fe_interview
 fe_interview copied to clipboard
fe_interview copied to clipboard
谈谈你对 Vue 生命周期的理解?
回答这个问题,我们先要概括的回答一下Vue生命周期是什么:
Vue 实例有一个完整的生命周期,也就是从开始创建、初始化数据、编译模版、挂载 Dom -> 渲染、更新 -> 渲染、卸载等一系列过程,我们称这是 Vue 的生命周期。
下面的表格展示了每个生命周期分别在什么时候被调用:
| 生命周期 | 描述 |
|---|---|
beforeCreate |
在实例初始化之后,数据观测(data observer) 之前被调用。 |
created |
实例已经创建完成之后被调用。在这一步,实例已完成以下的配置:数据观测(data observer),属性和方法的运算, watch/event 事件回调。但真实 dom 还没有生成,$el 还不可用 |
beforeMount |
在挂载开始之前被调用,相关的 render 函数首次被调用。 |
mounted |
el 被新创建的 vm.$el 替换,并挂载到实例上去之后调用该钩子。 |
beforeUpdate |
数据更新时调用,发生在虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁之前。 |
updated |
由于数据更改导致的虚拟 DOM 重新渲染和打补丁,在这之后会调用该钩子。 |
activited |
keep-alive 专属,组件被激活时调用 |
deactivated |
keep-alive 专属,组件被销毁时调用 |
beforeDestory |
实例销毁之前调用。在这一步,实例仍然完全可用。 |
destoryed |
Vue 实例销毁后调用。 |
这里放上官网的生命周期流程图:
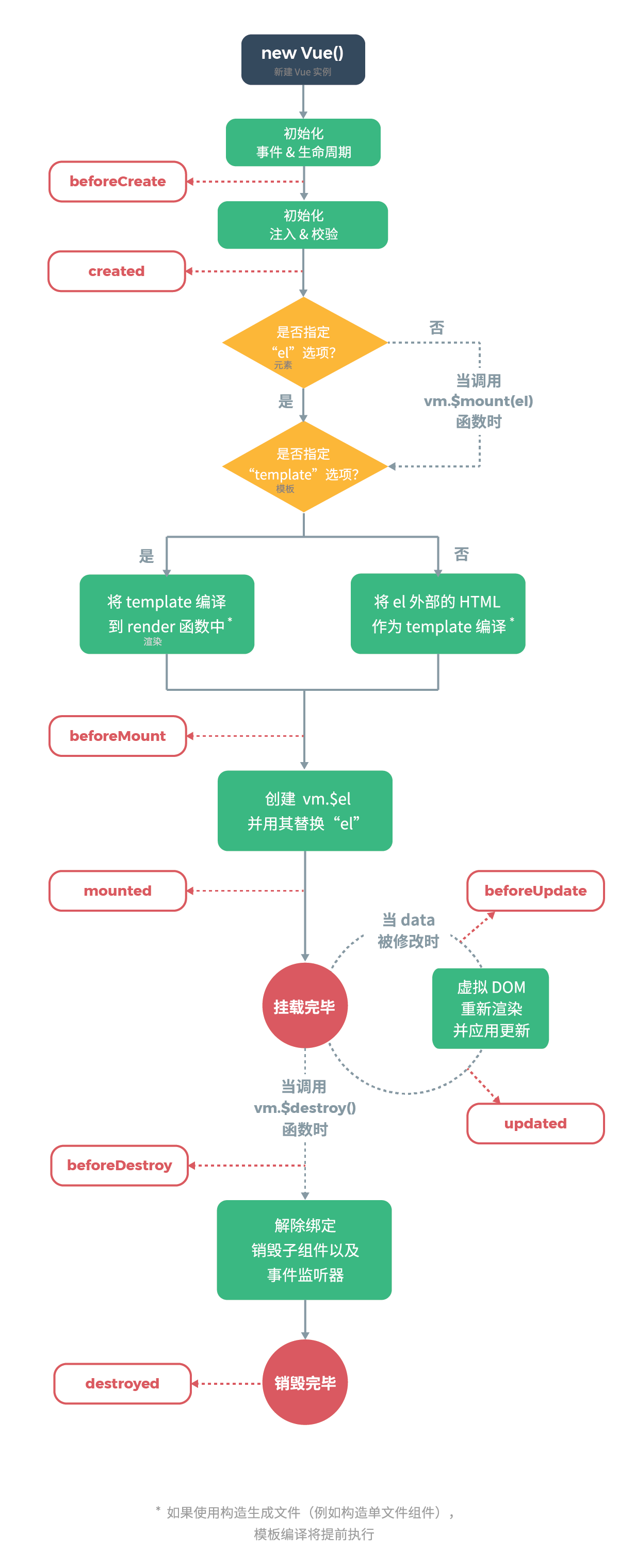
我这里用一张图梳理了源码中关于周期的全流程(长图预警):

-
Vue本质上是一个构造函数,定义在src/core/instance/index.js中:
// src/core/instance/index.js
function Vue(options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && !(this instanceof Vue)) {
warn("Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword");
}
this._init(options);
}
- 构造函数的核心是调用了
_init方法,_init定义在src/core/instance/init.js中:
// src/core/instance/init.js
Vue.prototype._init = function(options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this;
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++;
[1];
let startTag, endTag;
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`;
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`;
mark(startTag);
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true;
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
initInternalComponent(vm, options);
} else {
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
);
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") {
initProxy(vm);
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm;
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm;
initLifecycle(vm);
initEvents(vm);
initRender(vm);
callHook(vm, "beforeCreate");
initInjections(vm); // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm);
initProvide(vm); // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, "created")[2];
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false);
mark(endTag);
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag);
}
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el);
}
};
_init内调用了很多初始化函数,从函数名称可以看出分别是执行初始化生命周期(initLifecycle)、初始化事件中心(initEvents)、初始化渲染(initRender)、执行beforeCreate钩子(callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate'))、解析inject(initInjections)、初始化状态(initState)、解析provide(initProvide)、执行created钩子(callHook(vm, 'created'))。
- 在
_init函数的最后有判断如果有el就执行$mount方法。定义在src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js中:
// src/platforms/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
// ...
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount;
Vue.prototype.$mount = function(
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el);
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production" &&
warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
);
return this;
}
const options = this.$options;
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template;
if (template) {
if (typeof template === "string") {
// ...
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML;
} else {
// ...
return this;
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el);
}
if (template) {
// ...
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating);
};
// ...
export default Vue;
这里面主要做了两件事:
1、 重写了Vue函数的原型上的$mount函数
2、 判断是否有模板,并且将模板转化成render函数
最后调用了runtime的mount方法,用来挂载组件,也就是mountComponent方法。
-
mountComponent内首先调用了beforeMount方法,然后在初次渲染和更新后会执行vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)方法。最后渲染完成后调用mounted钩子。 -
beforeUpdate和updated钩子是在页面发生变化,触发更新后,被调用的,对应是在src/core/observer/scheduler.js的flushSchedulerQueue函数中。 -
beforeDestroy和destroyed都在执行$destroy函数时被调用。$destroy函数是定义在Vue.prototype上的一个方法,对应在src/core/instance/lifecycle.js文件中:
// src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function() {
const vm: Component = this;
if (vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
return;
}
callHook(vm, "beforeDestroy");
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true;
// remove self from parent
const parent = vm.$parent;
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm);
}
// teardown watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown();
}
let i = vm._watchers.length;
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown();
}
// remove reference from data ob
// frozen object may not have observer.
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--;
}
// call the last hook...
vm._isDestroyed = true;
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null);
// fire destroyed hook
callHook(vm, "destroyed");
// turn off all instance listeners.
vm.$off();
// remove __vue__ reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null;
}
// release circular reference (#6759)
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null;
}
};