experimental-lda
 experimental-lda copied to clipboard
experimental-lda copied to clipboard
Single Machine implementation of LDA
Modules
parallelLDAcontains various implementation of multi threaded LDAsingleLDAcontains various implementation of single threaded LDAtopwordsa tool to explore topics learnt by the LDA/HDPperplexitya tool to calculate perplexity on another dataset using word|topic matrixdatagenpackages txt files for our programpreprocessingfor converting from UCI or cLDA to simple txt file having one document per line
Organisation
- All codes are under
srcwithin respective folder - For running Topic Models many template scripts are provided under
scripts datais a placeholder folder where to put the databuildanddistfolder will be created to hold the executables
Requirements
- gcc >= 5.0 or Intel® C++ Compiler 2016 for using C++14 features
- split >= 8.21 (part of GNU coreutils)
How to use
We will show how to run our LDA on an UCI bag of words dataset
-
First of all compile by hitting make
make -
Download example dataset from UCI repository. For this a script has been provided.
scripts/get_data.sh -
Prepare the data for our program
scripts/prepare.sh data/nytimes 1For other datasets replace nytimes with dataset name or location.
-
Run LDA!
scripts/lda_runner.shInside the
lda_runner.shall the parameters e.g. number of topics, hyperparameters of the LDA, number of threads etc. can be specified. By default the outputs are stored underout/. Also you can specify which inference algorithm of LDA you want to run:simpleLDA: Plain vanilla Gibbs sampling by Griffiths04sparseLDA: Sparse LDA of Yao09aliasLDA: Alias LDAFTreeLDA: F++LDA (inspired from Yu14lightLDA: light LDA of Yuan14
The make file has some useful features:
-
if you have Intel® C++ Compiler, then you can instead
make intel -
or if you want to use Intel® C++ Compiler's cross-file optimization (ipo), then hit
make inteltogether -
Also you can selectively compile individual modules by specifying
make <module-name> -
or clean individually by
make clean-<module-name>
Performance
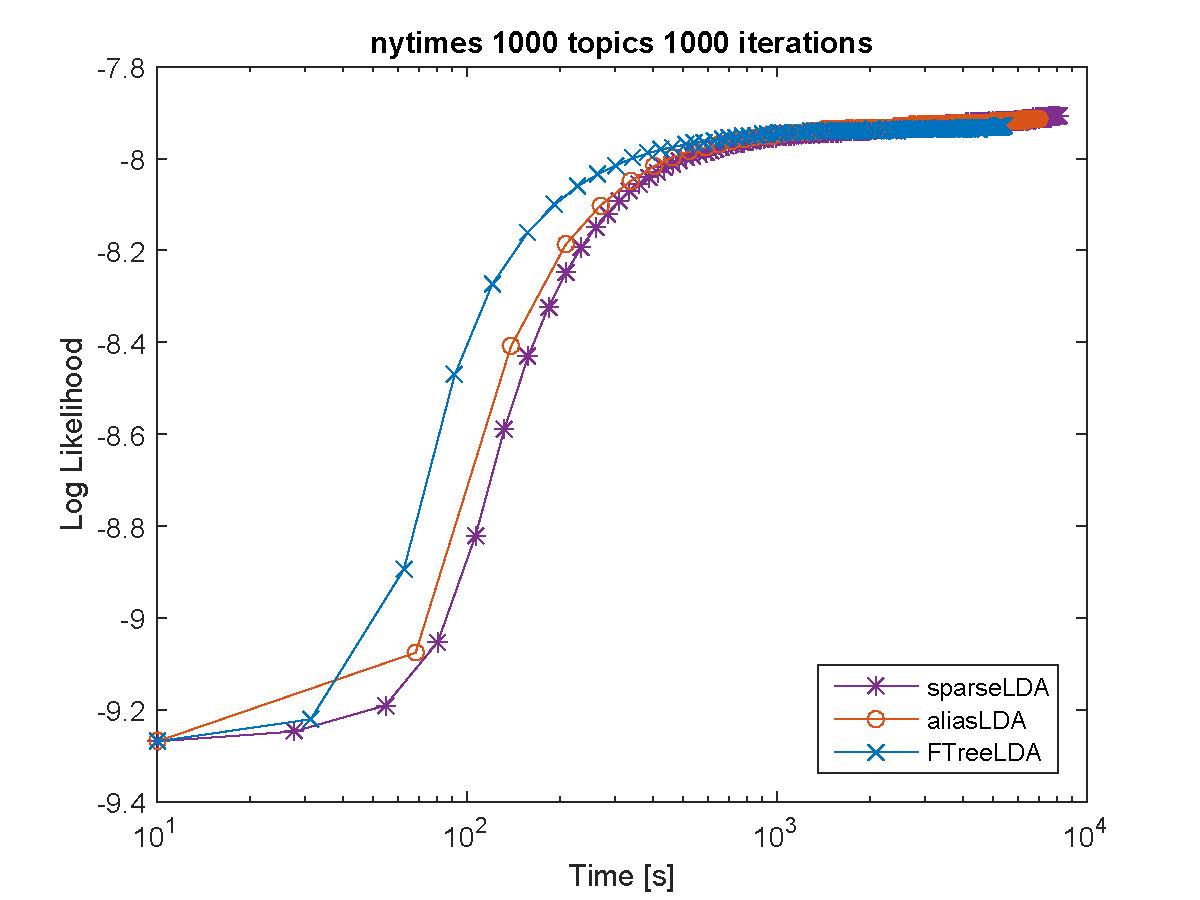
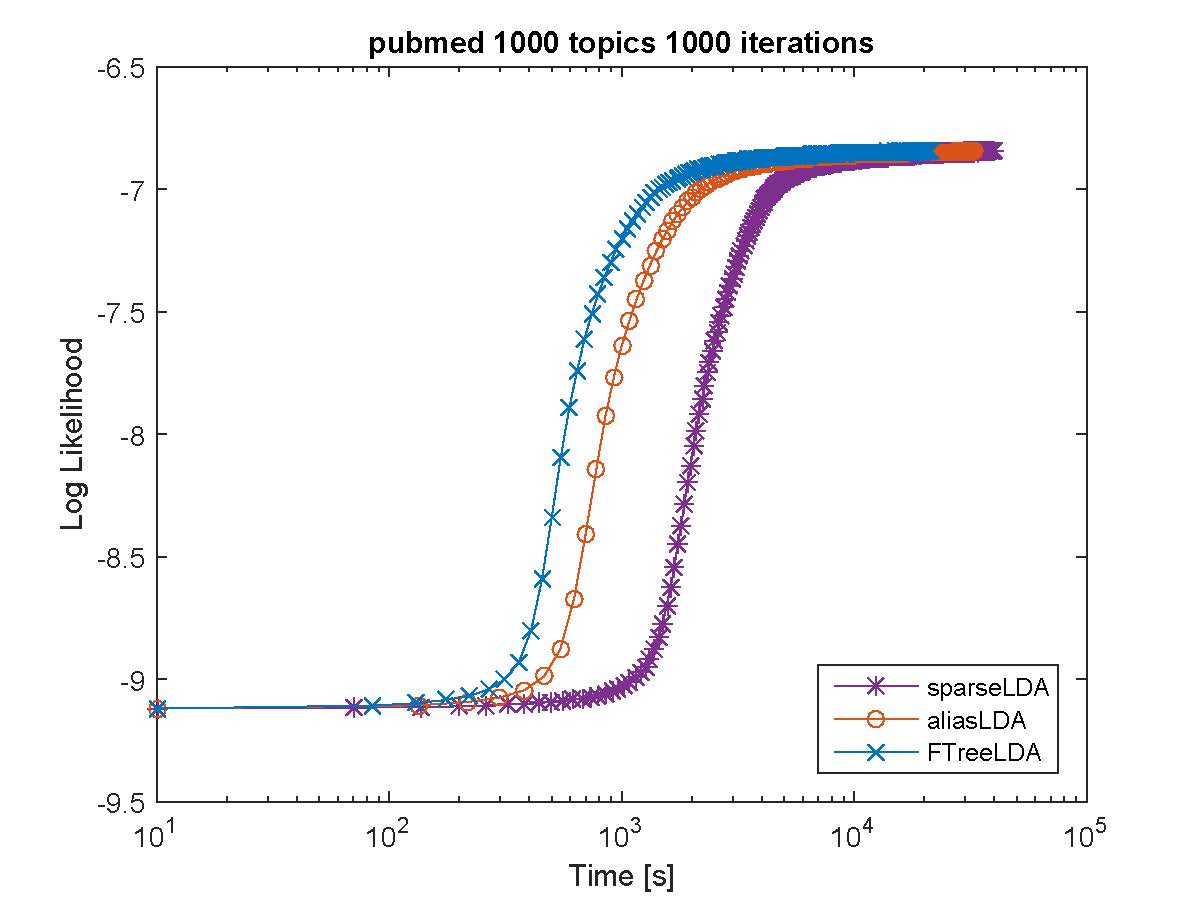
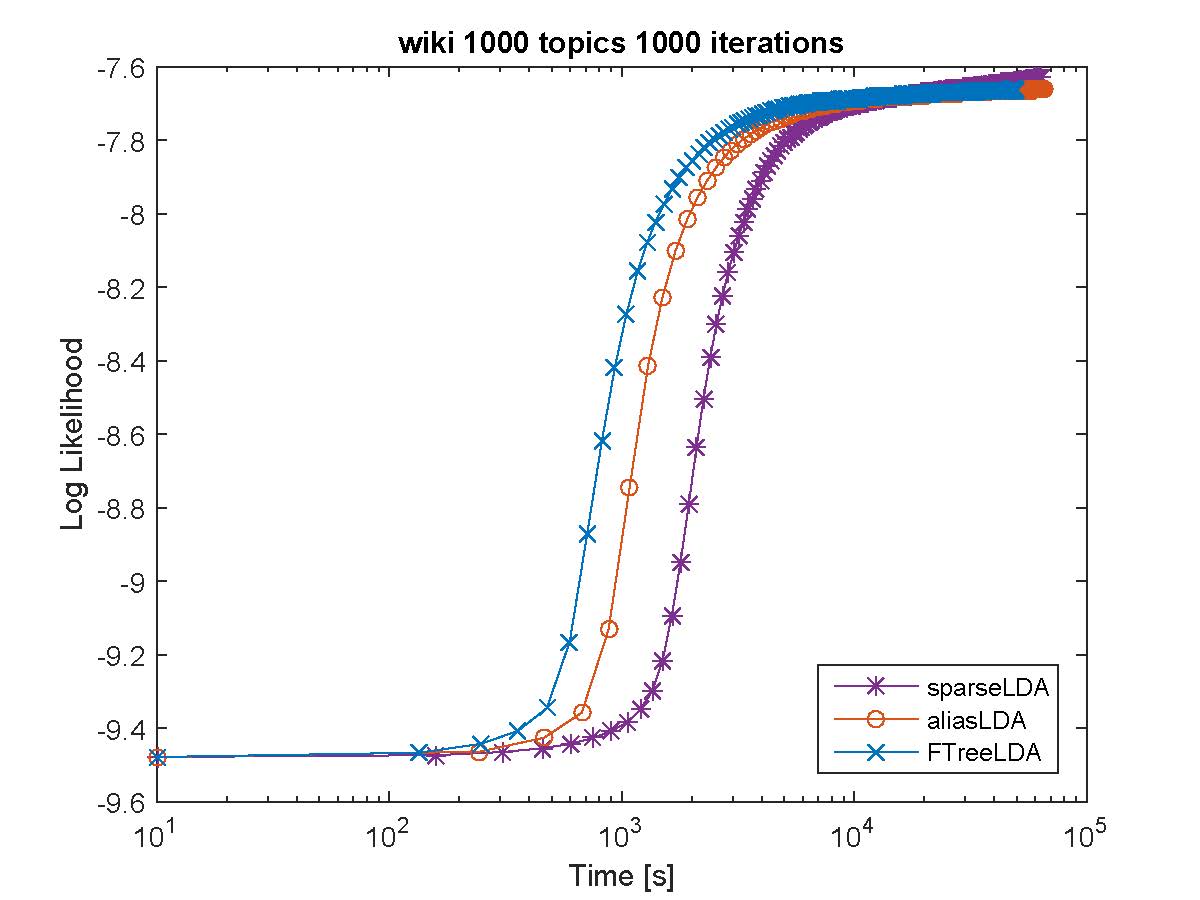
Based on our evaluation F++LDA works the best in terms of both speed and perplexity on a held-out dataset. For example on Amazon EC2 c4.8xlarge, we obtained more than 25 million/tokens per second. Below we provide performance comparison against various inference procedures on publicaly available datasets.
Datasets
| Dataset | V | L | D | L/V | L/D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NY Times | 101,330 | 99,542,127 | 299,753 | 982.36 | 332.08 |
| PubMed | 141,043 | 737,869,085 | 8,200,000 | 5,231.52 | 89.98 |
| Wikipedia | 210,218 | 1,614,349,889 | 3,731,325 | 7,679.41 | 432.65 |
Experimental datasets and their statistics. V denotes vocabulary size, L denotes the number of training tokens, D denotes
the number of documents, L/V indicates the average number of occurrences of a word, L/D indicates the average length of a
document.
log-Perplexity with time