blog
 blog copied to clipboard
blog copied to clipboard
Python中的字典对象
Python中的字典是使用哈希表Hash table来实现的。
0x00 字典的存储方式
Python3.6中的字典对象PyDictObject定义在Include/dictobject.h:
typedef struct _dictkeysobject PyDictKeysObject;
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
/* Number of items in the dictionary */
Py_ssize_t ma_used;
/* Dictionary version: globally unique, value change each time
the dictionary is modified */
uint64_t ma_version_tag;
PyDictKeysObject *ma_keys;
/* If ma_values is NULL, the table is "combined": keys and values
are stored in ma_keys.
If ma_values is not NULL, the table is splitted:
keys are stored in ma_keys and values are stored in ma_values */
PyObject **ma_values;
} PyDictObject;
从注释中可以看出,Python中的dict在内存中有两种形式:
combined-table:**ma_values这个指针则是空,keys和values都存储在ma_keys(也就是PyDictKeysObject)中;split-table:keys和values分别存储在ma_keys和ma_values中。
split-table这种形式是Python3.3引进的PEP 412 -- Key-Sharing Dictionary,主要是出于对优化同一个类的实例对象的属性字典(__dict__),共享同一份key,在面向对象编程中,实例化的对象较多的情况下,可以节省内存开销。
_dictkeysobject(PyDictKeysObject)定义在Objects/dict-common.h:
struct _dictkeysobject {
Py_ssize_t dk_refcnt;
/* Size of the hash table (dk_indices). It must be a power of 2. */
Py_ssize_t dk_size;
/* Function to lookup in the hash table (dk_indices):
- lookdict(): general-purpose, and may return DKIX_ERROR if (and
only if) a comparison raises an exception.
- lookdict_unicode(): specialized to Unicode string keys, comparison of
which can never raise an exception; that function can never return
DKIX_ERROR.
- lookdict_unicode_nodummy(): similar to lookdict_unicode() but further
specialized for Unicode string keys that cannot be the <dummy> value.
- lookdict_split(): Version of lookdict() for split tables. */
dict_lookup_func dk_lookup;
/* Number of usable entries in dk_entries. */
Py_ssize_t dk_usable;
/* Number of used entries in dk_entries. */
Py_ssize_t dk_nentries;
/* Actual hash table of dk_size entries. It holds indices in dk_entries,
or DKIX_EMPTY(-1) or DKIX_DUMMY(-2).
Indices must be: 0 <= indice < USABLE_FRACTION(dk_size).
The size in bytes of an indice depends on dk_size:
- 1 byte if dk_size <= 0xff (char*)
- 2 bytes if dk_size <= 0xffff (int16_t*)
- 4 bytes if dk_size <= 0xffffffff (int32_t*)
- 8 bytes otherwise (int64_t*)
Dynamically sized, 8 is minimum. */
union {
int8_t as_1[8];
int16_t as_2[4];
int32_t as_4[2];
#if SIZEOF_VOID_P > 4
int64_t as_8[1];
#endif
} dk_indices;
/* "PyDictKeyEntry dk_entries[dk_usable];" array follows:
see the DK_ENTRIES() macro */
};
_dictkeysobject(PyDictKeysObject)实现了Python字典的哈希表。实际上PyDictKeysObject的内存布局如下:
+---------------+
| dk_refcnt |
| dk_size |
| dk_lookup |
| dk_usable |
| dk_nentries |
+---------------+
| dk_indices |
| |
+---------------+
| dk_entries |
| |
+---------------+
dk_indices是实际的哈希表,对应一个slot数组,存储着index。哈希表的每个slot有4种状态:
Unused,这是每个slot的初始状态,slot中的index == DKIX_EMPTY,表示该slot没有被使用,这个状态可以转化为Active。Active,index >= 0,index对应到dk_entries的PyDictKeyEntry对象,me_key != NULL和me_value != NULL。Dummy,index == DKIX_DUMMY,当dict中一个元素被删除,slot就会从原来的Active状态变成Dummy状态,原先对应的PyDictKeyEntry对象不会被删掉,Dummy可以在key被再次插入的时候转化为Active状态,但是不能转化为Unused状态。这种状态只在combined-table中出现。Pending,index >= 0, key != NULL, and value == NULL,这种状态只在split-table中出现,表示还未插入到split-table中。
dk_size用来表示dk_indices数组的大小,dk_nentries用来表示在dk_entries中已使用的大小。
Python3.6以前的哈希表数组直接存储的是一个
PyDictKeyEntry对象,dk_indices是Python3.6优化dict引入的,More compact dictionaries with faster iteration,参考了PyPy的dict实现。
另外,dk_indices是一个union,实际上会根据dk_size大小动态的来决定用什么类型的变量来表示index。例如,如果dk_size不超过0xff,那么实际上用1字节的带符号整数(char)来存储index。之所以是带符号的整数,是因为index的值可能是负数(DKIX_EMPTY, DKIX_DUMMY, DKIX_ERROR)。
dk_entries是通过DK_ENTRIES这个宏来访问的,定义在Object/dictobject.c:
#define DK_SIZE(dk) ((dk)->dk_size)
#if SIZEOF_VOID_P > 4
#define DK_IXSIZE(dk) \
(DK_SIZE(dk) <= 0xff ? \
1 : DK_SIZE(dk) <= 0xffff ? \
2 : DK_SIZE(dk) <= 0xffffffff ? \
4 : sizeof(int64_t))
#else
#define DK_IXSIZE(dk) \
(DK_SIZE(dk) <= 0xff ? \
1 : DK_SIZE(dk) <= 0xffff ? \
2 : sizeof(int32_t))
#endif
#define DK_ENTRIES(dk) \
((PyDictKeyEntry*)(&(dk)->dk_indices.as_1[DK_SIZE(dk) * DK_IXSIZE(dk)]))
dk_entries中每一个元素称为一个entry,是一个PyDictKeyEntry对象,定义在Object/dict-common.h中:
typedef struct {
/* Cached hash code of me_key. */
Py_hash_t me_hash;
PyObject *me_key;
PyObject *me_value; /* This field is only meaningful for combined tables */
} PyDictKeyEntry;
me_key和me_value分别表示键/值,都使用了通用的PyObject指针,但是如果在me_key使用list这种不可哈希的数据结构,会报出unhashable type的TypeError错误。me_hash缓存了me_key的哈希值,可以避免每次查询都要重新计算一次哈希值。
dk_lookup指向一个搜索函数,在哈希表(dk_indices)中查找返回dk_entries中的index。
/* dict_lookup_func() returns index of entry which can be used like DK_ENTRIES(dk)[index].
* -1 when no entry found, -3 when compare raises error.
*/
typedef Py_ssize_t (*dict_lookup_func)
(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash, PyObject **value_addr);
0x01 字典对象的创建
字典对象通过PyDict_New方法来创建,定义在Object/dictobject.c:
PyObject *
PyDict_New(void)
{
PyDictKeysObject *keys = new_keys_object(PyDict_MINSIZE);
if (keys == NULL)
return NULL;
return new_dict(keys, NULL);
}
在创建dict时会调用new_keys_object函数,
static PyDictKeysObject *new_keys_object(Py_ssize_t size)
{
PyDictKeysObject *dk;
Py_ssize_t es, usable;
// [1]
assert(size >= PyDict_MINSIZE);
assert(IS_POWER_OF_2(size));
// [2]
usable = USABLE_FRACTION(size);
if (size <= 0xff) {
es = 1;
}
else if (size <= 0xffff) {
es = 2;
}
#if SIZEOF_VOID_P > 4
else if (size <= 0xffffffff) {
es = 4;
}
#endif
else {
es = sizeof(Py_ssize_t);
}
// [3]
if (size == PyDict_MINSIZE && numfreekeys > 0) {
dk = keys_free_list[--numfreekeys];
}
else {
// [4]
dk = PyObject_MALLOC(sizeof(PyDictKeysObject)
- Py_MEMBER_SIZE(PyDictKeysObject, dk_indices)
+ es * size
+ sizeof(PyDictKeyEntry) * usable);
if (dk == NULL) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return NULL;
}
}
DK_DEBUG_INCREF dk->dk_refcnt = 1;
dk->dk_size = size;
dk->dk_usable = usable;
dk->dk_lookup = lookdict_unicode_nodummy;
dk->dk_nentries = 0;
// [5]
memset(&dk->dk_indices.as_1[0], 0xff, es * size);
memset(DK_ENTRIES(dk), 0, sizeof(PyDictKeyEntry) * usable);
return dk;
}
[1] 传入size的值必须是大于等于PyDict_MINSIZE,且必须是2的幂次。
/* PyDict_MINSIZE is the starting size for any new dict.
* 8 allows dicts with no more than 5 active entries; experiments suggested
* this suffices for the majority of dicts (consisting mostly of usually-small
* dicts created to pass keyword arguments).
* Making this 8, rather than 4 reduces the number of resizes for most
* dictionaries, without any significant extra memory use.
*/
#define PyDict_MINSIZE 8
PyDict_MINSIZE是一个新的字典默认的大小。
[2] 通过size大小可以确定dk_entries最多可以容纳多少个PyDictKeyEntry对象。
/* USABLE_FRACTION is the maximum dictionary load.
* Increasing this ratio makes dictionaries more dense resulting in more
* collisions. Decreasing it improves sparseness at the expense of spreading
* indices over more cache lines and at the cost of total memory consumed.
*
* USABLE_FRACTION must obey the following:
* (0 < USABLE_FRACTION(n) < n) for all n >= 2
*
* USABLE_FRACTION should be quick to calculate.
* Fractions around 1/2 to 2/3 seem to work well in practice.
*/
#define USABLE_FRACTION(n) (((n) << 1)/3)
size为8的默认大小字典中,最多只能容纳5个PyDictKeyEntry对象。
[3] 这边也用到了Python对象中到处可见的对象池机制,创建默认大小为8的字典会尝试从keys_free_list里面直接获取可用的PyDictKeysObject对象。
/* Dictionary reuse scheme to save calls to malloc and free */
#ifndef PyDict_MAXFREELIST
#define PyDict_MAXFREELIST 80
#endif
...
static PyDictKeysObject *keys_free_list[PyDict_MAXFREELIST];
static int numfreekeys = 0;
和PyListObject的对象池机制类似,也是在PyDictKeyObject对象被销毁的过程中,将PyDictKeyObject对象放入keys_free_list对象池中:
#define DK_DECREF(dk) if (DK_DEBUG_DECREF (--(dk)->dk_refcnt) == 0) free_keys_object(dk)
...
static void
free_keys_object(PyDictKeysObject *keys)
{
PyDictKeyEntry *entries = DK_ENTRIES(keys);
Py_ssize_t i, n;
for (i = 0, n = keys->dk_nentries; i < n; i++) {
Py_XDECREF(entries[i].me_key);
Py_XDECREF(entries[i].me_value);
}
if (keys->dk_size == PyDict_MINSIZE && numfreekeys < PyDict_MAXFREELIST) {
keys_free_list[numfreekeys++] = keys;
return;
}
PyObject_FREE(keys);
}
[4] 如果keys_free_list对象池中没有可用的对象,或是创建大于默认大小的字典时,就会通过PyObject_MALLOC来申请内存创建PyDictKeyObject对象。需要注意的是,申请需要的内存大小时,需要减去dk_indices的默认大小8字节,因为这部分内存是根据size动态确认下来的。还需要加上PyDictKeyEntry对象数组dk_entries内存大小。
[5] 这边初始化了dk_indices和dk_entries。dk_indices填充了0xff,即DKIX_EMPTY(-1),dk_entries则初始化为空。
PyDictKeyObject创建完成之后就会调用new_dict来完成PyDictObject对象的创建:
/* Consumes a reference to the keys object */
static PyObject *
new_dict(PyDictKeysObject *keys, PyObject **values)
{
PyDictObject *mp;
assert(keys != NULL);
if (numfree) {
mp = free_list[--numfree];
assert (mp != NULL);
assert (Py_TYPE(mp) == &PyDict_Type);
_Py_NewReference((PyObject *)mp);
}
else {
mp = PyObject_GC_New(PyDictObject, &PyDict_Type);
if (mp == NULL) {
DK_DECREF(keys);
free_values(values);
return NULL;
}
}
mp->ma_keys = keys;
mp->ma_values = values;
mp->ma_used = 0;
mp->ma_version_tag = DICT_NEXT_VERSION();
assert(_PyDict_CheckConsistency(mp));
return (PyObject *)mp;
}
PyDictObject的对象池机制和PyListObject的对象池机制也类似,也是在PyDictObject对象销毁的时候放入free_list对象池。
static void
dict_dealloc(PyDictObject *mp)
{
PyObject **values = mp->ma_values;
PyDictKeysObject *keys = mp->ma_keys;
Py_ssize_t i, n;
/* bpo-31095: UnTrack is needed before calling any callbacks */
PyObject_GC_UnTrack(mp);
Py_TRASHCAN_SAFE_BEGIN(mp)
if (values != NULL) {
if (values != empty_values) {
for (i = 0, n = mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries; i < n; i++) {
Py_XDECREF(values[i]);
}
free_values(values);
}
DK_DECREF(keys);
}
else if (keys != NULL) {
assert(keys->dk_refcnt == 1);
DK_DECREF(keys);
}
if (numfree < PyDict_MAXFREELIST && Py_TYPE(mp) == &PyDict_Type)
free_list[numfree++] = mp;
else
Py_TYPE(mp)->tp_free((PyObject *)mp);
Py_TRASHCAN_SAFE_END(mp)
}
也会把PyDictObject对象所指向的PyDictKeysObject对象放入keys_free_list对象池中。
0x02 字典对象的操作
字典对象的类型PyDict_Type,定义在Object/dictobject.c:
PyTypeObject PyDict_Type = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
"dict",
sizeof(PyDictObject),
0,
(destructor)dict_dealloc, /* tp_dealloc */
0, /* tp_print */
0, /* tp_getattr */
0, /* tp_setattr */
0, /* tp_reserved */
(reprfunc)dict_repr, /* tp_repr */
0, /* tp_as_number */
&dict_as_sequence, /* tp_as_sequence */
&dict_as_mapping, /* tp_as_mapping */
...
};
我们主要来看字典对象的映射操作(tp_as_mapping),对应的函数是dict_as_mapping:
static PyMappingMethods dict_as_mapping = {
(lenfunc)dict_length, /*mp_length*/
(binaryfunc)dict_subscript, /*mp_subscript*/
(objobjargproc)dict_ass_sub, /*mp_ass_subscript*/
};
获取元素
static PyObject *
dict_subscript(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key)
{
Py_ssize_t ix;
Py_hash_t hash;
PyObject *value;
if (!PyUnicode_CheckExact(key) ||
(hash = ((PyASCIIObject *) key)->hash) == -1) {
hash = PyObject_Hash(key);
if (hash == -1)
return NULL;
}
ix = (mp->ma_keys->dk_lookup)(mp, key, hash, &value);
if (ix == DKIX_ERROR)
return NULL;
if (ix == DKIX_EMPTY || value == NULL) {
if (!PyDict_CheckExact(mp)) {
/* Look up __missing__ method if we're a subclass. */
PyObject *missing, *res;
_Py_IDENTIFIER(__missing__);
missing = _PyObject_LookupSpecial((PyObject *)mp, &PyId___missing__);
if (missing != NULL) {
res = PyObject_CallFunctionObjArgs(missing,
key, NULL);
Py_DECREF(missing);
return res;
}
else if (PyErr_Occurred())
return NULL;
}
_PyErr_SetKeyError(key);
return NULL;
}
Py_INCREF(value);
return value;
}
形如 d[key]这样的下标访问会调用dict_subscript来获取字典中的value。
dict_subscript会对key进行类型检查和hash检查,然后调用PyDictObject对象中的PyDictKeyObject对象的搜索函数dk_lookup来获取value,时间复杂度为O(1)。
搜索策略
Python3为PyDictObject对象提供了4种搜索策略:
lookdict,通用的搜索函数。lookdict_unicode,针对Unicode字符串keys优化的搜索函数。lookdict_unicode_nodummy,类似于lookdict_unicode搜索,专门用在已知没有dummy值的搜索。lookdict_split,被用在split-table的lookdict搜索。
我们先来看看通用的搜索函数lookdict,定义在Object/dictobject.c中:
/*
The basic lookup function used by all operations.
This is based on Algorithm D from Knuth Vol. 3, Sec. 6.4.
Open addressing is preferred over chaining since the link overhead for
chaining would be substantial (100% with typical malloc overhead).
The initial probe index is computed as hash mod the table size. Subsequent
probe indices are computed as explained earlier.
All arithmetic on hash should ignore overflow.
The details in this version are due to Tim Peters, building on many past
contributions by Reimer Behrends, Jyrki Alakuijala, Vladimir Marangozov and
Christian Tismer.
lookdict() is general-purpose, and may return DKIX_ERROR if (and only if) a
comparison raises an exception.
lookdict_unicode() below is specialized to string keys, comparison of which can
never raise an exception; that function can never return DKIX_ERROR when key
is string. Otherwise, it falls back to lookdict().
lookdict_unicode_nodummy is further specialized for string keys that cannot be
the <dummy> value.
For both, when the key isn't found a DKIX_EMPTY is returned.
*/
static Py_ssize_t _Py_HOT_FUNCTION
lookdict(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key,
Py_hash_t hash, PyObject **value_addr)
{
size_t i, mask, perturb;
PyDictKeysObject *dk;
PyDictKeyEntry *ep0;
top:
dk = mp->ma_keys;
ep0 = DK_ENTRIES(dk);
mask = DK_MASK(dk);
perturb = hash;
// [1]
i = (size_t)hash & mask;
for (;;) {
// [2]
Py_ssize_t ix = dk_get_index(dk, i);
// [3]
if (ix == DKIX_EMPTY) {
*value_addr = NULL;
return ix;
}
if (ix >= 0) {
// [4]
PyDictKeyEntry *ep = &ep0[ix];
assert(ep->me_key != NULL);
if (ep->me_key == key) {
*value_addr = ep->me_value;
return ix;
}
// [5]
if (ep->me_hash == hash) {
PyObject *startkey = ep->me_key;
Py_INCREF(startkey);
int cmp = PyObject_RichCompareBool(startkey, key, Py_EQ);
Py_DECREF(startkey);
if (cmp < 0) {
*value_addr = NULL;
return DKIX_ERROR;
}
if (dk == mp->ma_keys && ep->me_key == startkey) {
if (cmp > 0) {
*value_addr = ep->me_value;
return ix;
}
}
else {
/* The dict was mutated, restart */
goto top;
}
}
}
// [6]
perturb >>= PERTURB_SHIFT;
i = (i*5 + perturb + 1) & mask;
}
assert(0); /* NOT REACHED */
return 0;
}
[1] 我们需要将hash值映射到哈希表dk_indices中的某一个slot,这边将hash与DK_MASK(dk)作了一个与操作,保证了这个slot一定在哈希表上(小于dk_size)。
#define DK_MASK(dk) (((dk)->dk_size)-1)
这个如何保证呢?因为hash表的大小是2的幂次,对于一个值对2的幂次取余会等于对2的幂次 - 1做与运算。
In [1]: size = 2 << 5
In [2]: 100 % size
Out[2]: 36
In [3]: 100 & (size - 1)
Out[3]: 36
[2] 这边通过dk_get_index函数来获取对应到dk_entries的index。
/* lookup indices. returns DKIX_EMPTY, DKIX_DUMMY, or ix >=0 */
static inline Py_ssize_t
dk_get_index(PyDictKeysObject *keys, Py_ssize_t i)
{
Py_ssize_t s = DK_SIZE(keys);
Py_ssize_t ix;
if (s <= 0xff) {
int8_t *indices = keys->dk_indices.as_1;
ix = indices[i];
}
else if (s <= 0xffff) {
int16_t *indices = keys->dk_indices.as_2;
ix = indices[i];
}
#if SIZEOF_VOID_P > 4
else if (s > 0xffffffff) {
int64_t *indices = keys->dk_indices.as_8;
ix = indices[i];
}
#endif
else {
int32_t *indices = keys->dk_indices.as_4;
ix = indices[i];
}
assert(ix >= DKIX_DUMMY);
return ix;
}
[3] 如果index是一个DKIX_EMPTY标志,则该slot是可用的。
[4] 对于index >= 0的情况下,取出index对应在dk_entries中的entry,比较key的引用是否相等。因为两个key都是PyObject*指针,所以比较的是引用是否相等,而不是值相等。
[5] 如果key的引用不相等的话,会对两个key进行值检查。值检查的过程首先会检查两个对象的hash值是否相同,如果不相同,则其值也一定不相同,不用再继续下去了;而如果hash值相等,那么将通过PyObject_RichCompareBool进行比较。
PyObject_RichCompareBool定义在Object/object.c中:
/* Perform a rich comparison with integer result. This wraps
PyObject_RichCompare(), returning -1 for error, 0 for false, 1 for true. */
int
PyObject_RichCompareBool(PyObject *v, PyObject *w, int op)
{
PyObject *res;
int ok;
/* Quick result when objects are the same.
Guarantees that identity implies equality. */
if (v == w) {
if (op == Py_EQ)
return 1;
else if (op == Py_NE)
return 0;
}
res = PyObject_RichCompare(v, w, op);
if (res == NULL)
return -1;
if (PyBool_Check(res))
ok = (res == Py_True);
else
ok = PyObject_IsTrue(res);
Py_DECREF(res);
return ok;
}
PyObject_RichCompareBool提供指定的比较操作类型,当(v op w)成立时,返回1;当(v op w)不成立时,返回0;如果异常,就返回-1。
这边指定了Py_EQ操作,这将进行相等比较操作。
[6] 会有两种可能达到这里:
- index == DKIX_DUMMY
- hash相等,key不相等
这就产生了哈希表的冲突。Python字典中处理冲突的方法是开放定址法。
开放定址法是一个用探测手段来解决冲突的方法。CPython利用随机探查(Random Probing)来查找空闲的slot。
perturb >>= PERTURB_SHIFT;
i = (i*5 + perturb + 1) & mask;
搜索及冲突处理过程(图取自《Python dictionary implementation》):
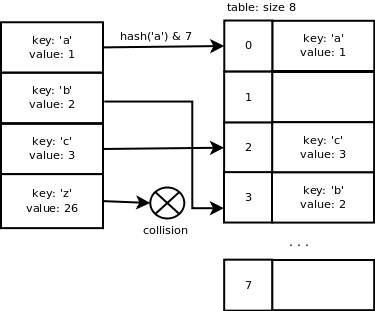
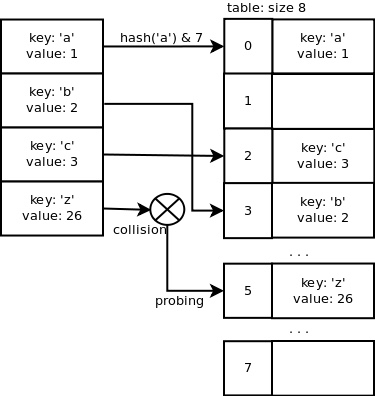
插入元素
static int
dict_ass_sub(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *v, PyObject *w)
{
if (w == NULL)
return PyDict_DelItem((PyObject *)mp, v);
else
return PyDict_SetItem((PyObject *)mp, v, w);
}
...
/* CAUTION: PyDict_SetItem() must guarantee that it won't resize the
* dictionary if it's merely replacing the value for an existing key.
* This means that it's safe to loop over a dictionary with PyDict_Next()
* and occasionally replace a value -- but you can't insert new keys or
* remove them.
*/
int
PyDict_SetItem(PyObject *op, PyObject *key, PyObject *value)
{
PyDictObject *mp;
Py_hash_t hash;
if (!PyDict_Check(op)) {
PyErr_BadInternalCall();
return -1;
}
assert(key);
assert(value);
mp = (PyDictObject *)op;
if (!PyUnicode_CheckExact(key) ||
(hash = ((PyASCIIObject *) key)->hash) == -1)
{
hash = PyObject_Hash(key);
if (hash == -1)
return -1;
}
/* insertdict() handles any resizing that might be necessary */
return insertdict(mp, key, hash, value);
}
形如d[key] = value这种操作会调用PyDict_SetItem来插入键值对。
PyDict_SetItem会对op对象进行类型检查,并检查key是否是字符串或是否可hash,然后调用insertdict函数来添加新的键值对。
/*
Internal routine to insert a new item into the table.
Used both by the internal resize routine and by the public insert routine.
Returns -1 if an error occurred, or 0 on success.
*/
static int
insertdict(PyDictObject *mp, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash, PyObject *value)
{
PyObject *old_value;
PyDictKeyEntry *ep;
Py_INCREF(key);
Py_INCREF(value);
// [1]
if (mp->ma_values != NULL && !PyUnicode_CheckExact(key)) {
if (insertion_resize(mp) < 0)
goto Fail;
}
// [2]
Py_ssize_t ix = mp->ma_keys->dk_lookup(mp, key, hash, &old_value);
if (ix == DKIX_ERROR)
goto Fail;
assert(PyUnicode_CheckExact(key) || mp->ma_keys->dk_lookup == lookdict);
MAINTAIN_TRACKING(mp, key, value);
/* When insertion order is different from shared key, we can't share
* the key anymore. Convert this instance to combine table.
*/
// [3]
if (_PyDict_HasSplitTable(mp) &&
((ix >= 0 && old_value == NULL && mp->ma_used != ix) ||
(ix == DKIX_EMPTY && mp->ma_used != mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries))) {
if (insertion_resize(mp) < 0)
goto Fail;
ix = DKIX_EMPTY;
}
// [4]
if (ix == DKIX_EMPTY) {
/* Insert into new slot. */
assert(old_value == NULL);
if (mp->ma_keys->dk_usable <= 0) {
/* Need to resize. */
if (insertion_resize(mp) < 0)
goto Fail;
}
Py_ssize_t hashpos = find_empty_slot(mp->ma_keys, hash);
ep = &DK_ENTRIES(mp->ma_keys)[mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries];
dk_set_index(mp->ma_keys, hashpos, mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries);
ep->me_key = key;
ep->me_hash = hash;
if (mp->ma_values) {
assert (mp->ma_values[mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries] == NULL);
mp->ma_values[mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries] = value;
}
else {
ep->me_value = value;
}
mp->ma_used++;
mp->ma_version_tag = DICT_NEXT_VERSION();
mp->ma_keys->dk_usable--;
mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries++;
assert(mp->ma_keys->dk_usable >= 0);
assert(_PyDict_CheckConsistency(mp));
return 0;
}
// [5]
if (_PyDict_HasSplitTable(mp)) {
mp->ma_values[ix] = value;
if (old_value == NULL) {
/* pending state */
assert(ix == mp->ma_used);
mp->ma_used++;
}
}
else {
assert(old_value != NULL);
DK_ENTRIES(mp->ma_keys)[ix].me_value = value;
}
mp->ma_version_tag = DICT_NEXT_VERSION();
Py_XDECREF(old_value); /* which **CAN** re-enter (see issue #22653) */
assert(_PyDict_CheckConsistency(mp));
Py_DECREF(key);
return 0;
Fail:
Py_DECREF(value);
Py_DECREF(key);
return -1;
}
[1] 这边检查了字典对象的ma_values值是否为空和key是否是字符串,如果ma_values为空且key不为字符串,表示这个字典对象是以split-table形式且共享key存储的类实例属性,插入一个不是字符串的key就需要转换成combined-table存储。
[2] 调用了dk_lookup来搜索index和value。
[3] 这边同[1],字典对象以split-table形式存储的,当插入一个不在shared key的key时,需要转换成combined-table。
[4] index == DKIX_EMPTY条件下插入新的键值对,分不同情况:
- 如果原来的哈希表没有足够的空间,就会调整哈希表大小,再插入。
- 如果是
split-table形式的哈希表,就插入到PyDictObejct对象的ma_values数组中。 - 否则就插入到对应的
entry中的me_value域。
[5] index != DKIX_EMPTY条件下替换旧的值,分两种情况:
- 如果是
split-table形式的哈希表,就替换掉原来对应到PyDictObejct对象的ma_values数组中的值。 - 否则就替换掉对应的
entry中的me_value域的值。
这边需要额外说下insertion_resize函数,调整哈希表大小和转换成combined-table都调用了这个函数。
static int
insertion_resize(PyDictObject *mp)
{
return dictresize(mp, GROWTH_RATE(mp));
}
insertion_resize函数本质上只是调用了dictresize函数,额外传了一个minsize参数,通过宏GROWTH_RATE计算得来的。
/* GROWTH_RATE. Growth rate upon hitting maximum load.
* Currently set to used*2 + capacity/2.
* This means that dicts double in size when growing without deletions,
* but have more head room when the number of deletions is on a par with the
* number of insertions.
* Raising this to used*4 doubles memory consumption depending on the size of
* the dictionary, but results in half the number of resizes, less effort to
* resize.
* GROWTH_RATE was set to used*4 up to version 3.2.
* GROWTH_RATE was set to used*2 in version 3.3.0
*/
#define GROWTH_RATE(d) (((d)->ma_used*2)+((d)->ma_keys->dk_size>>1))
根据GROWTH_RATE的计算方式,可以得出以下结论:
- 如果原有的数据量小于原有大小的1/4,那么它也会小于现有大小的1/4,但新的dict缩小了;
- 如果原有的数据量大于原有大小的1/4,那么它也会大于现有大小的1/4,但新的dict扩大了。
/*
Restructure the table by allocating a new table and reinserting all
items again. When entries have been deleted, the new table may
actually be smaller than the old one.
If a table is split (its keys and hashes are shared, its values are not),
then the values are temporarily copied into the table, it is resized as
a combined table, then the me_value slots in the old table are NULLed out.
After resizing a table is always combined,
but can be resplit by make_keys_shared().
*/
static int
dictresize(PyDictObject *mp, Py_ssize_t minsize)
{
Py_ssize_t newsize, numentries;
PyDictKeysObject *oldkeys;
PyObject **oldvalues;
PyDictKeyEntry *oldentries, *newentries;
/* Find the smallest table size > minused. */
for (newsize = PyDict_MINSIZE;
newsize < minsize && newsize > 0;
newsize <<= 1)
;
if (newsize <= 0) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
}
oldkeys = mp->ma_keys;
/* NOTE: Current odict checks mp->ma_keys to detect resize happen.
* So we can't reuse oldkeys even if oldkeys->dk_size == newsize.
* TODO: Try reusing oldkeys when reimplement odict.
*/
/* Allocate a new table. */
mp->ma_keys = new_keys_object(newsize);
if (mp->ma_keys == NULL) {
mp->ma_keys = oldkeys;
return -1;
}
// New table must be large enough.
assert(mp->ma_keys->dk_usable >= mp->ma_used);
if (oldkeys->dk_lookup == lookdict)
mp->ma_keys->dk_lookup = lookdict;
numentries = mp->ma_used;
oldentries = DK_ENTRIES(oldkeys);
newentries = DK_ENTRIES(mp->ma_keys);
oldvalues = mp->ma_values;
if (oldvalues != NULL) {
/* Convert split table into new combined table.
* We must incref keys; we can transfer values.
* Note that values of split table is always dense.
*/
for (Py_ssize_t i = 0; i < numentries; i++) {
assert(oldvalues[i] != NULL);
PyDictKeyEntry *ep = &oldentries[i];
PyObject *key = ep->me_key;
Py_INCREF(key);
newentries[i].me_key = key;
newentries[i].me_hash = ep->me_hash;
newentries[i].me_value = oldvalues[i];
}
DK_DECREF(oldkeys);
mp->ma_values = NULL;
if (oldvalues != empty_values) {
free_values(oldvalues);
}
}
else { // combined table.
if (oldkeys->dk_nentries == numentries) {
memcpy(newentries, oldentries, numentries * sizeof(PyDictKeyEntry));
}
else {
PyDictKeyEntry *ep = oldentries;
for (Py_ssize_t i = 0; i < numentries; i++) {
while (ep->me_value == NULL)
ep++;
newentries[i] = *ep++;
}
}
assert(oldkeys->dk_lookup != lookdict_split);
assert(oldkeys->dk_refcnt == 1);
if (oldkeys->dk_size == PyDict_MINSIZE &&
numfreekeys < PyDict_MAXFREELIST) {
DK_DEBUG_DECREF keys_free_list[numfreekeys++] = oldkeys;
}
else {
DK_DEBUG_DECREF PyObject_FREE(oldkeys);
}
}
build_indices(mp->ma_keys, newentries, numentries);
mp->ma_keys->dk_usable -= numentries;
mp->ma_keys->dk_nentries = numentries;
return 0;
}