PyGrinder
 PyGrinder copied to clipboard
PyGrinder copied to clipboard
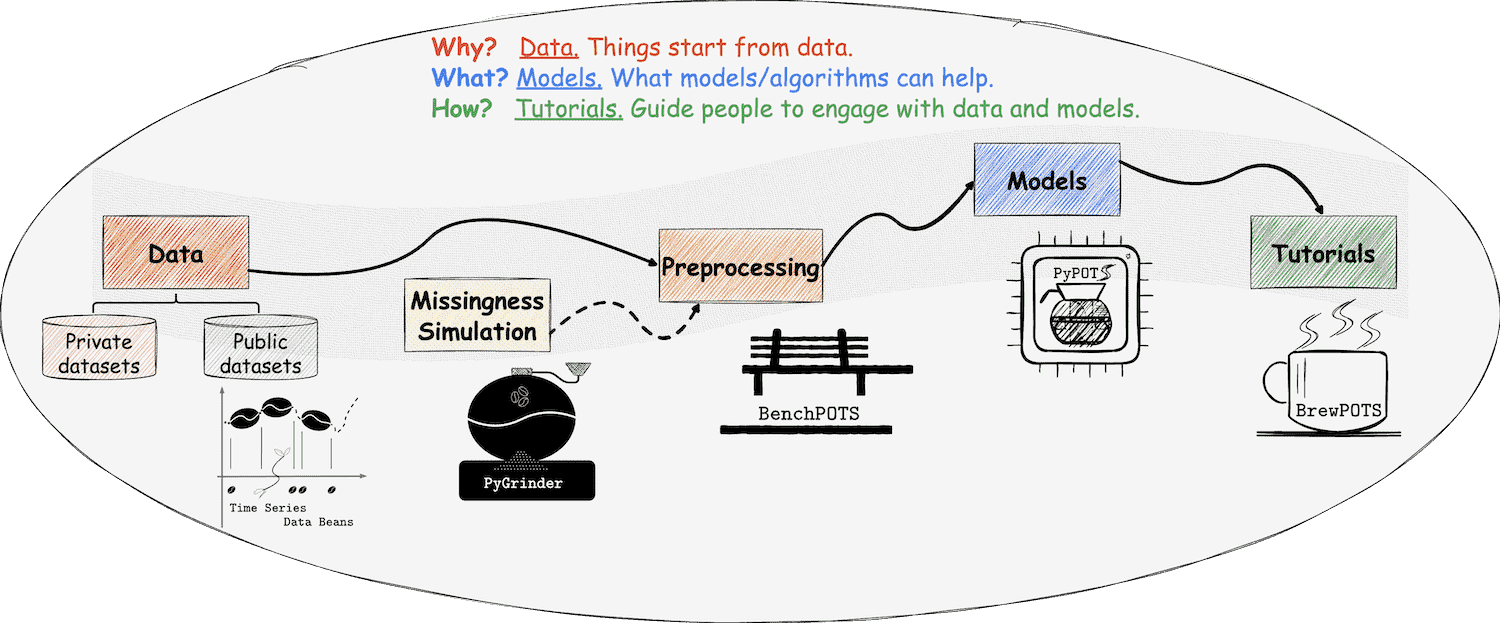
PyGrinder grinds data beans into the incomplete by introducing missing values with different missing patterns.
Welcome to PyGrinder
a Python toolkit for grinding data beans into the incomplete
PyGrinder is a part of
PyPOTS

In data analysis and modeling, sometimes we may need to corrupt the original data to achieve our goal, for instance, evaluating models' ability to reconstruct corrupted data or assessing the model's performance on only partially-observed data. PyGrinder is such a tool to help you corrupt your data, which provides several patterns to create missing values in the given data.
❖ Usage Examples
PyGrinder now is available on 
Install it with conda install pygrinder, you may need to specify the channel with option -c conda-forge
or install via PyPI:
pip install pygrinder
or install from source code:
pip install
https://github.com/WenjieDu/PyGrinder/archive/main.zip
import numpy as np
from pygrinder import (
mcar,
mar_logistic,
mnar_x,
mnar_t,
rdo,
seq_missing,
block_missing,
calc_missing_rate
)
# given a time-series dataset with 128 samples, each sample with 10 time steps and 36 data features
ts_dataset = np.random.randn(128, 10, 36)
# grind the dataset with MCAR pattern, 10% missing probability, and using 0 to fill missing values
X_with_mcar_data = mcar(ts_dataset, p=0.1)
# grind the dataset with MAR pattern
X_with_mar_data = mar_logistic(ts_dataset[:, 0, :], obs_rate=0.1, missing_rate=0.1)
# grind the dataset with MNAR pattern
X_with_mnar_x_data = mnar_x(ts_dataset, offset=0.1)
X_with_mnar_t_data = mnar_t(ts_dataset, cycle=20, pos=10, scale=3)
# grind the dataset with RDO pattern
X_with_rdo_data = rdo(ts_dataset, p=0.1)
# grind the dataset with Sequence-Missing pattern
X_with_seq_missing_data = seq_missing(ts_dataset, p=0.1, seq_len=5)
# grind the dataset with Block-Missing pattern
X_with_block_missing_data = block_missing(ts_dataset, factor=0.1, block_width=3, block_len=3)
# calculate the missing rate of the dataset
missing_rate = calc_missing_rate(X_with_mcar_data)
❖ Citing PyGrinder/PyPOTS
The paper introducing PyPOTS is available on arXiv, A short version of it is accepted by the 9th SIGKDD international workshop on Mining and Learning from Time Series (MiLeTS'23)). Additionally, PyPOTS has been included as a PyTorch Ecosystem project. We are pursuing to publish it in prestigious academic venues, e.g. JMLR (track for Machine Learning Open Source Software). If you use PyPOTS in your work, please cite it as below and 🌟star this repository to make others notice this library. 🤗
There are scientific research projects using PyPOTS and referencing in their papers. Here is an incomplete list of them.
@article{du2023pypots,
title={{PyPOTS: a Python toolbox for data mining on Partially-Observed Time Series}},
author={Wenjie Du},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18811},
year={2023},
}
or
Wenjie Du. PyPOTS: a Python toolbox for data mining on Partially-Observed Time Series. arXiv, abs/2305.18811, 2023.