Question related with sm4 ECB

in recently, I am working for sm4 interoperability between GM golang libs. https://github.com/Hyperledger-TWGC/GM-interoperability/pull/39
it seems when GMSSL doing with ECB mode, only used with byte with length 16 is there any way to deal with a data over length 16 in GmSSL?
attached a picture comparing with TJ lib.
or do we need pkcs7padding/pkcs7unpadding in this repo?
CBC is a general method, it can use any cipher (ECB mode) to do the work.
In Golang, just feed any block cipher to the NewCBCEncrypter to get a CBC cipher.
In fact, you only need this:
// #cgo CFLAGS: -g -Wall -Wno-unknown-pragmas
// #include <stdlib.h>
// #include "sm4.h"
import "C"
import (
"crypto/cipher"
"strconv"
)
type sm4Cipher struct {
enc, dec C.struct_SM4_KEY
}
var _ cipher.Block = (*sm4Cipher)(nil)
func (c *sm4Cipher) BlockSize() int {
return 16
}
func (c *sm4Cipher) Encrypt(dst, src []byte) {
C.sm4_encrypt(&c.enc, (*C.uchar)(&src[0]), (*C.uchar)(&dst[0]))
}
func (c *sm4Cipher) Decrypt(dst, src []byte) {
C.sm4_encrypt(&c.dec, (*C.uchar)(&src[0]), (*C.uchar)(&dst[0]))
}
type Sm4KeySizeError int
func (k Sm4KeySizeError) Error() string {
return "sm4: invalid key size " + strconv.Itoa(int(k))
}
// NewSm4Cipher creates and returns a new cipher.Block.
// The key argument should be the SM4 key, 16 bytes
func NewSm4Cipher(key []byte) (cipher.Block, error) {
k := len(key)
switch k {
default:
return nil, Sm4KeySizeError(k)
case 16:
break
}
c := &sm4Cipher{}
C.sm4_set_encrypt_key(&c.enc, (*C.uchar)(&key[0]))
C.sm4_set_decrypt_key(&c.dec, (*C.uchar)(&key[0]))
return c, nil
}
And here are the test cases:
import (
"github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
"testing"
"unsafe"
)
func TestSM4(t *testing.T) {
userKey := []byte{
0x01, 0x23, 0x45, 0x67, 0x89, 0xab, 0xcd, 0xef,
0xfe, 0xdc, 0xba, 0x98, 0x76, 0x54, 0x32, 0x10,
}
rk := []uint32{
0xf12186f9, 0x41662b61, 0x5a6ab19a, 0x7ba92077,
0x367360f4, 0x776a0c61, 0xb6bb89b3, 0x24763151,
0xa520307c, 0xb7584dbd, 0xc30753ed, 0x7ee55b57,
0x6988608c, 0x30d895b7, 0x44ba14af, 0x104495a1,
0xd120b428, 0x73b55fa3, 0xcc874966, 0x92244439,
0xe89e641f, 0x98ca015a, 0xc7159060, 0x99e1fd2e,
0xb79bd80c, 0x1d2115b0, 0x0e228aeb, 0xf1780c81,
0x428d3654, 0x62293496, 0x01cf72e5, 0x9124a012,
}
plaintext := []byte{
0x01, 0x23, 0x45, 0x67, 0x89, 0xab, 0xcd, 0xef,
0xfe, 0xdc, 0xba, 0x98, 0x76, 0x54, 0x32, 0x10,
}
ciphertext1 := []byte{
0x68, 0x1e, 0xdf, 0x34, 0xd2, 0x06, 0x96, 0x5e,
0x86, 0xb3, 0xe9, 0x4f, 0x53, 0x6e, 0x42, 0x46,
}
ciphertext2 := []byte{
0x59, 0x52, 0x98, 0xc7, 0xc6, 0xfd, 0x27, 0x1f,
0x04, 0x02, 0xf8, 0x04, 0xc3, 0x3d, 0x3f, 0x66,
}
c, err := NewSm4Cipher(userKey)
sm4Cipher := c.(*sm4Cipher)
assert.NoError(t, err)
slice := (*[32]uint32)(unsafe.Pointer(&sm4Cipher.enc.rk))[:32:32]
assert.Equal(t, rk, slice)
encrypted := make([]byte, 16)
c.Encrypt(encrypted, plaintext)
assert.Equal(t, ciphertext1, encrypted)
decrypted := make([]byte, 16)
c.Decrypt(decrypted, encrypted)
assert.Equal(t, plaintext, decrypted)
buf := make([]byte, 16)
copy(buf, plaintext)
for i := 0; i < 1000000; i++ {
c.Encrypt(buf, buf)
}
assert.Equal(t, ciphertext2, buf)
}
thanks a lot. @wxiaoguang , there are some back ground, as in TWGC gm working group, we had an agreement that use ECB for now to do interoperability.
- it's a good point to adding other sm4 mode there.
- it's very helpful for your code sample.
- back to ECB mode, do you think GmSSL repo need to add support with pkcs7padding/pkcs7unpadding?
TBH, at the moment, GmSSL libray was not well designed. And I believe it's also on the way to make the algorithms more general, see:
https://github.com/guanzhi/GmSSL/blob/c21972168d3ea5b0e22fa074584907247d46ffe5/include/gmssl/block_cipher.h
https://github.com/guanzhi/GmSSL/blob/c21972168d3ea5b0e22fa074584907247d46ffe5/src/block_cipher.c
A generalized pkcs7padding/pkcs7unpadding is helpful.
Take the code as example, there are sm4_cbc_padding_encrypt and aes_cbc_padding_encrypt, they all do padding, the logic is totally the same. The same situation to ctr or gcm.
A good design should be:
- Make AES/SM4 ciphers only provide basic block (ECB, single block) encryption/decryption
- Introduce general methods to do padding/ctr/gcm. Golang library's design is a very good example, and that's what OpenSSL does, too.
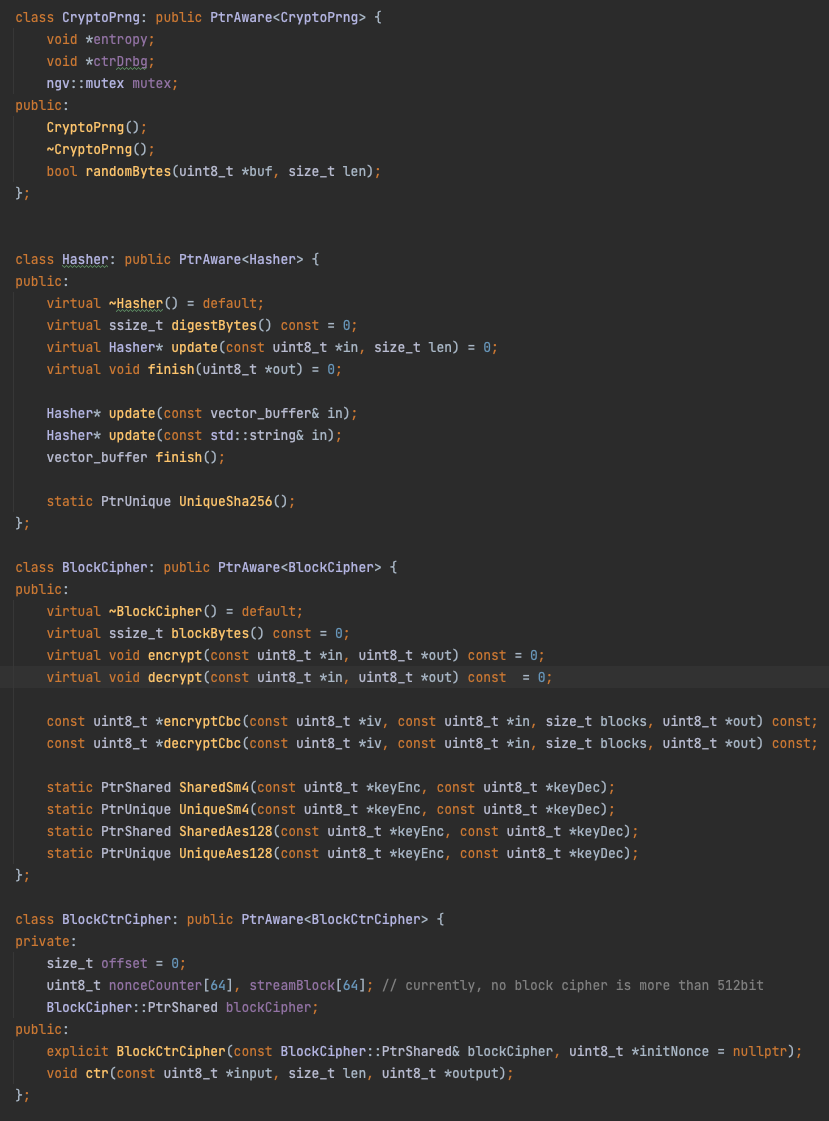
FYI, I also use many crypto algorithms in C++, this is my design (for example).
(UniqueXxx and SharedXxx are helper functions to call make_shared to return std::unique_ptr / std::shared_ptr objects)
auto hashSha256 = Hasher::UniqueSha256();
auto hashSm3 = Hasher::UniqueSm3();
sha256sum = hashSha256->update(...)->finish();
sm3sum = hashSm3->update(...)->finish();
auto cipherAes128 = BlockCipher::SharedAes128(keys);
auto cipherSm4 = BlockCipher::SharedSm4(keys);
cipherAes128->encrypt(...)
cipherAes128->encryptCbc(...)
cipherSm4->encrypt(...)
cipherSm4->encryptCbc(...)
auto ctrAes128 = BlockCtrCipher::NewShared(cipherAes128, nonce);
auto ctrSm4 = BlockCtrCipher::NewShared(cipherSm4, nonce);
ctrAes128->ctr(...)
ctrSm4->ctr(...)
请问c++ sm4 ecb用哪个接口设置填充?