blog
 blog copied to clipboard
blog copied to clipboard
Redis 中的 skiplist 实现
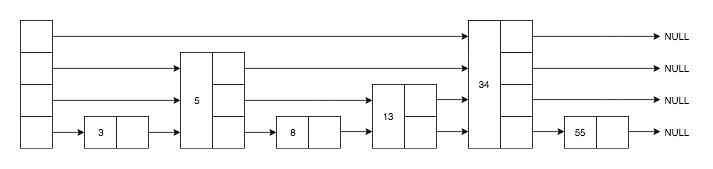
跳跃列表(skiplist)是一种有序数据结构。
Redis 中跳跃列表的结构体表示:
// 5.0.3/src/server.h
typedef struct zskiplist {
// 头节点指针、尾节点指针
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
// 节点数量
unsigned long length;
// 节点最大层数
int level;
} zskiplist;
节点数量 length 和 节点最大层数 level 的计算不包括头节点。 头节点指针 header 和尾节点 tail 表示的跳跃列表节点定义:
// 5.0.3/src/server.h
/* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
节点的各个属性表示:
- ele: 节点保存的简单动态字符串值
- score: 节点保存的分数,在跳跃列表中,各节点按照分数排列
- *backward: 节点的后退指针,指向当前节点的前一个节点
- level[]: 节点的层级表示,每个层级都有两个属性
- *forward: 前进指针,指向当前层级的向前跳跃的节点
- span: 跨度(前进指针所指向节点和当前节点的距离),用来计算节点的排名(rank)
跳跃列表的一个例子:
创建
// 5.0.3/src/server.h
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 64 /* Should be enough for 2^64 elements */
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Create a new skiplist. */
zskiplist *zslCreate(void) {
int j;
zskiplist *zsl;
zsl = zmalloc(sizeof(*zsl));
zsl->level = 1;
zsl->length = 0;
zsl->header = zslCreateNode(ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,0,NULL);
for (j = 0; j < ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; j++) {
zsl->header->level[j].forward = NULL;
zsl->header->level[j].span = 0;
}
zsl->header->backward = NULL;
zsl->tail = NULL;
return zsl;
}
zslCreate 函数创建一个新的跳跃列表,调用 zslCreateNode 函数创建一个头节点且初始化。
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Create a skiplist node with the specified number of levels.
* The SDS string 'ele' is referenced by the node after the call. */
zskiplistNode *zslCreateNode(int level, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *zn =
zmalloc(sizeof(*zn)+level*sizeof(struct zskiplistLevel));
zn->score = score;
zn->ele = ele;
return zn;
}
头节点的层级为 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL,不存储实际数据。
查找
Redis 跳跃列表的实现有没有提供直接查询节点的函数。 可以通过节点排位计算和排位查找来理解:
节点排位计算
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Find the rank for an element by both score and key.
* Returns 0 when the element cannot be found, rank otherwise.
* Note that the rank is 1-based due to the span of zsl->header to the
* first element. */
unsigned long zslGetRank(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long rank = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) <= 0))) {
rank += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* x might be equal to zsl->header, so test if obj is non-NULL */
if (x->ele && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
return rank;
}
}
return 0;
}
先查找节点:
- 从头节点 header 最高层 zsl->level-1 开始遍历,
- 如果当前层级指向的节点大于等于目标节点(score 相同的节点就比较 sds 值),就跳到层级指向的节点, 反之在当前节点下降一层,
- 累加跳跃节点的 span 值,
- 重复上面的步骤,直到找到相同 score 和 sds 的节点。
查找 score 等于 13 的节点,路径如下:
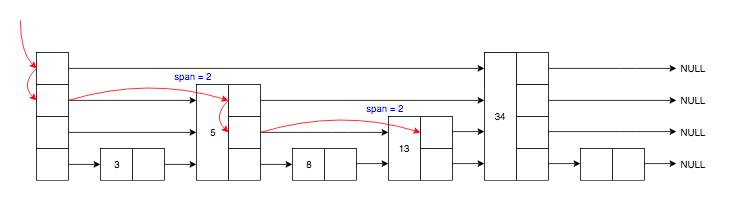
可以计算节点 rank 等于 4。
排名查找
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Finds an element by its rank. The rank argument needs to be 1-based. */
zskiplistNode* zslGetElementByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned long rank) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long traversed = 0;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward && (traversed + x->level[i].span) <= rank)
{
traversed += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
if (traversed == rank) {
return x;
}
}
return NULL;
}
指定 rank 来查找节点,从高层向低层累加跳跃节点的 span 值等于 rank 就结束查找。
插入
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Insert a new node in the skiplist. Assumes the element does not already
* exist (up to the caller to enforce that). The skiplist takes ownership
* of the passed SDS string 'ele'. */
zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];
int i, level;
serverAssert(!isnan(score));
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
插入节点要确保不会插入相同的节点(score 和 sds 都相同), 在插入节点之前,需要定位插入的位置,定位过程同查找节点过程不大一样:
- 从头节点 header 最高层 zsl->level-1 开始遍历,
- 如果当前层级指向的节点大于目标节点(score 相同的节点就比较 sds 值),就跳到层级指向的节点, 反之在当前节点下降一层,
- 记录每一层经过的节点,更新 update 节点指针数组,
- 重复上面的步骤,直到遍历层级第 0 层结束。
“搜索路径”每一层级最后经过的节点记录在 update 节点指针数组。
插入 score 等于 21 的节点,路径如下:
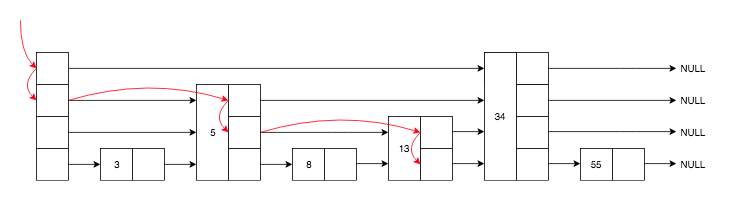
13 和 34 之间就是插入的位置。
/* we assume the element is not already inside, since we allow duplicated
* scores, reinserting the same element should never happen since the
* caller of zslInsert() should test in the hash table if the element is
* already inside or not. */
level = zslRandomLevel();
if (level > zsl->level) {
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;
}
插入节点的层数是通过 zslRandomLevel 函数随机分配的,如果层数大于当前跳跃列表的最大层数,更新 update 数组。
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;
return x;
}
创建新插入的节点,将 update 数组上的节点和新节点通过前向后向指针联系起来,以及更新这些节点的 span。
删除
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Delete an element with matching score/element from the skiplist.
* The function returns 1 if the node was found and deleted, otherwise
* 0 is returned.
*
* If 'node' is NULL the deleted node is freed by zslFreeNode(), otherwise
* it is not freed (but just unlinked) and *node is set to the node pointer,
* so that it is possible for the caller to reuse the node (including the
* referenced SDS string at node->ele). */
int zslDelete(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele, zskiplistNode **node) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* We may have multiple elements with the same score, what we need
* is to find the element with both the right score and object. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
if (x && score == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0) {
zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);
if (!node)
zslFreeNode(x);
else
*node = x;
return 1;
}
return 0; /* not found */
}
删除节点同插入节点,需要先将“搜索路径”找出来,然后判断向前一个节点 x->level[0].forward 是否是删除节点。
// 5.0.3/src/t_zset.c
/* Internal function used by zslDelete, zslDeleteByScore and zslDeleteByRank */
void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < zsl->level; i++) {
if (update[i]->level[i].forward == x) {
update[i]->level[i].span += x->level[i].span - 1;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x->level[i].forward;
} else {
update[i]->level[i].span -= 1;
}
}
if (x->level[0].forward) {
x->level[0].forward->backward = x->backward;
} else {
zsl->tail = x->backward;
}
while(zsl->level > 1 && zsl->header->level[zsl->level-1].forward == NULL)
zsl->level--;
zsl->length--;
}
删除指定节点,重排 update 数组上每个层级的节点前向后向指针和更新节点的 span。
更新
/* Update the score of an elmenent inside the sorted set skiplist.
* Note that the element must exist and must match 'score'.
* This function does not update the score in the hash table side, the
* caller should take care of it.
*
* Note that this function attempts to just update the node, in case after
* the score update, the node would be exactly at the same position.
* Otherwise the skiplist is modified by removing and re-adding a new
* element, which is more costly.
*
* The function returns the updated element skiplist node pointer. */
zskiplistNode *zslUpdateScore(zskiplist *zsl, double curscore, sds ele, double newscore) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
int i;
/* We need to seek to element to update to start: this is useful anyway,
* we'll have to update or remove it. */
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < curscore ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == curscore &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
/* Jump to our element: note that this function assumes that the
* element with the matching score exists. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
serverAssert(x && curscore == x->score && sdscmp(x->ele,ele) == 0);
/* If the node, after the score update, would be still exactly
* at the same position, we can just update the score without
* actually removing and re-inserting the element in the skiplist. */
if ((x->backward == NULL || x->backward->score < newscore) &&
(x->level[0].forward == NULL || x->level[0].forward->score > newscore))
{
x->score = newscore;
return x;
}
/* No way to reuse the old node: we need to remove and insert a new
* one at a different place. */
zslDeleteNode(zsl, x, update);
zskiplistNode *newnode = zslInsert(zsl,newscore,x->ele);
/* We reused the old node x->ele SDS string, free the node now
* since zslInsert created a new one. */
x->ele = NULL;
zslFreeNode(x);
return newnode;
}
更新操作也需要“搜索路径”。
对于要更新 score 的节点,如果新的 score 值不会带来位置上的调整,就直接修改 score 值, 否则先删除节点,再插入新 score 的节点。
您好,请问在“重复上面的步骤,直到找到相同 score 和 sds 的节点。”中, “相同score”这个约束时如何保证的呢?
@dvoprm 没太明白你的问题是什么
https://github.com/redis/redis/issues/3081 我在官方找到一个和我有相同想法的issue。
@dvoprm zslGetRank 确实没有检查 score,zslGetRank 是内部只在 zsetRank 被调用的函数,会通过 dict 来查找字符串的 score,不过理论上还是应该检查的