hal
 hal copied to clipboard
hal copied to clipboard
The C#/.NET Core implementation of Hypertext Application Language (HAL) specification.
HAL
The C#/.NET Core implementation of Hypertext Application Language (HAL) specification. This project provides the full support of JSON Hypertext Application Language which is described here.
What is HAL?
According to the official site of HAL, HAL is a simple format that gives a consistent and easy way to hyperlink between resources in a RESTful API.
HAL Specification
The HAL specification documentation can be found here.
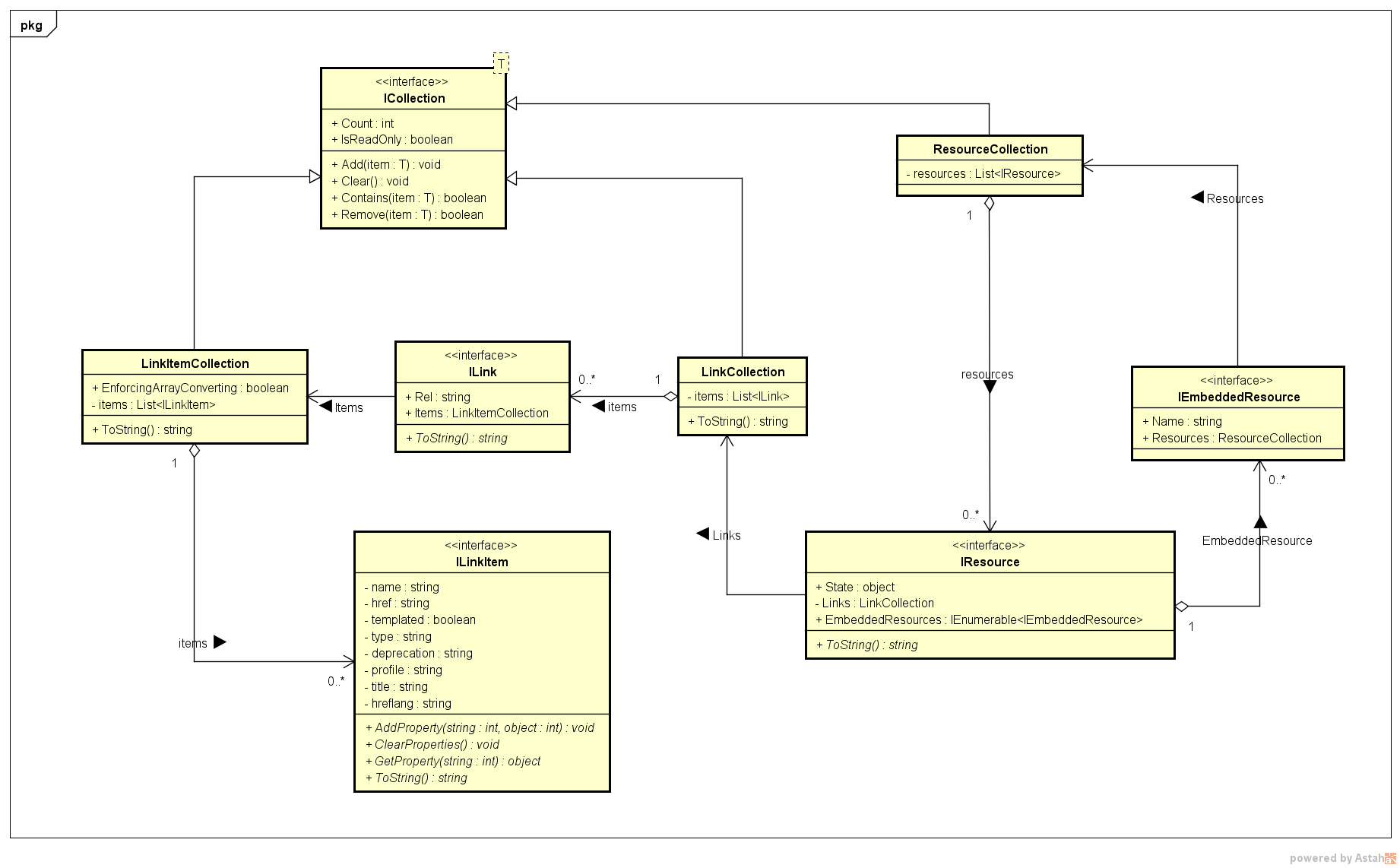
Implementation Model
Following class diagram shows the HAL model that has been implemented by this project.
How to Use
Adding the Package
- Refer to https://www.nuget.org/packages/Hal for the instructions of installing the NuGet package.
Example
The following C# Fluent API code:
var builder = new ResourceBuilder();
var resource = builder
.WithState(new { currentlyProcessing = 14, shippedToday = 20 })
.AddSelfLink().WithLinkItem("/orders")
.AddCuriesLink().WithLinkItem("http://example.com/docs/rels/{rel}", "ea", true)
.AddLink("next").WithLinkItem("/orders?page=2")
.AddLink("ea:find").WithLinkItem("/orders{?id}", templated: true)
.AddEmbedded("ea:order")
.Resource(new ResourceBuilder()
.WithState(new { total = 30.00F, currency = "USD", status = "shipped" })
.AddSelfLink().WithLinkItem("/orders/123")
.AddLink("ea:basket").WithLinkItem("/baskets/98712")
.AddLink("ea:customer").WithLinkItem("/customers/7809"))
.Resource(new ResourceBuilder()
.WithState(new { total = 20.00F, currency = "USD", status = "processing" })
.AddSelfLink().WithLinkItem("/orders/124")
.AddLink("ea:basket").WithLinkItem("/baskets/97213")
.AddLink("ea:customer").WithLinkItem("/customers/12369"))
.Build();
var json = resource.ToString();
Will result in the following HAL JSON:
{
"_links": {
"self": { "href": "/orders" },
"curies": [{ "name": "ea", "href": "http://example.com/docs/rels/{rel}", "templated": true }],
"next": { "href": "/orders?page=2" },
"ea:find": {
"href": "/orders{?id}",
"templated": true
}
},
"currentlyProcessing": 14,
"shippedToday": 20,
"_embedded": {
"ea:order": [{
"_links": {
"self": { "href": "/orders/123" },
"ea:basket": { "href": "/baskets/98712" },
"ea:customer": { "href": "/customers/7809" }
},
"total": 30.00,
"currency": "USD",
"status": "shipped"
}, {
"_links": {
"self": { "href": "/orders/124" },
"ea:basket": { "href": "/baskets/97213" },
"ea:customer": { "href": "/customers/12369" }
},
"total": 20.00,
"currency": "USD",
"status": "processing"
}]
}
}
Or you can use the object model below instead of the Fluent API to generate the same result:
var links = new LinkCollection
{
new Link("self") { Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/orders") } },
new Link("curies") { Items = new LinkItemCollection(true)
{
new LinkItem("http://example.com/docs/rels/{rel}") { Name = "ea", Templated = true }
}
},
new Link("next") { Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/orders?page=2") } },
new Link("ea:find")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/orders{?id}") { Templated = true } }
}
};
var embedded = new EmbeddedResource
{
Name = "ea:order",
Resources = new ResourceCollection
{
new Resource(new { total = 30.00F, currency = "USD", status = "shipped" })
{
Links = new LinkCollection
{
new Link("self")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/orders/123") }
},
new Link("ea:basket")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/baskets/98712") }
},
new Link("ea:customer")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/customers/7809") }
},
}
},
new Resource(new { total = 20.00F, currency = "USD", status = "processing" })
{
Links = new LinkCollection
{
new Link("self")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/orders/124") }
},
new Link("ea:basket")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/baskets/97213") }
},
new Link("ea:customer")
{
Items = new LinkItemCollection { new LinkItem("/customers/12369") }
},
}
}
}
};
var resource = new Resource(new { currentlyProcessing = 14, shippedToday = 20 })
{
Links = links,
EmbeddedResources = new EmbeddedResourceCollection { embedded }
};
var hal = resource.ToString();
ASP.NET Core Integration
HAL supports ASP.NET Core integration, which allows the application/hal+json content type to be returned by your API server.
To add HAL support to your ASP.NET Core application, firstly add the Hal.AspNetCoreIntegration NuGet package:
dotnet add package Hal.AspNetCoreIntegration
And decorate your controller with the SupportsHalAttribute attribute:
[ServiceFilter(typeof(SupportsHalAttribute))]
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
// ...
}
Then modify the Program.cs to add HAL support:
builder.Services.AddHalSupport();
builder.Services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.All;
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
});
The AddHalSupport method has three overloads:
-
Parameterless one: It enables the HAL by default and assumes that the name of the identifier property on your entity object is
Id. -
With
Action<SupportsHalOptions>parameter: It enables you to configure the HAL framework when it is integrated with your ASP.NET Core application. For example, suppose the name of the identifier property on your entity object is notIdbutID:
You will need to set the name of the id property topublic class MeetingRoom { public int ID { get; set; } // <-- This is the identifier property public string Name { get; set; } = string.Empty; public int Seats { get; set; } }IDin the options object, e.g.:builder.Services.AddHalSupport(options => { options.IdPropertyName = "ID"; }); -
With
IConfigurationSectionparameter: It also enables you to configure the HAL framework but this time it reads configuration from environment variables orappsettings.jsonfile:
Then you should use:"hal": { "enabled": true, "idPropertyName": "ID" }builder.Services.AddHalSupport(builder.Configuration.GetSection("hal"));
About the self Link of Each Object in an Enumeration Result
It is likely that an ASP.NET Core Web API controller would return a list of objects by some actions, for example:
[HttpGet("get-by-name/{name}")]
[ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status200OK)]
[ProducesResponseType(StatusCodes.Status404NotFound)]
public IActionResult GetByName(string name)
=> MeetingRoom.FakeRooms.Any(mr => mr.Name == name)
?
Ok(MeetingRoom.FakeRooms.Where(mr => mr.Name == name))
:
NotFound($"Meeting Room {name} not found.");
In the above example, the GetByName method will return all meeting rooms whose name equals to a given name. As a result, this API will return a list of objects. If HAL is enabled on this API, the response payload would look like this:
{
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:5139/api/MeetingRooms/get-by-name/Mars"
}
},
"count": 1,
"_embedded": {
"meetingRooms": [
{
"id": 4,
"name": "Mars",
"seats": 14,
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:5139/api/MeetingRooms/4"
}
}
}
]
}
}
Note that for each of the object in the meetingRooms array, it has the self link that points to the location of the current resource. By default, this location URL is calculated based on the following mechanism:
- Find the API controller instance of the current API call
- Find the only one method that matches the following criterias:
- The return type is either
IActionResultorTask<IActionResult> - There is only one parameter, and the type of the parameter is the same as the type of the ID property of the object
- The return type is either
- If there is only one method that has been found, use this method as the controller action to calculate the
selflink of the current object - If no method found, simply use the
selflink of the current API response payload as theselflink of each of the object (e.g.http://localhost:5139/api/MeetingRooms/get-by-name/Marsin the above case) - If multiple methods found, then try to locate the only one method that has been decorated with the
GetByIdMethodImplAttributeattribute, and use this method as the controller action to calculate theselflink of the current object - If no or still multiple methods found, simply use the
selflink of the current API response payload as theselflink of each of the object (e.g.http://localhost:5139/api/MeetingRooms/get-by-name/Marsin the above case)
You can try running the example in this code repo to understand how the above mechanism works.
HTTP or HTTPS
Usually, if the service is deployed in production (IWebHostEnvironment.IsProduction() returns true), the scheme of the generated self.href link will be https, otherwise, it will follow the original scheme of the request. However, you are able to override the scheme by using the useHttpsScheme option, e.g.:
"hal": {
"enabled": true,
"useHttpsScheme": false
}
In such case, the http will be the scheme. This is to fix the incorrect scheme issue that occurs when the service is deployed behind a reversed proxy like nginx or ALB deployed under HTTPS but the service itself listens to the insecure HTTP port.
Integrate with nginx Reverse Proxy
The application that is expected to be deployed behind an nginx reverse proxy should have the X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Proto, X-Forwarded-Host and X-Forwarded-Port forwarded when the HAL is enabled. Following is an example of the nginx.conf file:
events {
worker_connections 512;
}
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://hal-example:80;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection keep-alive;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $server_port;
}
}
}
Running the Out-of-the-Box Example
To debug the out-of-the-box example, in Visual Studio 2022, open hal.sln solution and set the Hal.Example project as the default startup project, then hit F5 to debug.
To learn how to build with docker and run the docker container behind the nginx proxy, use the following commands to build and run:
$ cd docker
$ docker-compose -f docker-compose.build.yaml build
$ docker-compose up
Once all containers are up and running, navigate to the following swagger page of the application to test:
http://localhost:8088/swagger/index.html