Generic-Facebook-App
 Generic-Facebook-App copied to clipboard
Generic-Facebook-App copied to clipboard
For Great Copy-Pasta Justice!
#Facebook Applications ###A Field Guide
##Summary Creating an application (Canvas Page)
- Where's your iFrame
- https / ssl
- client-side code
Open Graph: Actions and Objects
- Performing an action, sharing an object
- User-generated images
- Custom action approval and test users (http://developers.facebook.com/docs/opengraph/opengraph-approval/)
- client-side code
Facebook Tiles (Formerly tabs)
- Getting an app into a tile
- Retrieving GET data
- Client and server-side code
##The Content:
###Create an application There was a time when you could build Facebook applications within Facebook. Now, however, Facebook applications are on your servers, and use code you write. This means a Facebook application is loading a web-page you host from within an iFrame.
Your first step to create a Facebook application is to register it. When creating an application, there are many forms to fill out. This will not be a comprehensive guide.
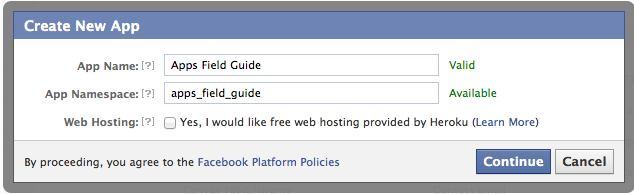
Register your app
After following the link above, click the Create New App button. You'll be presented with a screen asking for the name of the app, and it's namespace. The namespace will be both the URL of the canvas app (more on that later) and referenced in code to perform actions with the Open Graph API (again, more on that later).
Where's your iframe
Once you've registered your app, you need to tell Facebook where to pull in your website. Facebook pulls in YOUR website via an iFrame for its application, so you just need to let facebook know where that lives.
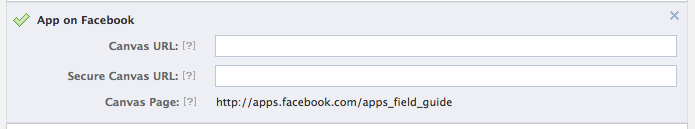
On the Basic app settings (Settings > Basic in left-hand navigation), there are two areas that need filling out.
- Basic Info::App Domain
- App Integration::Website with Facebook Login, App on Facebook, Mobile Web
The App Domain needs to be the base domain name of your server. If you're doing myfancyapp.mydomain.com, the App Domain is mydomain.com.
The App Integration is the exact URL of your website, for instance myfancyapp.com/mydomain/canvas/. Note that website need to end in a "directory" with a trailing slash "/". You can fill out all sections with the same URL.
Https / SSL
Note that the App on Facebook requres a secure URL ("Secure Canvas Url" and later "Secure Page Tab Url"). This means that your website needs to support https. It needs an SSl certificate. This is because many users now view Facebook via https. Your app will not work if it does not support it when a user is attempting to access content under https.
You should be able to load up your canvas app and see your site at http://apps.facebook.com/your_app_namespace/. Note that your app page must be setup to accept POST resquests to receive the signed_request POST variable sent to it. GET-only routes will fail.
You can also pass your app GET requests via the Facebook URL. For example, http://apps.facebook.com/your_app_namespace/?what=ever will make GET 'what=ever' available to your application page.
The same is NOT true for Facebook Tile (tab) pages. There's a more complicated method for retrieving such data explained below.
Client-side code
Here are some code snippets to help you get setup, login, etc.
//Called when FB object is loaded and ready
window.fbAsyncInit = function() {
FB.init({
appId : '01234567890', // Your App ID
status : true, // check login status
cookie : true, // enable cookies to allow the server to access the session
xfbml : true // parse XFBML
});
//FB global object is available now
/* Check if user is logged in and/or hasn't authorized app permissions */
FB.getLoginStatus(function(response) {
if (response.status === 'connected') {
// the user is logged in and has authenticated
console.log('Ready to roll');
} else if (response.status === 'not_authorized') {
// the user is logged in to Facebook, but not authenticated
console.log('Permissions revoked or not given');
} else {
// the user isn't logged in to Facebook.
console.log('Not logged in');
}
});
/* Log a user in */
FB.login(function(response) {
if (response.authResponse) {
//Logged in
console.log('logged in');
} else {
//User cancelled login or did not fully authorize.
console.log('not authorized or not logged in');
}
}, {scope:'publish_actions'}); //Give us permission to post to users wall
/* Check for changes in user status */
FB.Event.subscribe('auth.statusChange', function(response) {
if (response.authResponse) {
// user has auth'd your app and is logged into Facebook
console.log('ready to roll');
} else {
// user has not auth'd your app, or is not logged into Facebook
console.log('not authorized or not logged in');
}
});
}
// Load the SDK Asynchronously
(function(d){
var js, id = 'facebook-jssdk'; if (d.getElementById(id)) {return;}
js = d.createElement('script'); js.id = id; js.async = true;
js.src = "//connect.facebook.net/en_US/all.js";
d.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(js);
}(document));
###Open Graph: Doin' Stuff We want our users to do stuff, and share that on their wall/timeline. In the Open Graph settings, you can define what a user is doing, and it can be anything.
There are two types of objects an action can be performed on:
- Object: An object is a valid web URL with correspoding og:* meta tags to define what the object is.
- Place: A location that exists in FB, a location you can check into.
Example: User just Ate a Bug.
# Ate = action
# Bug = object
When ane actions is performed, it's just like hitting a Like button on a webpage in how it appears on a user's Timeline - Image, caption, optional user image, etc.
Make an action and object:
Head to the Open Graph settings while editing your application. Start by defining and Action and an Object. In our example, we're allowing people to Eat some Bugs.
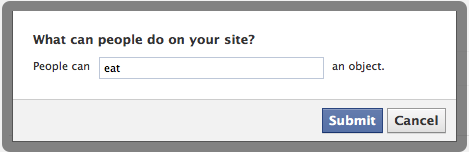
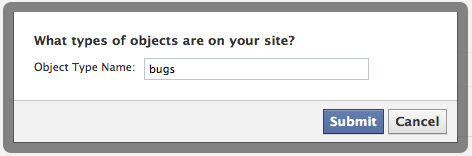
After these both are created, you need to set them up further with some extra options. Click into your newly created Action (Eat).
Configure the action:
- Under the Name of the action (Eat), enter in the corresponding Object (Bugs) in the Connected Object Types field.
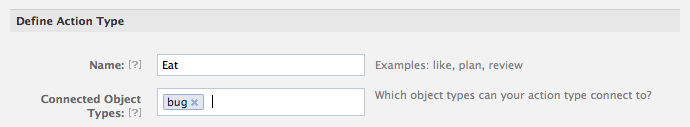
- Scroll down to Configure Story Attachment and add in any captions or info you want to in included in when the action is performed. If you click advanced, you can see/edit what the open graph action url will be (/me/apps_field_guide:eat).
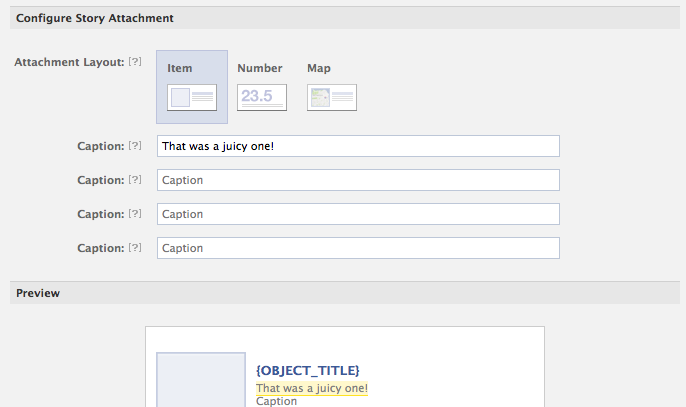
- Save that.
Configure the object:
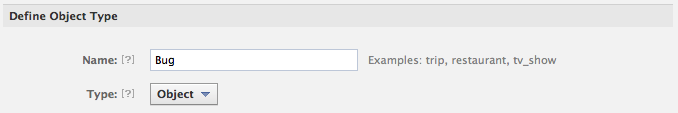
Now head to your Object type and click on it to edit (Bugs).
- Click on the object (Bug) to edit it
- Note you can make it an Object or Place. We're doing an Object here.
- You can add custom properties if you want. These will be needed in the og:* meta tags of your object URL
- Click on Get Code on the bottom to see what HTML code you'll need on the URL representing your object
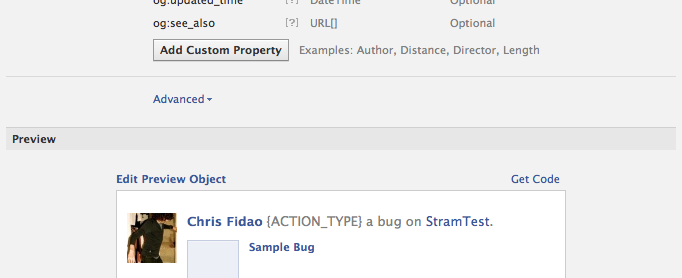
Now, how does this all fit together? You'll need:
- A page for a user to perform the action. This is a page with a button which lets the user login, authenticate the application, and Eat the Bug.
- A page that represents the bug. This page will have the og:type=bug meta tag, in addition to og:app_id and other meta data (See Get Code when editing your Object, as mentioned above, to get all this info).
Client-side code
/**
* This is for sharing
*
* @param: url - The URL of the item representing the Bug object (example.com/my-bug)
* @param: next - A javascript callback function (specific to this example)
*
* Note the API url we are using - For current logged-in user (/me), perform action
* fido_stream_test:eat (your_app_namespace:action). The parameter it takes is the
* object we created.
*/
this.fbPublish = function(url, next) {
FB.api(
'/me/fido_stream_test:eat',
'POST',
{bug: url},
function(response) {
if (!response || response.error) {
if(_debug) { console.log(response.error); }
if(typeof next === 'function') {
next(true, null);
}
} else {
if(_debug) { console.log('shared'); }
//SUCCESS!
if(typeof next === 'function') {
next(false, response.id);
}
}
}
);
}
###Tiles: Add application to your facebook page To add a facebook app to a facbeook page (Tab, now called a Tile), you need to be an admin of the application and the facebook page. The process to accomplish this used to be a button click, however the process is now a bit convuluted.
Here is the gist of it.
- Add a URL to the facebook tab section when editing your application.
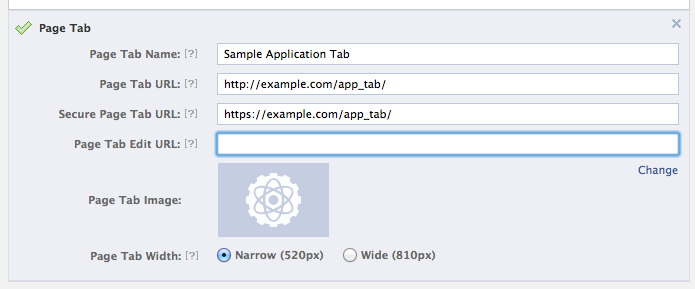
- Use the facebook url
https://www.facebook.com/dialog/pagetab?app_id=YOUR_APP_ID&next=YOUR_URLand replace YOUR_APP_ID with … your application id, and replace YOUR_URL with http://apps.facebook.com/your_namespace. This will ask which facebook page you wish to add your application to. After this, you can head to your page and see your application appear within a Facebook Tile page (Looks better than a canvas app!).
Note: That URL needs to be one that you "own" as part of the app, but it's just a URL to go to after you add the app to your page. It has no effect on your application.
###Server-side code.
Facebook Tile (Tab) pages and Facebook canvas applications both get data POSTed to them - A signed_request POST variable, which can get parsed using Facebook's documentation on the topic. Copy and paste that function to parse it out, or use their SDK to do it for you.
<?php
function parse_signed_request($signed_request, $secret) {
list($encoded_sig, $payload) = explode('.', $signed_request, 2);
// decode the data
$sig = base64_url_decode($encoded_sig);
$data = json_decode(base64_url_decode($payload), true);
if (strtoupper($data['algorithm']) !== 'HMAC-SHA256') {
error_log('Unknown algorithm. Expected HMAC-SHA256');
return null;
}
// check sig
$expected_sig = hash_hmac('sha256', $payload, $secret, $raw = true);
if ($sig !== $expected_sig) {
error_log('Bad Signed JSON signature!');
return null;
}
return $data;
}
function base64_url_decode($input) {
return base64_decode(strtr($input, '-_', '+/'));
}
//Fictitious Usage:
if( isset( $_POST['signed_request'] ) ) {
$data = parse_signed_request($_POST['signed_request'], $my_app_secret);
var_dump($data);
}
Canvas Apps
Canvas apps (Urls in the form of http://apps.facebook.com/your_app_namespace) pass GET data directly to your iframe. A url of http://apps.facebook.com/your_app_namespace?bug=ant will make the "bug" GET variable excessible to your iframe. Easy.
<?php
//Fictitious Example
if( isset( $_GET['bug'] ) ) {
$bug = trim($_GET['bug']);
$bug_object = $this->db->select()->from('bugs')->where('type', $bug);
}
Page Tile/Tabs
Tab pages do NOT get the GET data passed directly. Instead, they allow you to pass data indirectly. You may pass data via the add_data GET parameter, which gets POSTed to your iframe. For instance, a url of http://facebook.com/my_awesome_page?app_data=action:eat,object=bug will pass the string "action:eat,object:bug" as part of the POSTed signed_request, which was explained above.
<?php
function parse_appdata($data='') {
if($data === '') {
return array();
}
//Split by commas
$pairs = explode(',', $data);
if(count($pairs) === 0 || is_array($pairs) === FALSE) {
return array();
}
$return = array();
$temp = FALSE;
//Split by colons
foreach($pairs as $pair) {
$temp = explode(':', $pair);
if(count($temp) !== 2) {
continue;
}
$return[$temp[0]] = $temp[1];
}
return $return;
}
}
//Fictitious Usage:
if( isset( $_POST['signed_request'] ) ) {
$data = parse_signed_request($_POST['signed_request'], $my_app_secret);
//$data === action:eat,object:bug
$parsed_data = parse_appdata($data);
var_dump($data);
/*
$data === array(
'action' => 'eat',
'object' => 'bug'
)
*/
}
License:
Do whatever you want with this.