django-dynamic-admin
 django-dynamic-admin copied to clipboard
django-dynamic-admin copied to clipboard
Enable interactive selects in django-admin
Add simple interactions to the otherwise static django admin.
- PyPI
- GitHub
- Full documentation
- Creator & Maintainer: Ambient Digital
django-dynamic-admin-forms
Add simple interactions to the otherwise static django admin.
Installation
-
Install the package via pip:
pip install django-dynamic-admin-formsor via pipenv:
pipenv install django-dynamic-admin-forms -
Add the module to
INSTALLED_APPS:INSTALLED_APPS = ( "django_dynamic_admin_forms", "django.contrib.admin", )Ensure that the
dynamic_admin_formscomes before the defaultdjango.contrib.adminin the list of installed apps, because otherwise the templates, which are overwritten bydynamic_admin_formswon't be found. -
Ensure that the
dynamic_admin_formstemplates are found via usingAPP_DIRSsetting:TEMPLATES = [ { "BACKEND": "django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates", "APP_DIRS": True, }, ] -
Run
python manage.py collectstaticto include this apps Javascript code in yoursettings.STATIC_ROOTdirectory
Usage
-
Add the
django_dynamic_admin_forms.DynamicModelAdminMixinto your admin classes -
Add the
django_dynamic_admin_forms.urlsto your urlsfrom django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path, include urlpatterns = [ path("admin/", admin.site.urls), path("dynamic-admin-form/", include("django_dynamic_admin_forms.urls")), ] -
In addition to the standard
fieldsdeclaration, specify a list ofdynamic_fields -
For each dynamic field, add a method
get_dynamic_{field_name}_fieldto the admin- Input:
data: Dict[str, Any]- the cleaned form data - Output:
queryset: Optional[Queryset]- The values to select fromvalue: Any- The value, the field should have (must be compatible to the field type)hidden: Bool- True, if field should be hidden
- Input:
-
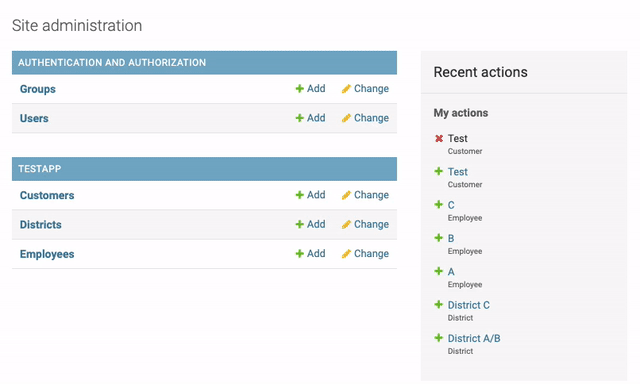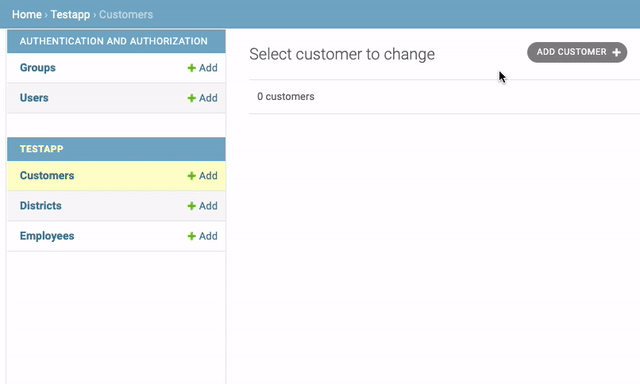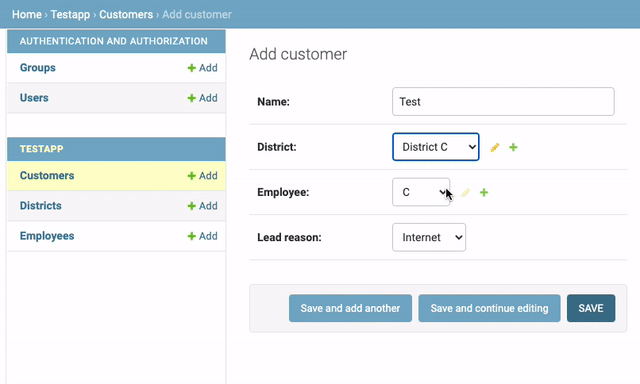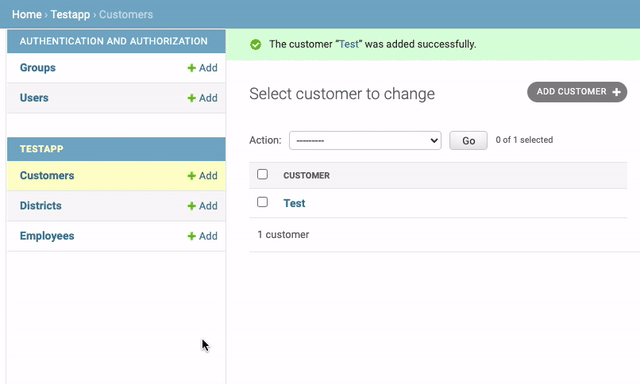
A rather non-sensical example:
from django.contrib import admin from .models import MyModel from django_dynamic_admin_forms.admin import DynamicModelAdminMixin @admin.register(MyModel) class MyModelAdmin(DynamicModelAdminMixin, admin.ModelAdmin): fields = ("name", "city") dynamic_fields = ("city",) def get_dynamic_city_field(self, data): # automatically choose first city that matches first letter of name name = data.get("name") if not name: queryset = City.objects.all() value = data.get("city") else: queryset = City.objects.filter(name__startswith=name[0]) value = queryset.first() hidden = not queryset.exists() return queryset, value, hidden
How it works
Whenever a dynamic form changes, an event handler makes a request to a special endpoint, which returns new HTML to swap
into the existing form. This new HTML is directly generated by django.contrib.admin, so we only have to set the
outerHTML of the correct HTML elements to update the form.
Limitations
- does not work in conjunction with inlines
- does not validate that the selected value is really part of the original queryset
- if anybody can modify your DOM, they could potentially inject invalid values
- you have to write
Model.clean()methods to guard against that
- only tested with Django 3.2
Development
For local development, create a virtual environment
in the testproj folder:
$ cd testproj
$ python3 -m venv .venv
$ source .venv/bin/activate
$ cd ..
$ flit install --symlink
Now the package should be available in your virtual environment and any changes should be directly visible.
Alternatively, copy the directory dynamic_admin_forms
into any normal django project, so that the python interpreter
finds the local version instead of the installed (old) version.
Running E2E tests
To run end-to-end tests locally:
$ cd testproj
$ python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 & # start server
$ python manage.py loaddata fixtures/fixtures-dev.json
$ cd ../e2e
$ yarn install # or npm install (only needed first time)
$ yarn cypress # or npm run cypress
Installation
-
Install the package via pip:
pip install django-dynamic-admin-formsor via pipenv:
pipenv install django-dynamic-admin-forms -
Add the module to
INSTALLED_APPS:INSTALLED_APPS = ( "django_dynamic_admin_forms", "django.contrib.admin", )Ensure that the
dynamic_admin_formscomes before the defaultdjango.contrib.adminin the list of installed apps, because otherwise the templates, which are overwritten bydynamic_admin_formswon't be found. -
Ensure that the
dynamic_admin_formstemplates are found via usingAPP_DIRSsetting:TEMPLATES = [ { "BACKEND": "django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates", "APP_DIRS": True, }, ] -
Run
python manage.py collectstaticto include this apps Javascript code in yoursettings.STATIC_ROOTdirectory
Contribute
Setup package for development
- Create a Python virtualenv and activate it
- Install "pip-tools" with
pip install -U pip-tools - Compile the requirements with
pip-compile --extra dev, -o requirements.txt pyproject.toml --resolver=backtracking - Sync the dependencies with your virtualenv with
pip-sync
Add functionality
- Create a new branch for your feature
- Change the dependency in your requirements.txt to a local (editable) one that points to your local file system:
-e /Users/workspace/django-dynamic-admin-formsor via pippip install -e /Users/workspace/django-dynamic-admin-forms - Ensure the code passes the tests
- Create a pull request
Run tests
-
Run tests
pytest --ds settings tests -
Check coverage
coverage run -m pytest --ds settings tests coverage report -m
Git hooks (via pre-commit)
We use pre-push hooks to ensure that only linted code reaches our remote repository and pipelines aren't triggered in vain.
To enable the configured pre-push hooks, you need to install pre-commit and run once:
pre-commit install -t pre-push -t pre-commit --install-hooks
This will permanently install the git hooks for both, frontend and backend, in your local
.git/hooks folder.
The hooks are configured in the .pre-commit-config.yaml.
You can check whether hooks work as intended using the run command:
pre-commit run [hook-id] [options]
Example: run single hook
pre-commit run ruff --all-files --hook-stage push
Example: run all hooks of pre-push stage
pre-commit run --all-files --hook-stage push
Update documentation
- To build the documentation run:
sphinx-build docs/ docs/_build/html/. - Open
docs/_build/html/index.htmlto see the documentation.
Translation files
If you have added custom text, make sure to wrap it in _() where _ is
gettext_lazy (from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _).
How to create translation file:
- Navigate to
django-dynamic-admin-forms python manage.py makemessages -l de- Have a look at the new/changed files within
django_dynamic_admin_forms/locale
How to compile translation files:
- Navigate to
django-dynamic-admin-forms python manage.py compilemessages- Have a look at the new/changed files within
django_dynamic_admin_forms/locale
Publish to ReadTheDocs.io
- Fetch the latest changes in GitHub mirror and push them
- Trigger new build at ReadTheDocs.io (follow instructions in admin panel at RTD) if the GitHub webhook is not yet set up.
Publish to PyPi
-
Update documentation about new/changed functionality
-
Update the
Changelog -
Increment version in main
__init__.py -
Create pull request / merge to master
-
This project uses the flit package to publish to PyPI. Thus publishing should be as easy as running:
flit publishTo publish to TestPyPI use the following ensure that you have set up your .pypirc as shown here and use the following command:
flit publish --repository testpypi
Maintenance
Please note that this package supports the ambient-package-update.
So you don't have to worry about the maintenance of this package. All important configuration and setup files are
being rendered by this updater. It works similar to well-known updaters like pyupgrade or django-upgrade.
To run an update, refer to the documentation page of the "ambient-package-update".