security Related artifacts for an image: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
└── 💾 Attestations for an image tag: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app:sha256-294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc.att
├── 🍒 sha256:86f0c07ab8720d5676dd38aa3c46c2179475f760d7fdbdeb8374292a00f86226
├── 🍒 sha256:937fea3f79cff9469147cadb127e7721fb66eaee20e228756cad7c20b77296d8
├── 🍒 sha256:e4a4239487d5a33cd3836d2654c7b76148b1810d1005c34796be3499021ed297
├── 🍒 sha256:28dc5117fe59531af747159a7227f3f0a21175581b13873cce15912e3aaef204
└── 🍒 sha256:c4b6fb8b2b0e352135d21635d6724c93587370a179e61c39a32089d4d85274e8
└── 🔐 Signatures for an image tag: ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app:sha256-294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc.sig
└── 🍒 sha256:010e941fc66633c54e29f2576dcb1e1c642a8c9313781b668dec26903a7998af
First, we'll verify that the image was signed by the platform team's build-and-push workflow:
$ cosign verify \
--annotations liatr.io/signed-off-by=platform-team \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
--rekor-url https://rekor.sigstore.dev \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The specified annotations were verified.
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
The verify subcommand will also output the signature, so we can manually inspect the other fields for more information:
Image signature (click to expand)
[
{
"critical": {
"identity": {
"docker-reference": "ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app"
},
"image": {
"docker-manifest-digest": "sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc"
},
"type": "cosign container image signature"
},
"optional": {
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.1": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com",
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.2": "workflow_dispatch",
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.3": "54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d",
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.4": "app",
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.5": "liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app",
"1.3.6.1.4.1.57264.1.6": "refs/heads/main",
"Bundle": {
"SignedEntryTimestamp": "MEUCIQDLeeJTlGROlwuXen9V8c0vA0gNjh1kCgFI21I7hDlBDQIgQ9mpdPXzkNt3Sg/KupxNTUH6JvcOEa0JvAxdimybue8=",
"Payload": {
"body": "eyJhcGlWZXJzaW9uIjoiMC4wLjEiLCJraW5kIjoiaGFzaGVkcmVrb3JkIiwic3BlYyI6eyJkYXRhIjp7Imhhc2giOnsiYWxnb3JpdGhtIjoic2hhMjU2IiwidmFsdWUiOiIwMTBlOTQxZmM2NjYzM2M1NGUyOWYyNTc2ZGNiMWUxYzY0MmE4YzkzMTM3ODFiNjY4ZGVjMjY5MDNhNzk5OGFmIn19LCJzaWduYXR1cmUiOnsiY29udGVudCI6Ik1FWUNJUUNnMW4vVkZqV2xlL3V2bWpYMWszL3dTYWhKb3Y5c0hPY0VsRnp2L2gvT3Z3SWhBT0VvYnVLNFd6VzhQQ2cvVUptT2V2ODRHb0YwQ0RqRjVHQmlVN0s0dUFkcyIsInB1YmxpY0tleSI6eyJjb250ZW50IjoiTFMwdExTMUNSVWRKVGlCRFJWSlVTVVpKUTBGVVJTMHRMUzB0Q2sxSlNVaEJSRU5EUW05WFowRjNTVUpCWjBsVlEwVmhOVmhxTm5sSFdqSjZXazloVDAweFNta3JjRkJGTTJJMGQwTm5XVWxMYjFwSmVtb3dSVUYzVFhjS1RucEZWazFDVFVkQk1WVkZRMmhOVFdNeWJHNWpNMUoyWTIxVmRWcEhWakpOVWpSM1NFRlpSRlpSVVVSRmVGWjZZVmRrZW1SSE9YbGFVekZ3WW01U2JBcGpiVEZzV2tkc2FHUkhWWGRJYUdOT1RXcE5kMDVVU1RKTmFrbDNUVlJGTTFkb1kwNU5hazEzVGxSSk1rMXFTWGhOVkVVelYycEJRVTFHYTNkRmQxbElDa3R2V2tsNmFqQkRRVkZaU1V0dldrbDZhakJFUVZGalJGRm5RVVZsY1hORlFuZDBUMXBUU1hkSldUaEZSVmhQVGswMWJVdFFPQ3RUYW5wcE1EZEpkQzhLV2pkTk1ESm1hbE5rZEhCWFkwNTBjelpEZG5CNGNXeFhLekZVWm10TlRWVnFRVzkyY2l0WlFUQjRXbFZIYlRWM2R6WlBRMEpoVVhkbloxZG5UVUUwUndwQk1WVmtSSGRGUWk5M1VVVkJkMGxJWjBSQlZFSm5UbFpJVTFWRlJFUkJTMEpuWjNKQ1owVkdRbEZqUkVGNlFXUkNaMDVXU0ZFMFJVWm5VVlZyZDJaSENqTXlMMXBXVDBJNVIxZFNhSFJXYzFFeGJGbFdWemhaZDBoM1dVUldVakJxUWtKbmQwWnZRVlV6T1ZCd2VqRlphMFZhWWpWeFRtcHdTMFpYYVhocE5Ga0tXa1E0ZDJWbldVUldVakJTUVZGSUwwSklRWGRpYjFwellVaFNNR05JVFRaTWVUbHVZVmhTYjJSWFNYVlpNamwwVERKNGNGbFlVbmxoVnpoMldqSm5kQXBrU0VveFl6TlNiRnBETVdsa1YyeHpXa2hOZEdReU9YbGhNbHB6WWpOa2VreDVOVzVoV0ZKdlpGZEpkbVF5T1hsaE1scHpZak5rZWt3eVNqRmhWM2hyQ2t4WFJuVmFRekYzWkZoT2IweHViR2hpVjNoQlkyMVdiV041T1c5YVYwWnJZM2s1ZEZsWGJIVk5SR3RIUTJselIwRlJVVUpuTnpoM1FWRkZSVXN5YURBS1pFaENlazlwT0haa1J6bHlXbGMwZFZsWFRqQmhWemwxWTNrMWJtRllVbTlrVjBveFl6SldlVmt5T1hWa1IxWjFaRU0xYW1JeU1IZElkMWxMUzNkWlFncENRVWRFZG5wQlFrRm5VVkprTWpsNVlUSmFjMkl6WkdaYVIyeDZZMGRHTUZreVozZE9aMWxMUzNkWlFrSkJSMFIyZWtGQ1FYZFJiMDVVVW1oTlIxVXhDazlFU1hwWmFrMTNXWHBTYlZscWFHdE5SMXB0VDFST2FVNVVUWGxhVkZrd1drUnJNRTU2YUd4TlJFVjVXa1JCVWtKbmIzSkNaMFZGUVZsUEwwMUJSVVVLUWtGT2FHTklRWGRMZDFsTFMzZFpRa0pCUjBSMmVrRkNRbEZSWkdKSGJHaGtTRXB3WW5rNWJtRkRNVEJqYmxaNlpFZFdhMHhYU2pGaFYzaHJZM2t4YUFwalNFRjNTRkZaUzB0M1dVSkNRVWRFZG5wQlFrSm5VVkJqYlZadFkzazViMXBYUm10amVUbDBXVmRzZFUxRWMwZERhWE5IUVZGUlFtYzNPSGRCVVdkRkNreFJkM0poU0ZJd1kwaE5Oa3g1T1RCaU1uUnNZbWsxYUZrelVuQmlNalY2VEcxa2NHUkhhREZaYmxaNldsaEthbUl5TlRCYVZ6VXdURzFPZG1KVVFqZ0tRbWR2Y2tKblJVVkJXVTh2VFVGRlNrSkhORTFpUjJnd1pFaENlazlwT0haYU1td3dZVWhXYVV4dFRuWmlVemx6WVZkR01HTnRiSFpNTW1SdlRGaFNlUXBrV0U0d1dsZFJkRmx1Vm5CaVIxSjZURmhrZG1OdGRHMWlSemt6WTNrNGRWb3liREJoU0ZacFRETmtkbU50ZEcxaVJ6a3pZM2s1YVdSWGJITmFRekZvQ21KdFVYUmpTRlo2WVVNMU5WbFhNWE5SU0Vwc1dtNU5kbUZIVm1oYVNFMTJZbGRHY0dKcVFUUkNaMjl5UW1kRlJVRlpUeTlOUVVWTFFrTnZUVXRFUVhvS1dtcG5OVTU2YXpGWmFtaHJUbTFOTkZsdFNUTk9NazE1VGtSWmVWcFhVVFJOZWxwb1RXcG9iVnBVUW1oTlZFSnFXVmRWZDBoUldVdExkMWxDUWtGSFJBcDJla0ZDUTNkUlVFUkJNVzVoV0ZKdlpGZEpkR0ZIT1hwa1IxWnJUVVZCUjBOcGMwZEJVVkZDWnpjNGQwRlJkMFZOWjNkM1lVaFNNR05JVFRaTWVUbHVDbUZZVW05a1YwbDFXVEk1ZEV3eWVIQlpXRko1WVZjNGRsb3laM1JrU0VveFl6TlNiRnBETVdsa1YyeHpXa2hOZEZsWVFuZE5SR2RIUTJselIwRlJVVUlLWnpjNGQwRlJNRVZMWjNkdlRsUlNhRTFIVlRGUFJFbDZXV3BOZDFsNlVtMVphbWhyVFVkYWJVOVVUbWxPVkUxNVdsUlpNRnBFYXpCT2VtaHNUVVJGZVFwYVJFRm1RbWR2Y2tKblJVVkJXVTh2VFVGRlQwSkNSVTFFTTBwc1dtNU5kbUZIVm1oYVNFMTJZbGRHY0dKcVFWcENaMjl5UW1kRlJVRlpUeTlOUVVWUUNrSkJjMDFEVkZrd1RYcHJOVTFVVVhsT2FrRnhRbWR2Y2tKblJVVkJXVTh2VFVGRlVVSkNkMDFIYldnd1pFaENlazlwT0haYU1td3dZVWhXYVV4dFRuWUtZbE01YzJGWFJqQmpiV3gyVFVKalIwTnBjMGRCVVZGQ1p6YzRkMEZTUlVWRFVYZElUbFJqZVU1cVdYaFBSRUp5UW1kdmNrSm5SVVZCV1U4dlRVRkZVd3BDUmpCTlZ6Sm9NR1JJUW5wUGFUaDJXakpzTUdGSVZtbE1iVTUyWWxNNWMyRlhSakJqYld4MlRESmtiMHhZVW5sa1dFNHdXbGRSZEZsdVZuQmlSMUo2Q2t4WFJuZGpRemgxV2pKc01HRklWbWxNTTJSMlkyMTBiV0pIT1ROamVUbG9ZMGhCZFdWWFJuUmlSVUo1V2xkYWVrd3lhR3haVjFKNlRESXhhR0ZYTkhjS1QwRlpTMHQzV1VKQ1FVZEVkbnBCUWtWM1VYRkVRMmN4VGtkRmQxcFVWVFJOYWs1cFRYcENhazVIV21sUFIxRjNXbTFaTlUweVNURk5la3BzVG1wU2F3cFBWRkV6VDBkVmQwMVVTbXROUTBWSFEybHpSMEZSVVVKbk56aDNRVkpSUlVWM2QxSmtNamw1WVRKYWMySXpaR1phUjJ4NlkwZEdNRmt5WjNkWmQxbExDa3QzV1VKQ1FVZEVkbnBCUWtaUlVsWkVSazV2WkVoU2QyTjZiM1pNTW1Sd1pFZG9NVmxwTldwaU1qQjJZa2RzYUdSSVNuQmllVGx1WVVNeE1HTnVWbm9LWkVkV2EweFhTakZoVjNoclkza3hhR05JUVhaWlYwNHdZVmM1ZFdONU9YbGtWelY2VEhwVmQwOVVWWGxPVkZsNVRtcHJkbGxZVWpCYVZ6RjNaRWhOZGdwTlZFTkNhVkZaUzB0M1dVSkNRVWhYWlZGSlJVRm5VamRDU0d0QlpIZENNVUZPTURsTlIzSkhlSGhGZVZsNGEyVklTbXh1VG5kTGFWTnNOalF6YW5sMENpODBaVXRqYjBGMlMyVTJUMEZCUVVKcFJtOVZhMWhOUVVGQlVVUkJSVmwzVWtGSloyTk1VSEpwTjJWcVp5dGhjMnA2Tm5OdGJHOXNUekpXUmtoSFZVNEtNa2hSV0RsTWFtOTFiakJUWW01QlEwbEhjRlpHUkhaWFpXTk9WbEIwVkU1elRWSTVaSFZuWnpGaGJWcEpWM0pRYlV0WlFYaFFNM0ZZZDNaUlRVRnZSd3BEUTNGSFUwMDBPVUpCVFVSQk1tdEJUVWRaUTAxUlEwbFBNakY1TlhSUVpHMUJkRGhJY1ROdFdEbE1SbEZGZEdWeWVHTjNVM0Z2YTFobE1USldSbVZLQ2xWRWMyVTBjSGhhU1VoaFpWYzVUa2hRVDNSdWRsQnJRMDFSUkZOSGRIWkdOVVprUjBsa1RFRjJZMnQxZDNJeFEyeHBXSE5uV25GNlkyMHpZVkY0WlVrS2RIZHhlbFJqV2taS1NXWnFha3hOTmtoTVRrWnNVRkpDTlRsTlBRb3RMUzB0TFVWT1JDQkRSVkpVU1VaSlEwRlVSUzB0TFMwdENnPT0ifX19fQ==",
"integratedTime": 1685138477,
"logIndex": 21791129,
"logID": "c0d23d6ad406973f9559f3ba2d1ca01f84147d8ffc5b8445c224f98b9591801d"
}
},
"Issuer": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com",
"Subject": "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main",
"githubWorkflowName": "app",
"githubWorkflowRef": "refs/heads/main",
"githubWorkflowRepository": "liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app",
"githubWorkflowSha": "54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d",
"githubWorkflowTrigger": "workflow_dispatch",
"liatr.io/github-actions-run-link": "https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app/actions/runs/5095256269",
"liatr.io/signed-off-by": "platform-team"
}
}
]
Now we'll verify each attestation that the pipeline produced using the cosign verify-attestation command
https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2https://cosign.sigstore.dev/attestation/vuln/v1https://spdx.dev/Documenthttps://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2
First up is the custom pull request attestation. It was produced in the build-and-push workflow, so attestation verification looks similar to verifying the image:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1 \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
--rekor-url https://rekor.sigstore.dev \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
Certificate subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main
Certificate issuer URL: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
GitHub Workflow Trigger: workflow_dispatch
GitHub Workflow SHA: 54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d
GitHub Workflow Name: app
GitHub Workflow Trigger liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
GitHub Workflow Ref: refs/heads/main
Now we can do the same for the SLSA provenance attestation. This is an attestation type that's natively understood by cosign, so we can use --type slsaprovenance:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type slsaprovenance \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
--rekor-url https://rekor.sigstore.dev \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
Certificate subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main
Certificate issuer URL: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
GitHub Workflow Trigger: workflow_dispatch
GitHub Workflow SHA: 54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d
GitHub Workflow Name: app
GitHub Workflow Trigger liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
GitHub Workflow Ref: refs/heads/main
Next, we can check for the vulnerability attestation produced in the scan-image workflow. This is another attestation type that cosign is familiar with, so we can use --type vuln:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type vuln \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/scan-image.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
--rekor-url https://rekor.sigstore.dev \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
Certificate subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/scan-image.yaml@refs/heads/main
Certificate issuer URL: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
GitHub Workflow Trigger: workflow_dispatch
GitHub Workflow SHA: 54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d
GitHub Workflow Name: app
GitHub Workflow Trigger liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
GitHub Workflow Ref: refs/heads/main
Similarly, we can verify the SBOM attestation. Like the SLSA provenance and vulnerability attestation types, this is another format the cosign understands natively:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type spdxjson \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
--rekor-url https://rekor.sigstore.dev \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
Certificate subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main
Certificate issuer URL: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
GitHub Workflow Trigger: workflow_dispatch
GitHub Workflow SHA: 54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d
GitHub Workflow Name: app
GitHub Workflow Trigger liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
GitHub Workflow Ref: refs/heads/main
Lastly, we can check the verification summary attestation produced by liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-attestations:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type https://slsa.dev/verification_summary/v0.2 \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Verification for ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc --
The following checks were performed on each of these signatures:
- The cosign claims were validated
- Existence of the claims in the transparency log was verified offline
- The code-signing certificate was verified using trusted certificate authority certificates
Certificate subject: https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/policy-verification.yaml@refs/heads/main
Certificate issuer URL: https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com
GitHub Workflow Trigger: workflow_dispatch
GitHub Workflow SHA: 54a0e5823b30c4fb8d0ff93b532e64d9478e012d
GitHub Workflow Name: app
GitHub Workflow Trigger liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app
GitHub Workflow Ref: refs/heads/main
Even after verifying the image signature and attestations, there may still be checks we wish to do on the individual attestations, which is where policy comes in. For instance, we could check the pull request attestation indicates that multiple reviewers approved a change or that our container isn't vulnerable to a particular CVE.
Of course, it's also helpful to know what failed verification looks like. What happens if an image is missing an attestation? We can simulate that by asking cosign to verify an attestation we know doesn't exist:
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type foo \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Error: none of the attestations matched the predicate type: foo, found: https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1,https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2,https://spdx.dev/Document
main.go:74: error during command execution: none of the attestations matched the predicate type: foo, found: https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1,https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2,https://spdx.dev/Document
We tried to ask cosign to verify the existence of a foo attestation, signed by the build-and-push workflow, and because there is no foo attestation, cosign will report that it wasn't able to find one.
The output will be similar if we ask cosign to verify an attestation that does exist, but was signed by a different identity.
In this case, we'll try to verify that the vuln attestation was signed by the build-and-push workflow, when it was actually signed by the scan-image workflow.
$ cosign verify-attestation \
--type vuln \
--certificate-oidc-issuer https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com \
--certificate-identity https://github.com/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-workflows/.github/workflows/build-and-push.yaml@refs/heads/main \
--certificate-github-workflow-repository liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app \
ghcr.io/liatrio/gh-trusted-builds-app@sha256:294bafb143807a4afe6b90e6b8b208b9616798effc48e4018b6b9eef9a6ef6bc
Error: none of the attestations matched the predicate type: vuln, found: https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1,https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2,https://spdx.dev/Document
main.go:74: error during command execution: none of the attestations matched the predicate type: vuln, found: https://liatr.io/attestations/github-pull-request/v1,https://slsa.dev/provenance/v0.2,https://spdx.dev/Document
In this case, the output is very similar, even though we know that the vuln attestation does exist. However, cosign first filters the signatures by the signer identities, so it's only looking at the identity that we specified (i.e., the build-and-push workflow).
Additional Resources
- Sigstore Security Model - an overview of the security model for different Sigstore components.
- in-toto specification
- Fulcio certificate issuance overview
- Fulcio certificate extensions
- transparency.dev - an overview of the verifiable data structures behind Rekor and Fulcio's certificate transparency log.