ex_openai
 ex_openai copied to clipboard
ex_openai copied to clipboard
Auto-generated Elixir SDK for OpenAI APIs with full typespecs, docs and streaming support
Elixir SDK for OpenAI APIs
ExOpenAI is an (unofficial) Elixir SDK for interacting with the OpenAI APIs
This SDK is fully auto-generated using metaprogramming and should always reflect the latest state of the OpenAI API.
Note: Due to the nature of auto-generating something, you may encounter stuff that isn't working yet. Make sure to report if you notice anything acting up.
- Elixir SDK for OpenAI APIs
- Features
- Installation
- Supported endpoints (basically everything)
- Editor features: Autocomplete, specs, docs
- Autocompletion/type-hinting through LSP / ElixirSense
- Typechecking and diagnostics through strict @spec definitions
- Inline docs and signatures thanks to @spec and @doc
- Editor features: Autocomplete, specs, docs
- To Do's / What's not working yet
- Configuration
- Usage
- Using ChatGPT APIs
- Using Assistant APIs
- Usage of endpoints that require files to upload
- File endpoints that require filename information (Audio transcription)
- Usage of Audio related
- Streaming data
- Streaming with a callback function
- Streaming with a separate process
- Caveats
- How to update once OpenAI changes something?
- Some stuff built using this SDK (add yours with a PR!)
- How auto-generation works / how can I extend this?
- License
- Attribution
Features
- Up-to-date and complete thanks to metaprogramming and code-generation
- Implements everything the OpenAI has to offer
- Strictly follows the official OpenAI APIs for argument/function naming
- Handling of required arguments as function parameters and optional arguments as Keyword list in true Elixir-fashion
- Auto-generated embedded function documentation
- Auto-generated @spec definitions for dialyzer, for strict parameter typing
- Support for streaming responses with SSE
Installation
Add :ex_openai as a dependency in your mix.exs file.
def deps do
[
{:ex_openai, "~> 1.6"}
]
end
Supported endpoints (basically everything)
- "/assistants/{assistant_id}"
- "/assistants/{assistant_id}/files/{file_id}"
- "/assistants"
- "/assistants/{assistant_id}/files"
- "/audio/speech"
- "/audio/transcriptions"
- "/audio/translations"
- "/chat/completions"
- "/completions"
- "/edits"
- "/embeddings"
- "/files/{file_id}"
- "/files/{file_id}/content"
- "/files"
- "/fine-tunes/{fine_tune_id}"
- "/fine-tunes/{fine_tune_id}/events"
- "/fine-tunes/{fine_tune_id}/cancel"
- "/fine-tunes"
- "/fine_tuning/jobs"
- "/fine_tuning/jobs/{fine_tuning_job_id}"
- "/fine_tuning/jobs/{fine_tuning_job_id}/events"
- "/fine_tuning/jobs/{fine_tuning_job_id}/cancel"
- "/images/edits"
- "/images/generations"
- "/images/variations"
- "/models/{model}"
- "/models"
- "/moderations"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/messages/{message_id}/files"
- "/threads/{thread_id}"
- "/threads"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs/{run_id}/steps"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/messages/{message_id}/files/{file_id}"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs/{run_id}/submit_tool_outputs"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs/{run_id}/steps/{step_id}"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/messages"
- "/threads/runs"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/messages/{message_id}"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs/{run_id}/cancel"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs"
- "/threads/{thread_id}/runs/{run_id}"
Editor features: Autocomplete, specs, docs
Autocompletion/type-hinting through LSP / ElixirSense

Typechecking and diagnostics through strict @spec definitions

Inline docs and signatures thanks to @spec and @doc

To Do's / What's not working yet
- Streams don't have complete typespecs yet
Configuration
import Config
config :ex_openai,
# find it at https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys
api_key: System.get_env("OPENAI_API_KEY"),
# find it at https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys
organization_key: System.get_env("OPENAI_ORGANIZATION_KEY"),
# optional, other clients allow overriding via the OPENAI_API_URL/OPENAI_API_BASE environment variable,
# if unset the the default is https://api.openai.com/v1
base_url: System.get_env("OPENAI_API_URL"),
# optional, passed to [HTTPoison.Request](https://hexdocs.pm/httpoison/HTTPoison.Request.html) options
http_options: [recv_timeout: 50_000],
# optional, default request headers. The following header is required for Assistant endpoints, which are in beta as of December 2023.
http_headers: [
{"OpenAI-Beta", "assistants=v2"}
],
# optional http client, useful for testing purposes on dependent projects
# if unset the default client is ExOpenAI.Client
http_client: ExOpenAI.Client
You can also pass api_key and organization_key directly by passing them into the opts argument when calling the openai apis:
ExOpenAI.Models.list_models(openai_api_key: "abc", openai_organization_key: "def")
Usage
Make sure to checkout the docs: https://hexdocs.pm/ex_openai
ExOpenAI.Models.list_models
{:ok,
%{
data: [
%{
"created": 1649358449,
"id": "babbage",
"object": "model",
"owned_by": "openai",
"parent": nil,
"permission": [
%{
"allow_create_engine": false,
"allow_fine_tuning": false,
"allow_logprobs": true,
"allow_sampling": true,
"allow_search_indices": false,
"allow_view": true,
"created": 1669085501,
"group": nil,
"id": "modelperm-49FUp5v084tBB49tC4z8LPH5",
"is_blocking": false,
"object": "model_permission",
"organization": "*"
}
],
"root": "babbage"
},
...
Required parameters are converted into function arguments, optional parameters into the opts keyword list:
ExOpenAI.Completions.create_completion "text-davinci-003", "The sky is"
{:ok,
%{
choices: [
%{
"finish_reason": "length",
"index": 0,
"logprobs": nil,
"text": " blue\n\nThe sky is a light blue hue that may have a few white"
}
],
created: 1677929239,
id: "cmpl-6qKKllDPsQRtyJ5oHTbkQVS9w7iKM",
model: "text-davinci-003",
object: "text_completion",
usage: %{
"completion_tokens": 16,
"prompt_tokens": 3,
"total_tokens": 19
}
}}
Using ChatGPT APIs
msgs = [
%ExOpenAI.Components.ChatCompletionRequestUserMessage{role: :user, content: "Hello!"},
%ExOpenAI.Components.ChatCompletionRequestAssistantMessage{role: :assistant, content: "What's up?"},
%ExOpenAI.Components.ChatCompletionRequestUserMessage{role: :user, content: "What ist the color of the sky?"}
]
{:ok, res} =
ExOpenAI.Chat.create_chat_completion(msgs, "gpt-3.5-turbo",
logit_bias: %{
"8043" => -100
}
)
Using Assistant APIs
{:ok, assistant} =
ExOpenAI.Assistants.create_assistant(:"gpt-4o",
name: "Math Teacher",
instruction:
"You are a personal math tutor. Write and run code to answer math questions.",
tools: [%{type: "code_interpreter"}]
)
{:ok, thread} = ExOpenAI.Threads.create_thread()
{:ok, _msg} =
ExOpenAI.Threads.create_message(
thread.id,
"I need to solve the equation `3x + 11 = 14`. Can you help me?",
"user"
)
{:ok, _run} =
ExOpenAI.Threads.create_run(
thread.id,
assistant.id
)
# sleep for 5 seconds
# :timer.sleep(5000)
{:ok, messages} = ExOpenAI.Threads.list_messages(thread.id)
Usage of endpoints that require files to upload
Load your file into memory, then pass it into the file parameter
duck = File.read!("#{__DIR__}/testdata/duck.png")
{:ok, res} = ExOpenAI.Images.create_image_variation(duck)
IO.inspect(res.data)
File endpoints that require filename information (Audio transcription)
Some endpoints (like audio transcription) require the original filename so the API knows what the encoding of something is. You can pass a {filename, bitstring} tuple into anything that requires a file:
audio = File.read!("/Users/david/Downloads/output.wav")
output = ExOpenAI.Audio.create_transcription {"foobar.wav", audio}, "whisper-1"
IO.inspect(output)
{:ok,
%ExOpenAI.Components.CreateTranscriptionResponse{
text: "Hello, hello, hello, just a test."
}}
Usage of Audio related
Streaming data
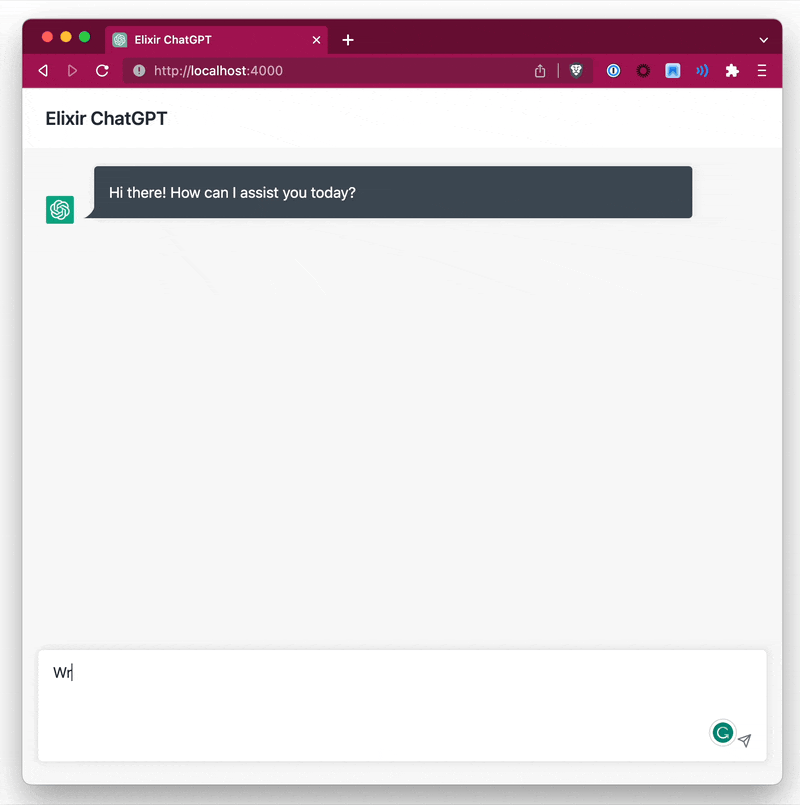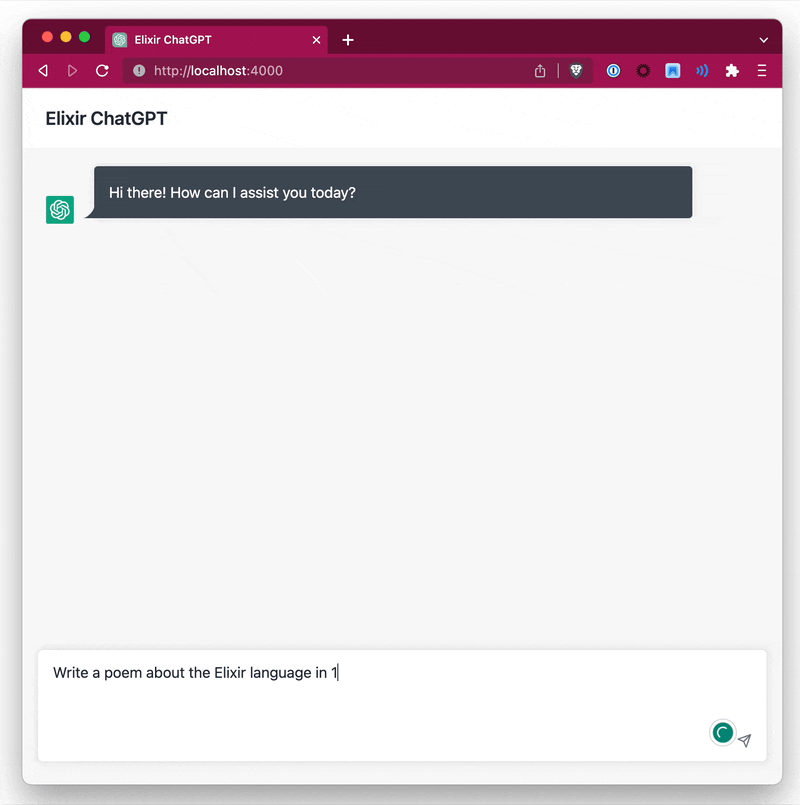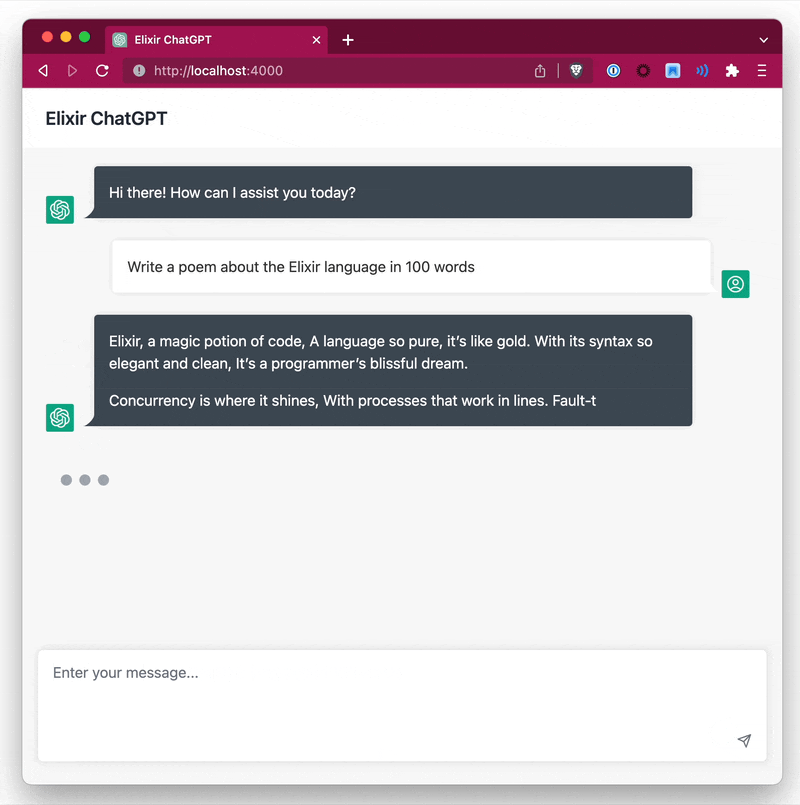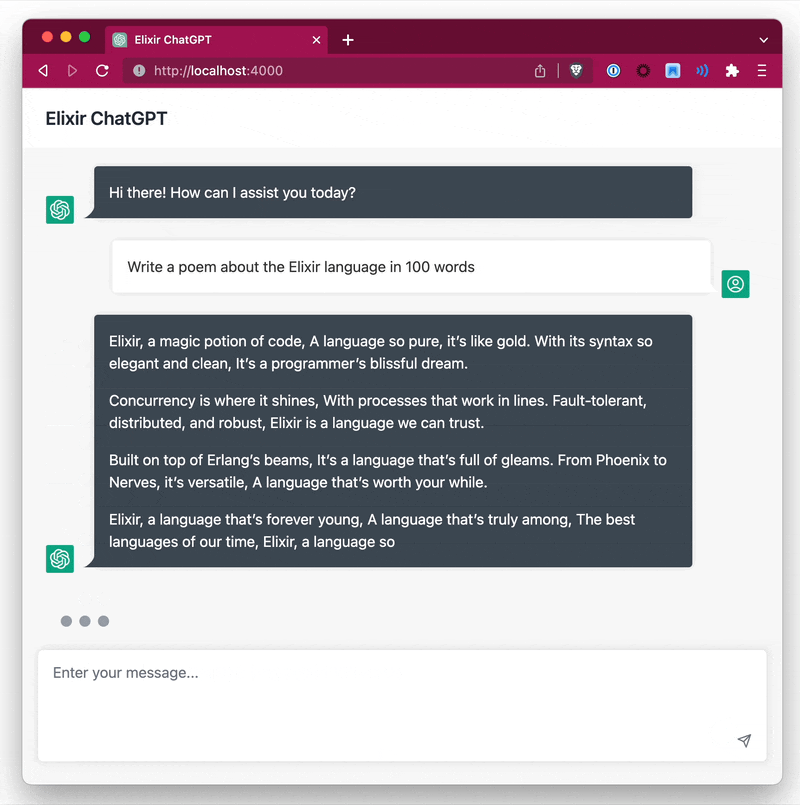
You have 2 options to stream data, either by specifying a callback function or by specifying a separate PID
Streaming with a callback function
Pass a callback function to stream_to when invoking a call and set stream: to true:
callback = fn
:finish -> IO.puts "Done"
{:data, data} -> IO.puts "Data: #{inspect(data)}"
{:error, err} -> IO.puts "Error: #{inspect(err)}"
end
ExOpenAI.Completions.create_completion "text-davinci-003", "hello world", stream: true, stream_to: callback
Streaming with a separate process
Create a new client for receiving the streamed data with use ExOpenAI.StreamingClient. You'll have to implement the @behaviour ExOpenAI.StreamingClient which defines 3 callback functions:
defmodule MyStreamingClient do
use ExOpenAI.StreamingClient
@impl true
# callback on data
def handle_data(data, state) do
IO.puts("got data: #{inspect(data)}")
{:noreply, state}
end
@impl true
# callback on error
def handle_error(e, state) do
IO.puts("got error: #{inspect(e)}")
{:noreply, state}
end
@impl true
# callback on finish
def handle_finish(state) do
IO.puts("finished!!")
{:noreply, state}
end
end
Then use it in requests that support streaming by setting stream: true and specifying stream_to: pid:
{:ok, pid} = MyStreamingClient.start_link nil
ExOpenAI.Completions.create_completion "text-davinci-003", "hello world", stream: true, stream_to: pid
Your client will now receive the streamed chunks
Caveats
- Type information for streamed data is not correct yet. For Completions.create_completion it's fine, however Chat.create_chat_completion requests use a different struct with a
deltafield - Return types for when setting
stream: trueis incorrect, dialyzer may complain
How to update once OpenAI changes something?
Run mix update_openai_docs and commit the new docs.yaml file
Some stuff built using this SDK (add yours with a PR!)
- Elixir ChatGPT
- https://fixmyjp.d.sh
- https://github.com/dvcrn/gpt-slack-bot
- https://david.coffee/mini-chatgpt-in-elixir-and-genserver/
How auto-generation works / how can I extend this?
The code got a little complicated but here is the basic gist of it: codegen.ex is responsible for parsing the docs.yml file into Elixir types. This is then used in ex_openai.ex to generate modules.
The endpoint path is used to generate the group name, for example "/completions" turns into ExOpenAI.Completions.*.
- "parse_component_schema" parses the entire docs.yml file and spits out a bunch of "property" structs that look like this:
ChatCompletionRequestMessage:
type: object
properties:
role:
type: string
enum: ["system", "user", "assistant", "function"]
description: The role of the messages author. One of `system`, `user`, `assistant`, or `function`.
content:
type: string
nullable: true
description: The contents of the message. `content` is required for all messages, and may be null for assistant messages with function calls.
name:
type: string
description: The name of the author of this message. `name` is required if role is `function`, and it should be the name of the function whose response is in the `content`. May contain a-z, A-Z, 0-9, and underscores, with a maximum length of 64 characters.
required:
- role
- content
... turns into:
%{
description: "",
kind: :component, # can be 'oneOf' or 'component'
required_props: [
%{
name: "content",
type: "string",
description: "The contents of the message. `content` is required for all messages, and may be null for assistant messages with function calls.",
example: ""
},
%{
name: "role",
type: {:enum, [:system, :user, :assistant, :function]},
description: "The role of the messages author. One of `system`, `user`, `assistant`, or `function`.",
example: ""
}
],
optional_props: [
%{
name: "name",
type: "string",
description: "The name of the author of this message. `name` is required if role is `function`, and it should be the name of the function whose response is in the `content`. May contain a-z, A-Z, 0-9, and underscores, with a maximum length of 64 characters.",
example: ""
}
]
}
Important point here: "type" is parsed into an elixir representation that we can work with later. For example string -> string, or enum: ["system", "user", "assistant", "function"] -> {:enum, [:system, :user, :assistant, :function]}
- Type gets constructed by calling
parse_typefrom the property parsing. This is a Elixir function with different pattern matching, for example, enum looks like this:
def parse_type(%{"type" => "string", "enum" => enum_entries}),
do: {:enum, Enum.map(enum_entries, &String.to_atom/1)}
- The final type is converted into a Elixir typespec by calling
type_to_spec:
def type_to_spec({:enum, l}) when is_list(l) do
Enum.reduce(l, &{:|, [], [&1, &2]})
end
def type_to_spec("number"), do: quote(do: float())
def type_to_spec("integer"), do: quote(do: integer())
def type_to_spec("boolean"), do: quote(do: boolean())
- All of this is put together in
ex_openai.exto generate the actual modules, the spec is then used to generate documentation.
License
The package is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.
Attribution
- Inspired by https://github.com/BlakeWilliams/Elixir-Slack
- Client/config handling from https://github.com/mgallo/openai.ex


