blog
 blog copied to clipboard
blog copied to clipboard
Redis 中的 ziplist 实现
压缩列表(ziplist)是 Redis 中列表对象、哈希对象和有序集合对象的底层实现之一。
为了节约内存而存在,由一块连续内存空间来表示:

- zlbytes(4 byte): 整个压缩列表占用字节数
- zltail(4 byte): 压缩列表尾节点到压缩列表起始地址的偏移量
- zllen(2 byte): 压缩列表中的节点个数
- entry(? byte): 压缩列表节点
- zlend(1 byte): 压缩列表结束标志,0xFF
压缩列表元数据(zlbytes、zltail 和 zllen)大小为 10 byte:
/* The size of a ziplist header: two 32 bit integers for the total
* bytes count and last item offset. One 16 bit integer for the number
* of items field. */
#define ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE (sizeof(uint32_t)*2+sizeof(uint16_t))
压缩列表各个元数据的起始位置可以通过下面的宏来操作:
/* Return total bytes a ziplist is composed of. */
#define ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) (*((uint32_t*)(zl)))
/* Return the offset of the last item inside the ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) (*((uint32_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t))))
/* Return the length of a ziplist, or UINT16_MAX if the length cannot be
* determined without scanning the whole ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) (*((uint16_t*)((zl)+sizeof(uint32_t)*2)))
获取压缩列表中的头尾节点指针可以通过下面的宏:
/* Return the pointer to the first entry of a ziplist. */
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) ((zl)+ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE)
/* Return the pointer to the last entry of a ziplist, using the
* last entry offset inside the ziplist header. */
#define ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl) ((zl)+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl)))
节点
一个压缩列表包括多个节点(entry),每个节点可以保存一个字符数组或者整数,节点大小不定。
节点内存表示:

节点包含了两个元数据:
- prevlen: 前一个节点的长度
- encoding: 节点数据的编码类型信息
prevlen 以字节为单位,当反向遍历压缩列表时,可以定位到前一个节点的起始位置。prevlen 的大小可以是 1 字节或者 5 字节:
- 如果前一节点的长度小于 254 字节,那么 prevlen 的大小为 1 字节。
- 如果前一节点的长度大于等于 254 字节,那么 prevlen 的大小为 5 字节,其中属性的第一字节会被设置为 0xFE(十进制值 254 ),而之后的四个字节则用于保存前一节点的长度。
宏 ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE 和 ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN 分别计算 prevlen 的内存大小以及存储的前一个节点长度。
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
#define ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN 254
/* Return the number of bytes used to encode the length of the previous
* entry. The length is returned by setting the var 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize) do { \
if ((ptr)[0] < ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN) { \
(prevlensize) = 1; \
} else { \
(prevlensize) = 5; \
} \
} while(0);
/* Return the length of the previous element, and the number of bytes that
* are used in order to encode the previous element length.
* 'ptr' must point to the prevlen prefix of an entry (that encodes the
* length of the previous entry in order to navigate the elements backward).
* The length of the previous entry is stored in 'prevlen', the number of
* bytes needed to encode the previous entry length are stored in
* 'prevlensize'. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(ptr, prevlensize, prevlen) do { \
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(ptr, prevlensize); \
if ((prevlensize) == 1) { \
(prevlen) = (ptr)[0]; \
} else if ((prevlensize) == 5) { \
assert(sizeof((prevlen)) == 4); \
memcpy(&(prevlen), ((char*)(ptr)) + 1, 4); \
memrev32ifbe(&prevlen); \
} \
} while(0);
encoding 表示节点的类型(字符数组或整数),如果是字符数组,字符数组的长度也存储在 encoding 中。 Redis 通过 encoding 的高位 2 bit 来识别具体存储的数据。
-
高位以 00、01 和 10 为前缀表示字符数组,其他位表示数组长度。
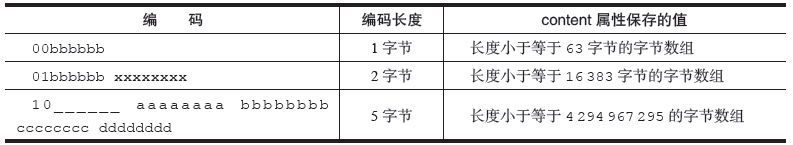
-
高位以 11 为前缀表示整数,其他位表示整数的类型。
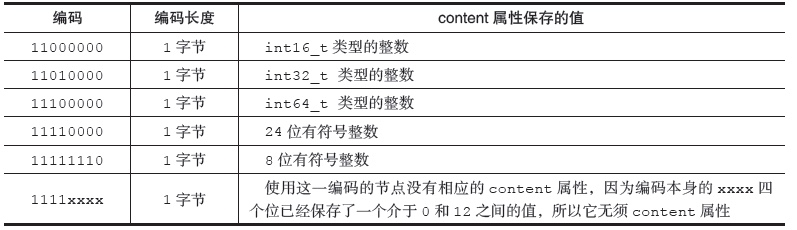 1111xxxx 低位 4 bit 的范围在(0001 ~1101)
1111xxxx 低位 4 bit 的范围在(0001 ~1101)
宏 ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH 计算 encoding 表示的类型和占用的内存大小以及数据长度。
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Extract the encoding from the byte pointed by 'ptr' and set it into
* 'encoding' field of the zlentry structure. */
#define ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING(ptr, encoding) do { \
(encoding) = (ptr[0]); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) (encoding) &= ZIP_STR_MASK; \
} while(0)
/* Decode the entry encoding type and data length (string length for strings,
* number of bytes used for the integer for integer entries) encoded in 'ptr'.
* The 'encoding' variable will hold the entry encoding, the 'lensize'
* variable will hold the number of bytes required to encode the entry
* length, and the 'len' variable will hold the entry length. */
#define ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(ptr, encoding, lensize, len) do { \
ZIP_ENTRY_ENCODING((ptr), (encoding)); \
if ((encoding) < ZIP_STR_MASK) { \
if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_06B) { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = (ptr)[0] & 0x3f; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_14B) { \
(lensize) = 2; \
(len) = (((ptr)[0] & 0x3f) << 8) | (ptr)[1]; \
} else if ((encoding) == ZIP_STR_32B) { \
(lensize) = 5; \
(len) = ((ptr)[1] << 24) | \
((ptr)[2] << 16) | \
((ptr)[3] << 8) | \
((ptr)[4]); \
} else { \
panic("Invalid string encoding 0x%02X", (encoding)); \
} \
} else { \
(lensize) = 1; \
(len) = zipIntSize(encoding); \
} \
} while(0);
/* Return bytes needed to store integer encoded by 'encoding'. */
unsigned int zipIntSize(unsigned char encoding) {
switch(encoding) {
case ZIP_INT_8B: return 1;
case ZIP_INT_16B: return 2;
case ZIP_INT_24B: return 3;
case ZIP_INT_32B: return 4;
case ZIP_INT_64B: return 8;
}
if (encoding >= ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN && encoding <= ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX)
return 0; /* 4 bit immediate */
panic("Invalid integer encoding 0x%02X", encoding);
return 0;
}
节点信息可以用 zlentry 结构体来表示:
/* We use this function to receive information about a ziplist entry.
* Note that this is not how the data is actually encoded, is just what we
* get filled by a function in order to operate more easily. */
typedef struct zlentry {
unsigned int prevrawlensize; /* Bytes used to encode the previous entry len*/
unsigned int prevrawlen; /* Previous entry len. */
unsigned int lensize; /* Bytes used to encode this entry type/len.
For example strings have a 1, 2 or 5 bytes
header. Integers always use a single byte.*/
unsigned int len; /* Bytes used to represent the actual entry.
For strings this is just the string length
while for integers it is 1, 2, 3, 4, 8 or
0 (for 4 bit immediate) depending on the
number range. */
unsigned int headersize; /* prevrawlensize + lensize. */
unsigned char encoding; /* Set to ZIP_STR_* or ZIP_INT_* depending on
the entry encoding. However for 4 bits
immediate integers this can assume a range
of values and must be range-checked. */
unsigned char *p; /* Pointer to the very start of the entry, that
is, this points to prev-entry-len field. */
} zlentry;
/* Return a struct with all information about an entry. */
void zipEntry(unsigned char *p, zlentry *e) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, e->prevrawlensize, e->prevrawlen);
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + e->prevrawlensize, e->encoding, e->lensize, e->len);
e->headersize = e->prevrawlensize + e->lensize;
e->p = p;
}
zipEntry 用来解码一个节点,用 zlentry 结构体来表示。
创建
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Create a new empty ziplist. */
unsigned char *ziplistNew(void) {
unsigned int bytes = ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+1;
unsigned char *zl = zmalloc(bytes);
ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl) = intrev32ifbe(bytes);
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE);
ZIPLIST_LENGTH(zl) = 0;
zl[bytes-1] = ZIP_END;
return zl;
}
ziplistNew 创建一个空的压缩列表,大小为 ZIPLIST_HEADER_SIZE+1(压缩列表元数据结构 + 结束标示) ,没有包含节点的空间。
获取
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Return the total number of bytes used by the entry pointed to by 'p'. */
unsigned int zipRawEntryLength(unsigned char *p) {
unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len);
return prevlensize + lensize + len;
}
/* Returns an offset to use for iterating with ziplistNext. When the given
* index is negative, the list is traversed back to front. When the list
* doesn't contain an element at the provided index, NULL is returned. */
unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index) {
unsigned char *p;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
if (index < 0) {
index = (-index)-1;
p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
while (prevlen > 0 && index--) {
p -= prevlen;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
}
}
} else {
p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl);
while (p[0] != ZIP_END && index--) {
p += zipRawEntryLength(p);
}
}
return (p[0] == ZIP_END || index > 0) ? NULL : p;
}
ziplistIndex 函数通过指定 index 来获取节点位置指针。
如果 index 为正,从头节点 ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD 开始步长为 zipRawEntryLength(当前节点的长度) 的正向遍历,
如果 index 为负,从尾节点 ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL 步长为节点的 prevlen 值(前一个节点的长度)的反向遍历。
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Get entry pointed to by 'p' and store in either '*sstr' or 'sval' depending
* on the encoding of the entry. '*sstr' is always set to NULL to be able
* to find out whether the string pointer or the integer value was set.
* Return 0 if 'p' points to the end of the ziplist, 1 otherwise. */
unsigned int ziplistGet(unsigned char *p, unsigned char **sstr, unsigned int *slen, long long *sval) {
zlentry entry;
if (p == NULL || p[0] == ZIP_END) return 0;
if (sstr) *sstr = NULL;
zipEntry(p, &entry);
if (ZIP_IS_STR(entry.encoding)) {
if (sstr) {
*slen = entry.len;
*sstr = p+entry.headersize;
}
} else {
if (sval) {
*sval = zipLoadInteger(p+entry.headersize,entry.encoding);
}
}
return 1;
}
知道节点的位置后,通过 ziplistGet 函数获取节点的数据。
查找
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Find pointer to the entry equal to the specified entry. Skip 'skip' entries
* between every comparison. Returns NULL when the field could not be found. */
unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) {
int skipcnt = 0;
unsigned char vencoding = 0;
long long vll = 0;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
ziplistFind 函数从 p 指针位置开始查找节点直到压缩列表末尾,skip 指定查找的步长。
unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;
unsigned char *q;
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);
ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len);
q = p + prevlensize + lensize;
获取当前的节点的信息。
if (skipcnt == 0) {
/* Compare current entry with specified entry */
...
/* Reset skip count */
skipcnt = skip;
} else {
/* Skip entry */
skipcnt--;
}
/* Move to next entry */
p = q + len;
}
return NULL;
}
以步长为 skip 查找目标节点。
插入
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* Insert an entry at "p". */
unsigned char *ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen);
}
ziplistInsert 将 s 插入到 zl 压缩列表的 p 位置。
/* Insert item at "p". */
unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen;
unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0;
size_t offset;
int nextdiff = 0;
unsigned char encoding = 0;
long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value
that is easy to see if for some reason
we use it uninitialized. */
zlentry tail;
/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen);
} else {
unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);
if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {
prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail);
}
}
计算插入位置前一个节点长度 prevlen。
- 如果不是压缩列表末尾,直接读取 p 指针节点的 prevlen;
- 如果是压缩列表末尾,计算 zl 尾节点的长度。
/* See if the entry can be encoded */
if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {
/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */
reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);
} else {
/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipStoreEntryEncoding will use the
* string length to figure out how to encode it. */
reqlen = slen;
}
/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and
* the length of the payload. */
reqlen += zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,prevlen);
reqlen += zipStoreEntryEncoding(NULL,encoding,slen);
尝试解码 s 字符数组获得编码信息,计算新插入节点需要的内存大小 reqlen 字节。
- 编码时先按整数来解析数据内容,如果解析成功,则按照整数编码方式存储;
- 解析失败,则按照字符数组编码存储。
/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to
* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in
* its prevlen field. */
int forcelarge = 0;
nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;
if (nextdiff == -4 && reqlen < 4) {
nextdiff = 0;
forcelarge = 1;
}
如果不是在末尾插入节点的话,要确保插入位置旧节点 prevlen 的大小足够存储新节点的长度。
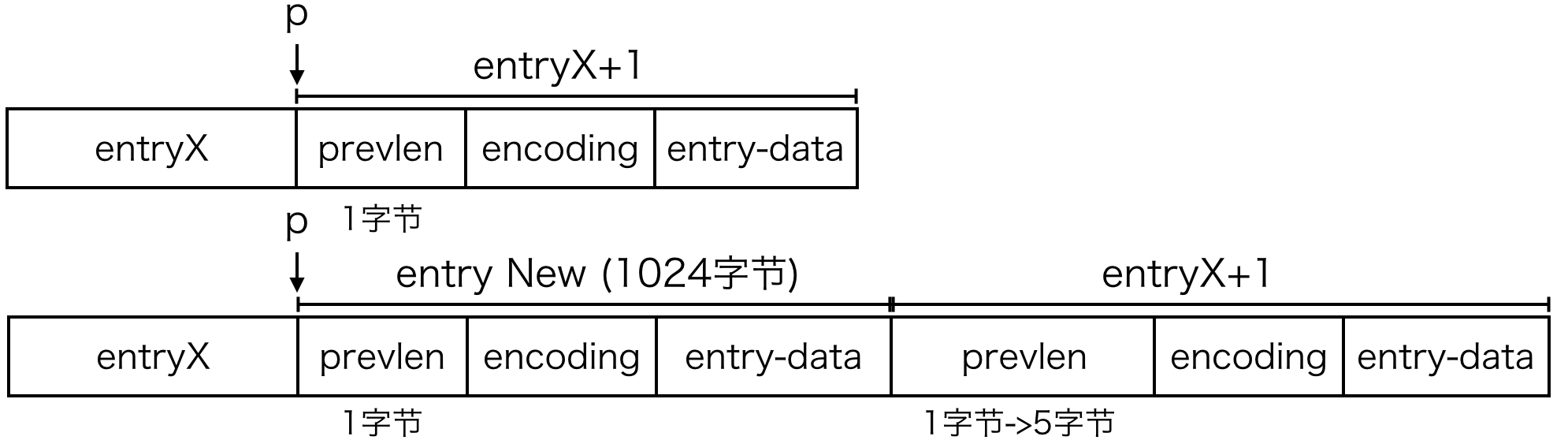
假设旧节点 prevlen 大小为 1 字节,新插入的节点大于 254 字节,那么 nextdiff 等于 5 - 1(旧节点的 prevlen 大小要更新为 5 字节)。 反之旧节点 prevlen 大小为 5 字节,新插入的节点小于 254 字节,nextdiff 等于 -4。
/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */
offset = p-zl;
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff);
p = zl+offset;
ziplistResize 函数调用 realloc 重新分配内存空间,新内存大小为 curlen+reqlen+nextdiff,并重新计算 p 指针位置。
/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */
if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */
memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);
/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */
if (forcelarge)
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+reqlen,reqlen);
else
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);
/* Update offset for tail */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);
...
}
} else {
/* This element will be the new tail. */
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);
}
调整内存位置,插入位置开始的内存往后挪,空出要插入的节点空间。
memmove 将从 p-nextdiff 开始 curlen-offset-1+nextdiff 字节的内容移动到 p+reqlen 位置。
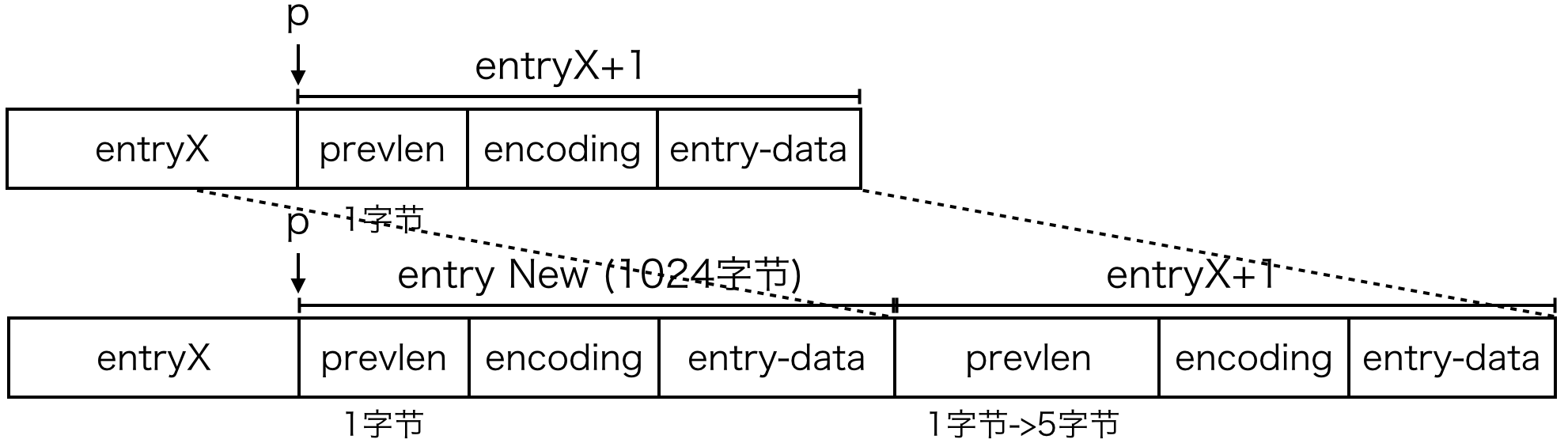
从 p-nextdiff 开始是为了保证 p 位置上的旧节点可以改变 prevlen 的大小。
这边有个问题,如果插入位置的旧节点需要扩展 prevlen 的大小,那么可能导致后面节点的 prevlen 的大小也跟着更新。这也就是下面函数 __ziplistCascadeUpdate 处理的连锁更新。
/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so
* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */
if (nextdiff != 0) {
offset = p-zl;
zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);
p = zl+offset;
}
/* Write the entry */
p += zipStorePrevEntryLength(p,prevlen);
p += zipStoreEntryEncoding(p,encoding,slen);
if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {
memcpy(p,s,slen);
} else {
zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);
}
ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);
return zl;
}
在插入位置写入新的节点。
连锁更新
// 5.0.3/src/ziplist.c
/* When an entry is inserted, we need to set the prevlen field of the next
* entry to equal the length of the inserted entry. It can occur that this
* length cannot be encoded in 1 byte and the next entry needs to be grow
* a bit larger to hold the 5-byte encoded prevlen. This can be done for free,
* because this only happens when an entry is already being inserted (which
* causes a realloc and memmove). However, encoding the prevlen may require
* that this entry is grown as well. This effect may cascade throughout
* the ziplist when there are consecutive entries with a size close to
* ZIP_BIG_PREVLEN, so we need to check that the prevlen can be encoded in
* every consecutive entry.
*
* Note that this effect can also happen in reverse, where the bytes required
* to encode the prevlen field can shrink. This effect is deliberately ignored,
* because it can cause a "flapping" effect where a chain prevlen fields is
* first grown and then shrunk again after consecutive inserts. Rather, the
* field is allowed to stay larger than necessary, because a large prevlen
* field implies the ziplist is holding large entries anyway.
*
* The pointer "p" points to the first entry that does NOT need to be
* updated, i.e. consecutive fields MAY need an update. */
unsigned char *__ziplistCascadeUpdate(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p) {
size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), rawlen, rawlensize;
size_t offset, noffset, extra;
unsigned char *np;
zlentry cur, next;
while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {
zipEntry(p, &cur);
rawlen = cur.headersize + cur.len;
rawlensize = zipStorePrevEntryLength(NULL,rawlen);
/* Abort if there is no next entry. */
if (p[rawlen] == ZIP_END) break;
zipEntry(p+rawlen, &next);
/* Abort when "prevlen" has not changed. */
if (next.prevrawlen == rawlen) break;
if (next.prevrawlensize < rawlensize) {
/* The "prevlen" field of "next" needs more bytes to hold
* the raw length of "cur". */
offset = p-zl;
extra = rawlensize-next.prevrawlensize;
zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+extra);
p = zl+offset;
/* Current pointer and offset for next element. */
np = p+rawlen;
noffset = np-zl;
/* Update tail offset when next element is not the tail element. */
if ((zl+intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))) != np) {
ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =
intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+extra);
}
/* Move the tail to the back. */
memmove(np+rawlensize,
np+next.prevrawlensize,
curlen-noffset-next.prevrawlensize-1);
zipStorePrevEntryLength(np,rawlen);
/* Advance the cursor */
p += rawlen;
curlen += extra;
} else {
if (next.prevrawlensize > rawlensize) {
/* This would result in shrinking, which we want to avoid.
* So, set "rawlen" in the available bytes. */
zipStorePrevEntryLengthLarge(p+rawlen,rawlen);
} else {
zipStorePrevEntryLength(p+rawlen,rawlen);
}
/* Stop here, as the raw length of "next" has not changed. */
break;
}
}
return zl;
}
__ziplistCascadeUpdate 根据后续节点是否需要改变 prevlen 的大小进而重新分配内存。 这种方式看起来效率很低,但是实际上只有处于临界大小的 prevlen 才会进行连锁更新。