AngularJS-translation
 AngularJS-translation copied to clipboard
AngularJS-translation copied to clipboard
AngularJS - Conceptual Overview
原文地址 AngularJS - Conceptual Overview
本文简介Angular的主要组件和其工作原理:
启动阶段
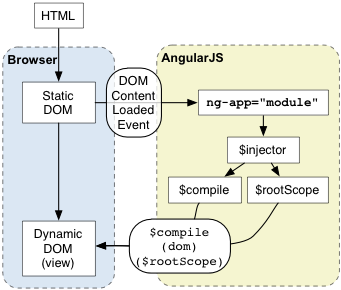
(以下面的Hello World为例)
- 浏览器加载HTML,解析之,建立DOM
- 浏览器加载angular.js
- Angular等待 DOMContentLoaded事件触发
- Angular查找定义了程序边界的ng-app指令
- 用ng-app中指定的模块配置$injector
- 用$injector配置$compile服务和$rootScope
- 用$compile服务编译DOM并与$rootScope建立关系
- ng-init指令设置scope的name属性为'World'
- {{name}}被替换为name属性的值,形成'Hello World!'
<!doctype html>
<html ng-app>
<head>
<script src="http://code.angularjs.org/1.0.6/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p ng-init=" name='World' ">Hello {{name}}!</p>
</body>
</html>
Hello World!
运行时
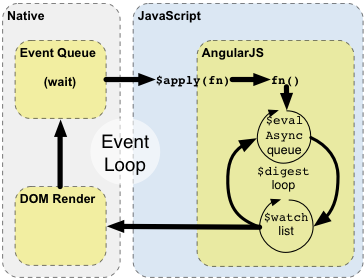
上面的图片和下面的实例解释了Angular与浏览器事件循环如何相互作用、影响
- 浏览器事件循环等待事件到达。一个事件可以是用户交互、定时器事件、网络事件(服务器响应)
- 事件对应的回调函数被(一个个)执行。(执行时)进入JavaScript作用范围。在回调函数中可以修改DOM结构
- 一旦回调函数被执行,浏览器离开JavaScript作用范围,根据DOM发生的变化,重新渲染视图。
通过提供自己的事件处理循环,Angular修改了正常的JavaScript执行过程。这个修改将JavaScript执行分为传统JavaScript执行环境和Angular执行环境。只有在后者执行的代码才能享用Angular的数据绑定,异常处理,属性监控,等等(服务)。你可以在正常JavaScript执行环境中用**$apply函数进入到Angular执行环境。不过请记住,在大多数地方(控制器,服务)$apply**已经为你的处理事件的(Angular)指令调用。只有在实现自定义的事件回调函数或第三方类库的回调函数中才需要显式调用_$apply_。
Enter Angular execution context by calling scope.$apply(stimulusFn). Where stimulusFn is the work you wish to do in Angular execution context. Angular executes the stimulusFn(), which typically modifies application state. Angular enters the $digest loop. The loop is made up of two smaller loops which process $evalAsync queue and the $watch list. The $digest loop keeps iterating until the model stabilizes, which means that the $evalAsync queue is empty and the $watch list does not detect any changes. The $evalAsync queue is used to schedule work which needs to occur outside of current stack frame, but before the browser's view render. This is usually done with setTimeout(0), but the setTimeout(0) approach suffers from slowness and may cause view flickering since the browser renders the view after each event. The $watch list is a set of expressions which may have changed since last iteration. If a change is detected then the $watch function is called which typically updates the DOM with the new value. Once the Angular $digest loop finishes the execution leaves the Angular and JavaScript context. This is followed by the browser re-rendering the DOM to reflect any changes.
[to be continue...]