Arebis.Logging.GrayLog
 Arebis.Logging.GrayLog copied to clipboard
Arebis.Logging.GrayLog copied to clipboard
.NET GrayLog client library written in C#
Arebis.Logging.GrayLog
.NET GrayLog client library written in C#
Arebis.Logging.GrayLog is now part of the Arebis.Common repository.
Features and Limitations
The Arebis GrayLog library is a simple library to write logging records to GrayLog using the UDP protocol. The implementation sends messages by GZIP compressing them, and chuncking them if needed, according to the specifications of the Graylog Extended Log Format (GELF).
NuGet package: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Arebis.Logging.GrayLog/
Source code and documentation: https://github.com/codetuner/Arebis.Logging.GrayLog
GELF specifications: http://docs.graylog.org/en/latest/pages/gelf.html
Sample Usage
A simple "Hello World" logging application can be created as follows:
Create a project and add the NuGet package "Arebis.Logging.GrayLog" to your project.
Then use the following code to write a "Hello World !" log message:
using (var logger = new GrayLogUdpClient())
{
logger.Send("Hello World !");
}
This results in the following logging:
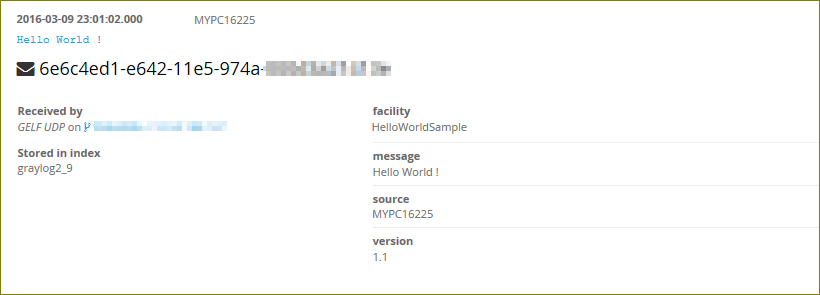
The Send() method has the following signature:
public void Send(string shortMessage, string fullMessage = null, object data = null)
The data argument can be a string, a dictionary (System.Collections.IDictionary) an enumerable (System.Collections.IEnumerable), or an object of which the properties will be sent.
A more complete example:
using (var logger = new GrayLogUdpClient())
{
logger.Send("Hello", "Welcome John", new { Username = "John", Email = "[email protected]" });
}
Which results in the following logging:
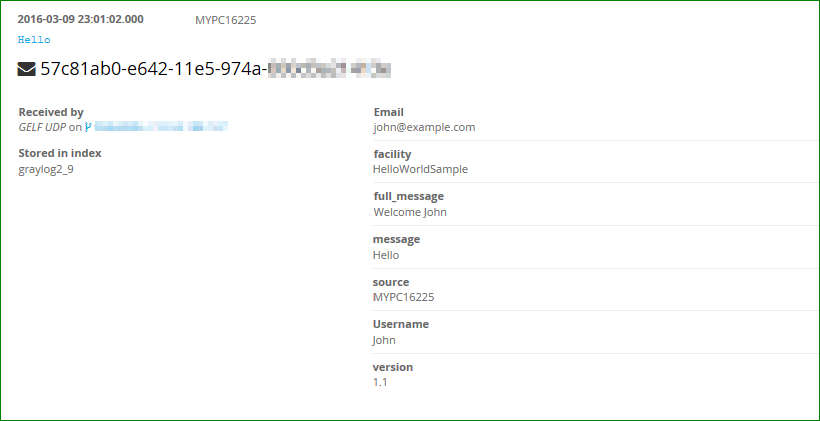
There is also a convenience method to send Exception objects:
using (var logger = new GrayLogUdpClient())
{
try
{
// Example of a thrown exception:
throw new ApplicationException("Something went wrong.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Optionally add additional data to the exception's Data collection:
ex.Data.Add("context", "Attempt to send an email.");
ex.Data.Add("level", SyslogLevel.Error);
// Log the exception:
logger.Send(ex);
}
}
Which results in the following logging:
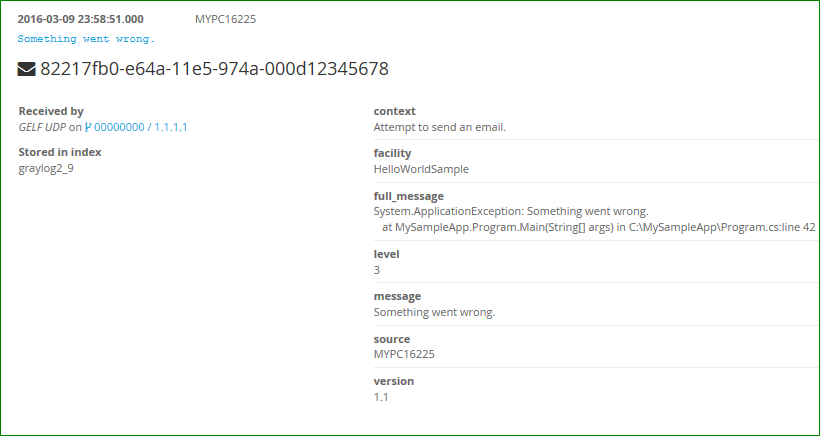
These samples assume you have configured your GrayLog connection data into the App.config or Web.config. You need at least following AppSetting keys:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="GrayLogFacility" value="HelloWorldSample"/>
<add key="GrayLogHost" value="localhost"/>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
The GrayLogFacility setting specifies the facility argument to set for all messages. The GrayLogHost is the server name of your GrayLog instance. You can also specify the GrayLogUdpPort setting if you want to override the default port number 12201.
Additionally, you can set a compression treshold with the AppSetting key GrayLogCompressionTreshold. By default this value is 0 and means compression is always enabled. Setting this value to i.e. 500 would mean to apply compression only when message body is more than 500 bytes. A value of -1 disables compression completely.
For further usage details and manual, check the project's WIKI page.