blog
 blog copied to clipboard
blog copied to clipboard
Kubernetes 的 apiserver 实现 - 服务启动
Library for writing a Kubernetes-style API server.
apiserver 是基于 go-restful 实现的一个 API server,下面是一个 demo 例子,我们将通过它来了解 apiserver 的服务启动过程。
// apiserver-sample
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/serializer"
genericserver "k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server"
genericoptions "k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server/options"
)
var (
// Scheme defines methods for serializing and deserializing API objects.
Scheme = runtime.NewScheme()
// Codecs provides methods for retrieving codecs and serializers for specific
// versions and content types.
Codecs = serializer.NewCodecFactory(Scheme)
)
func main() {
genericConfig := genericserver.NewConfig(Codecs)
secureServingOption := NewSecureServingOptions()
if err := secureServingOption.WithLoopback().ApplyTo(
&genericConfig.SecureServing, &genericConfig.LoopbackClientConfig); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
completedConfig := genericConfig.Complete(nil)
apiserver, err := completedConfig.New("apiserver", genericserver.NewEmptyDelegate())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
stopCh := genericserver.SetupSignalHandler()
fmt.Println("serving...")
apiserver.SecureServingInfo.Serve(apiserver.Handler, apiserver.ShutdownTimeout, stopCh)
<-stopCh
}
代码有几个主要的结构体:
- genericConfig 对应的 Config 结构体
- genericConfig.SecureServing 对应的 SecureServingInfo 结构体
- apiserver 对应的 GenericAPIServer 结构体
SecureServingInfo
SecureServingInfo 在 apiserver 中的作用与 http.ListenAndServe 类似。
// pkg/server/deprecated_insecure_serving.go
type SecureServingInfo struct {
// Listener is the secure server network listener.
Listener net.Listener
// Cert is the main server cert which is used if SNI does not match. Cert must be non-nil and is
// allowed to be in SNICerts.
Cert dynamiccertificates.CertKeyContentProvider
...
}
// Serve runs the secure http server. It fails only if certificates cannot be loaded or the initial listen call fails.
// The actual server loop (stoppable by closing stopCh) runs in a go routine, i.e. Serve does not block.
// It returns a stoppedCh that is closed when all non-hijacked active requests have been processed.
func (s *SecureServingInfo) Serve(handler http.Handler, shutdownTimeout time.Duration, stopCh <-chan struct{}) (<-chan struct{}, error) {
if s.Listener == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("listener must not be nil")
}
tlsConfig, err := s.tlsConfig(stopCh)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
secureServer := &http.Server{
Addr: s.Listener.Addr().String(),
Handler: handler,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
TLSConfig: tlsConfig,
}
...
return RunServer(secureServer, s.Listener, shutdownTimeout, stopCh)
}
SecureServingInfo 结构体持有 net.Listener 对象,Serve 方法构建 http.Server 对象并开启服务处理请求。
SecureServingInfo 提供了基于 HTTPS 的安全服务,相对的,apiserver 在之前的版本也支持非安全的 HTTP。
// pkg/server/deprecated_insecure_serving.go
// DeprecatedInsecureServingInfo is the main context object for the insecure http server.
// HTTP does NOT include authentication or authorization.
// You shouldn't be using this. It makes sig-auth sad.
type DeprecatedInsecureServingInfo struct {
// Listener is the secure server network listener.
Listener net.Listener
// optional server name for log messages
Name string
}
从命名上可以知道 DeprecatedInsecureServingInfo 是已经弃用的结构体,不推荐使用。
You shouldn't be using this. It makes sig-auth sad.
SecureServingInfo 可以通过 SecureServingOptions 结构来构建。
// apiserver-sample
func NewSecureServingOptions() *genericoptions.SecureServingOptions {
o := genericoptions.SecureServingOptions{
BindAddress: net.ParseIP("0.0.0.0"),
BindPort: 6443,
Required: true,
ServerCert: genericoptions.GeneratableKeyCert{
PairName: "apiserver",
CertDirectory: "/var/run/apiserver",
},
}
if err := o.MaybeDefaultWithSelfSignedCerts("localhost", nil, []net.IP{net.ParseIP("127.0.0.1")}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
return &o
}
// secureServingOption := NewSecureServingOptions()
// secureServingOption.ApplyTo(&secureServingInfo)
Config / CompletedConfig
Config 作为 apiserver 的配置结构:
// pkg/server/config.go
// Config is a structure used to configure a GenericAPIServer.
// Its members are sorted roughly in order of importance for composers.
type Config struct {
// SecureServing is required to serve https
SecureServing *SecureServingInfo
...
// ExternalAddress is the host name to use for external (public internet) facing URLs (e.g. Swagger)
// Will default to a value based on secure serving info and available ipv4 IPs.
ExternalAddress string
...
}
// NewConfig returns a Config struct with the default values
func NewConfig(codecs serializer.CodecFactory) *Config {
defaultHealthChecks := []healthz.HealthChecker{healthz.PingHealthz, healthz.LogHealthz}
return &Config{
Serializer: codecs,
BuildHandlerChainFunc: DefaultBuildHandlerChain,
...
}
}
NewConfig 函数可以创建一个具有默认值的 Config,这边先不具体展开讲解每个配置。 通过 Complete 方法可以完整的填充 Config 结构。
// pkg/server/config.go
// Complete fills in any fields not set that are required to have valid data and can be derived
// from other fields. If you're going to `ApplyOptions`, do that first. It's mutating the receiver.
func (c *Config) Complete(informers informers.SharedInformerFactory) CompletedConfig {
if len(c.ExternalAddress) == 0 && c.PublicAddress != nil {
c.ExternalAddress = c.PublicAddress.String()
}
// if there is no port, and we listen on one securely, use that one
if _, _, err := net.SplitHostPort(c.ExternalAddress); err != nil {
if c.SecureServing == nil {
klog.Fatalf("cannot derive external address port without listening on a secure port.")
}
_, port, err := c.SecureServing.HostPort()
if err != nil {
klog.Fatalf("cannot derive external address from the secure port: %v", err)
}
c.ExternalAddress = net.JoinHostPort(c.ExternalAddress, strconv.Itoa(port))
}
...
Complete 方法填充的字段数据可以从其他字段派生出来。 像 ExternalAddress 这个外部访问的地址配置,可以从 SecureServing 这个结构体获得。
completedConfig 作为 Config 结构的完整表示。
// pkg/server/config.go
type completedConfig struct {
*Config
//===========================================================================
// values below here are filled in during completion
//===========================================================================
// SharedInformerFactory provides shared informers for resources
SharedInformerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory
}
type CompletedConfig struct {
// Embed a private pointer that cannot be instantiated outside of this package.
*completedConfig
}
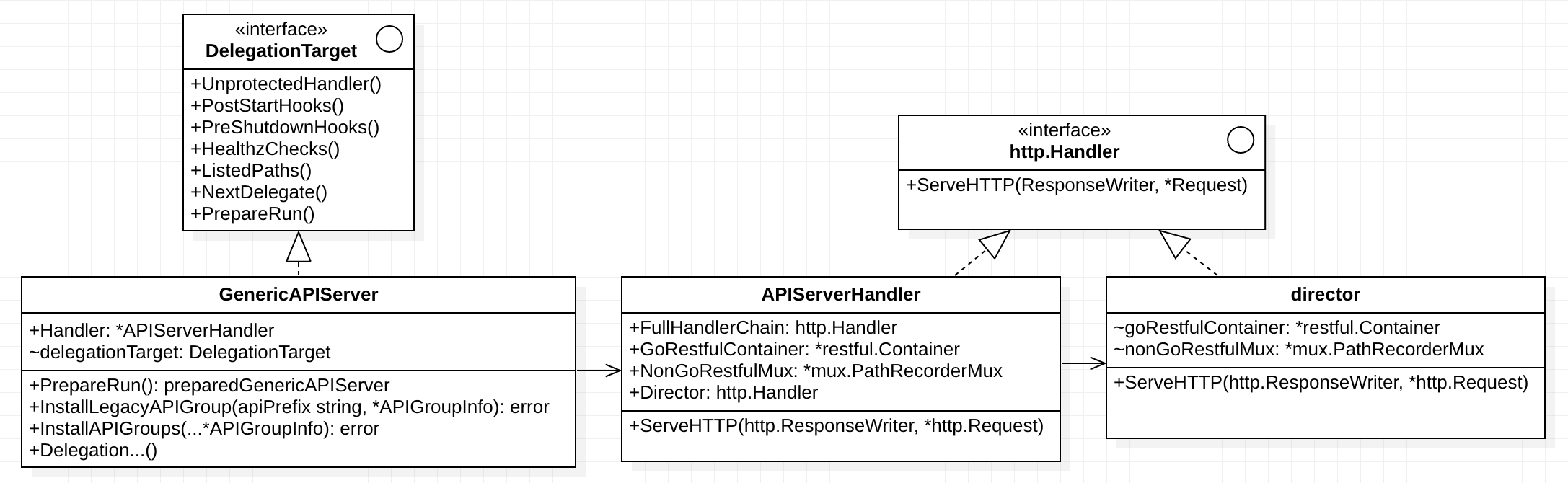
GenericAPIServer
GenericAPIServer 是 apiserver 提供服务的结构体,维护 apiserver 的状态。
// pkg/server/genericapiserver.go
// GenericAPIServer contains state for a Kubernetes cluster api server.
type GenericAPIServer struct {
...
// Handler holds the handlers being used by this API server
Handler *APIServerHandler
// delegationTarget is the next delegate in the chain. This is never nil.
delegationTarget DelegationTarget
}
GenericAPIServer 的属性这边只解释列出来几个:
- Handler 指针是 apiserver 的服务处理入口,维护着 http 处理函数。
- delegationTarget 是作为委托对象存在,GenericAPIServer 自身也是一个可委托对象。
通过 completedConfig 可以创建一个新的 GenericAPIServer。
// pkg/server/config.go
// New creates a new server which logically combines the handling chain with the passed server.
// name is used to differentiate for logging. The handler chain in particular can be difficult as it starts delgating.
// delegationTarget may not be nil.
func (c completedConfig) New(name string, delegationTarget DelegationTarget) (*GenericAPIServer, error) {
...
handlerChainBuilder := func(handler http.Handler) http.Handler {
return c.BuildHandlerChainFunc(handler, c.Config)
}
apiServerHandler := NewAPIServerHandler(name, c.Serializer, handlerChainBuilder, delegationTarget.UnprotectedHandler())
s := &GenericAPIServer{
...
delegationTarget: delegationTarget,
...
Handler: apiServerHandler,
listedPathProvider: apiServerHandler,
...
}
...
s.listedPathProvider = routes.ListedPathProviders{s.listedPathProvider, delegationTarget}
installAPI(s, c.Config)
...
return s, nil
}
New 方法接收一个 name 和 delegationTarge 委托对象,创建 APIServerHandler 来构造 GenericAPIServer。
APIServerHandler
APIServerHandler 是通过 NewAPIServerHandler 函数创建的。
// pkg/server/handler.go
func NewAPIServerHandler(name string, s runtime.NegotiatedSerializer, handlerChainBuilder HandlerChainBuilderFn, notFoundHandler http.Handler) *APIServerHandler {
nonGoRestfulMux := mux.NewPathRecorderMux(name)
if notFoundHandler != nil {
nonGoRestfulMux.NotFoundHandler(notFoundHandler)
}
gorestfulContainer := restful.NewContainer()
gorestfulContainer.ServeMux = http.NewServeMux()
gorestfulContainer.Router(restful.CurlyRouter{}) // e.g. for proxy/{kind}/{name}/{*}
gorestfulContainer.RecoverHandler(func(panicReason interface{}, httpWriter http.ResponseWriter) {
logStackOnRecover(s, panicReason, httpWriter)
})
gorestfulContainer.ServiceErrorHandler(func(serviceErr restful.ServiceError, request *restful.Request, response *restful.Response) {
serviceErrorHandler(s, serviceErr, request, response)
})
director := director{
name: name,
goRestfulContainer: gorestfulContainer,
nonGoRestfulMux: nonGoRestfulMux,
}
return &APIServerHandler{
FullHandlerChain: handlerChainBuilder(director),
GoRestfulContainer: gorestfulContainer,
NonGoRestfulMux: nonGoRestfulMux,
Director: director,
}
}
NewAPIServerHandler 创建的 APIServerHandler 由多种 http.Handler 组成:
- GoRestfulContainer,基于 go-restful 的 container,
- NonGoRestfulMux,apiserver 内部实现的 PathRecorderMux,处理非 restful 的接口。
以及作为两者路由分发器的 director 和 apiserver 完整处理链 FullHandlerChain。
APIServerHandler 的 http 处理函数是以 FullHandlerChain 开始的:
// pkg/server/handler.go
// ServeHTTP makes it an http.Handler
func (a *APIServerHandler) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
a.FullHandlerChain.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
FullHandlerChain 处理链是由 DefaultBuildHandlerChain(director) 构造的。
// pkg/server/config.go
func DefaultBuildHandlerChain(apiHandler http.Handler, c *Config) http.Handler {
handler := genericapifilters.WithAuthorization(apiHandler, c.Authorization.Authorizer, c.Serializer)
if c.FlowControl != nil {
handler = genericfilters.WithPriorityAndFairness(handler, c.LongRunningFunc, c.FlowControl)
} else {
handler = genericfilters.WithMaxInFlightLimit(handler, c.MaxRequestsInFlight, c.MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight, c.LongRunningFunc)
}
handler = genericapifilters.WithImpersonation(handler, c.Authorization.Authorizer, c.Serializer)
handler = genericapifilters.WithAudit(handler, c.AuditBackend, c.AuditPolicyChecker, c.LongRunningFunc)
failedHandler := genericapifilters.Unauthorized(c.Serializer, c.Authentication.SupportsBasicAuth)
failedHandler = genericapifilters.WithFailedAuthenticationAudit(failedHandler, c.AuditBackend, c.AuditPolicyChecker)
handler = genericapifilters.WithAuthentication(handler, c.Authentication.Authenticator, failedHandler, c.Authentication.APIAudiences)
handler = genericfilters.WithCORS(handler, c.CorsAllowedOriginList, nil, nil, nil, "true")
handler = genericfilters.WithTimeoutForNonLongRunningRequests(handler, c.LongRunningFunc, c.RequestTimeout)
handler = genericfilters.WithWaitGroup(handler, c.LongRunningFunc, c.HandlerChainWaitGroup)
handler = genericapifilters.WithRequestInfo(handler, c.RequestInfoResolver)
if c.SecureServing != nil && !c.SecureServing.DisableHTTP2 && c.GoawayChance > 0 {
handler = genericfilters.WithProbabilisticGoaway(handler, c.GoawayChance)
}
handler = genericfilters.WithPanicRecovery(handler)
return handler
}
DefaultBuildHandlerChain 构造出来的处理链是以各种过滤器开头(包含鉴权、流控等),director 结尾的链。
我们再来看下 director 的分发请求功能。
// pkg/server/handler.go
type director struct {
name string
goRestfulContainer *restful.Container
nonGoRestfulMux *mux.PathRecorderMux
}
func (d director) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
path := req.URL.Path
// check to see if our webservices want to claim this path
for _, ws := range d.goRestfulContainer.RegisteredWebServices() {
switch {
case ws.RootPath() == "/apis":
// if we are exactly /apis or /apis/, then we need special handling in loop.
// normally these are passed to the nonGoRestfulMux, but if discovery is enabled, it will go directly.
// We can't rely on a prefix match since /apis matches everything (see the big comment on Director above)
if path == "/apis" || path == "/apis/" {
klog.V(5).Infof("%v: %v %q satisfied by gorestful with webservice %v", d.name, req.Method, path, ws.RootPath())
// don't use servemux here because gorestful servemuxes get messed up when removing webservices
// TODO fix gorestful, remove TPRs, or stop using gorestful
d.goRestfulContainer.Dispatch(w, req)
return
}
case strings.HasPrefix(path, ws.RootPath()):
// ensure an exact match or a path boundary match
if len(path) == len(ws.RootPath()) || path[len(ws.RootPath())] == '/' {
klog.V(5).Infof("%v: %v %q satisfied by gorestful with webservice %v", d.name, req.Method, path, ws.RootPath())
// don't use servemux here because gorestful servemuxes get messed up when removing webservices
// TODO fix gorestful, remove TPRs, or stop using gorestful
d.goRestfulContainer.Dispatch(w, req)
return
}
}
}
// if we didn't find a match, then we just skip gorestful altogether
klog.V(5).Infof("%v: %v %q satisfied by nonGoRestful", d.name, req.Method, path)
d.nonGoRestfulMux.ServeHTTP(w, req)
}
所以,apiserver 的 http 处理过程是这样的:
FullHandlerChain -> Director -> {GoRestfulContainer,NonGoRestfulMux}
installAPI
installAPI 注册通用的 API 接口。
func installAPI(s *GenericAPIServer, c *Config) {
if c.EnableIndex {
routes.Index{}.Install(s.listedPathProvider, s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux)
}
if c.EnableProfiling {
routes.Profiling{}.Install(s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux)
if c.EnableContentionProfiling {
goruntime.SetBlockProfileRate(1)
}
// so far, only logging related endpoints are considered valid to add for these debug flags.
routes.DebugFlags{}.Install(s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux, "v", routes.StringFlagPutHandler(logs.GlogSetter))
}
if c.EnableMetrics {
if c.EnableProfiling {
routes.MetricsWithReset{}.Install(s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux)
} else {
routes.DefaultMetrics{}.Install(s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux)
}
}
routes.Version{Version: c.Version}.Install(s.Handler.GoRestfulContainer)
if c.EnableDiscovery {
s.Handler.GoRestfulContainer.Add(s.DiscoveryGroupManager.WebService())
}
}
根据 Config 的配置加载多个 apiserver 基础的接口。
- EnableIndex 对应的 /index 接口
- EnableProfiling 对应的 /debug/* 接口
- EnableMetrics 对应的 /metrics 接口
- Version 对应的 /version 接口
- EnableDiscovery 对应的 /apis 接口
前面四个基础接口都定义在 pkg/server/routes routes 包里面,分别被注册到 NonGoRestfulMux 和 GoRestfulContainer 这两个路由注册器上。
到这里可以利用 SecureServingInfo 和 APIServerHandler 来启动服务处理请求。 完整的 demo 代码见 gist
# curl -k https://127.0.0.1:6443
{
"paths": [
"/apis",
"/metrics"
]
}
GenericAPIServer 还提供了 PrepareRun 的方法来启动 API 安装,通过封装的 preparedGenericAPIServer.Run() 来启动服务。
apiserver.PrepareRun().Run(stopCh)
// pkg/server/genericapiserver.go
// preparedGenericAPIServer is a private wrapper that enforces a call of PrepareRun() before Run can be invoked.
type preparedGenericAPIServer struct {
*GenericAPIServer
}
// Run spawns the secure http server. It only returns if stopCh is closed
// or the secure port cannot be listened on initially.
func (s preparedGenericAPIServer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
delayedStopCh := make(chan struct{})
// close socket after delayed stopCh
err := s.NonBlockingRun(delayedStopCh)
if err != nil {
return err
}
<-stopCh
...
}
// NonBlockingRun spawns the secure http server. An error is
// returned if the secure port cannot be listened on.
func (s preparedGenericAPIServer) NonBlockingRun(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// Use an internal stop channel to allow cleanup of the listeners on error.
internalStopCh := make(chan struct{})
var stoppedCh <-chan struct{}
if s.SecureServingInfo != nil && s.Handler != nil {
var err error
stoppedCh, err = s.SecureServingInfo.Serve(s.Handler, s.ShutdownTimeout, internalStopCh)
}
...
}
PrepareRun 在启动服务之前额外处理了 API 安装。
// pkg/server/genericapiserver.go
// PrepareRun does post API installation setup steps. It calls recursively the same function of the delegates.
func (s *GenericAPIServer) PrepareRun() preparedGenericAPIServer {
s.delegationTarget.PrepareRun()
...
s.installHealthz()
s.installLivez()
s.installReadyz()
...
return preparedGenericAPIServer{s}
}
可见,PrepareRun 安装了 GenericAPIServer 自身服务的一些检查接口:
- installHealthz 安装 /healthz 接口
- installLivez 安装 /livez 接口
- installReadyz 安装 /readyz 接口
以及委托对象的 PrepareRun。
以 installHealthz 为例:
// pkg/server/healthz.go
// installHealthz creates the healthz endpoint for this server
func (s *GenericAPIServer) installHealthz() {
s.healthzLock.Lock()
defer s.healthzLock.Unlock()
s.healthzChecksInstalled = true
healthz.InstallHandler(s.Handler.NonGoRestfulMux, s.healthzChecks...)
}
func InstallHandler(mux mux, checks ...HealthChecker) {
InstallPathHandler(mux, "/healthz", checks...)
}
检查的处理逻辑来自 GenericAPIServer.healthzChecks,也就是来自 Config 配置中的 HealthzChecks。
// NewConfig returns a Config struct with the default values
func NewConfig(codecs serializer.CodecFactory) *Config {
defaultHealthChecks := []healthz.HealthChecker{healthz.PingHealthz, healthz.LogHealthz}
return &Config{
HealthzChecks: append([]healthz.HealthChecker{}, defaultHealthChecks...),
ReadyzChecks: append([]healthz.HealthChecker{}, defaultHealthChecks...),
LivezChecks: append([]healthz.HealthChecker{}, defaultHealthChecks...),
...
}
默认情况下,/healthz、/livez 和 /readyz 这三个接口都检查了:
- healthz.PingHealthz,简单的 ping 实现;
- healthz.LogHealthz,检查 log 是否阻塞。
以 apiserver.PrepareRun().Run(stopCh) 方式启动服务,我们可以看到下面的 API:
# curl -k https://127.0.0.1:6443
{
"paths": [
"/apis",
"/healthz",
"/healthz/log",
"/healthz/ping",
"/livez",
"/livez/log",
"/livez/ping",
"/metrics",
"/readyz",
"/readyz/log",
"/readyz/ping",
"/readyz/shutdown"
]
}