habanero
 habanero copied to clipboard
habanero copied to clipboard
Load Testing framework in erlang with real-time feedback
habañero
Habanero is a lightweight, HTTP load testing tool written in Erlang.
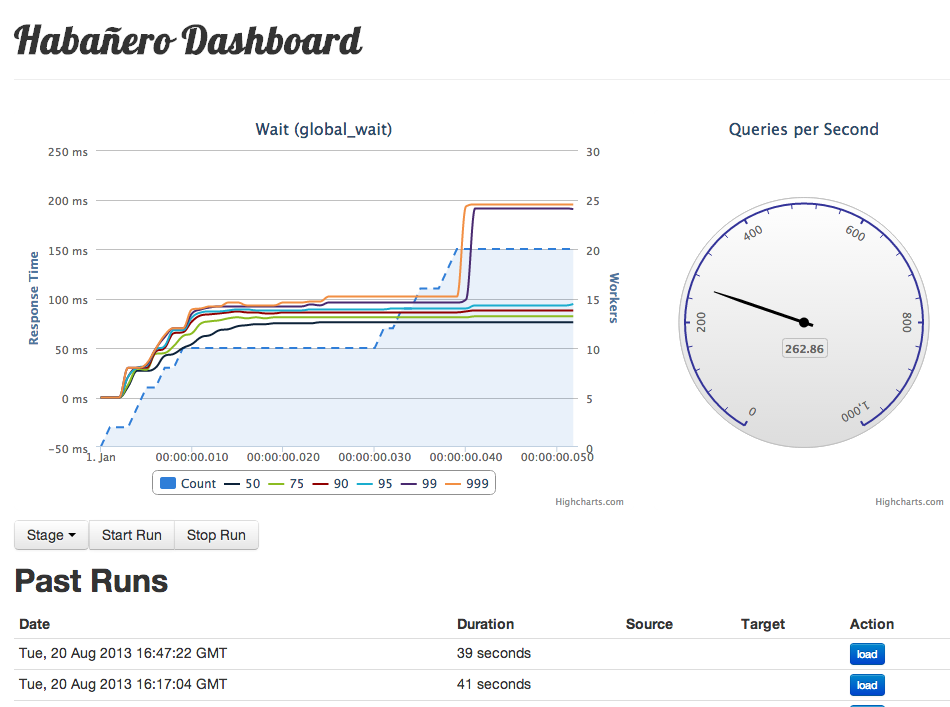
Quick start
Habanero requires Erlang R15B03 or higher. On OS X, Erlang is available via Homebrew.
brew install erlang
Once Erlang is installed, run make to compile habanero:
make
Habanero can be started in interactive mode:
./habanero.sh
...or detached:
./habanero.sh -detached
By default, the habanero dashboard is available at http://0.0.0.0:5566.
Configuring Tests
Pipelines
The core of habanero's execution model is the pipeline. This configurable in habanero.config.
%% Sample pipeline executes a GET request on index.html on localhost.
{pipeline, [
{sample_get, [
%% Returns [Method, Url, Headers]
{compose_request, {
return, [
get,
"http://localhost/index.html",
[{"User-Agent", "Habanero/1.0"}]
]}
},
{transition, {return, sample_get}}
]}
]}
Stages
Pipelines are composed of one or more stages. You can imagine a pipeline as a directed graph where each node represents an HTTP request. The above example shows a simple pipeline with a single request.
Each stage is comprised of two configurable phases: compose request and transition.
Phases
Compose request defines the request parameters. This phase must return a list of one of two forms.
An empty body request, e.g. GET or HEAD, in the form [Method, Url, Headers]:
{compose_request, {
return, [get,"http://localhost/index.html",[{"User-Agent", "Habanero/1.0"}]]}
},
Or a request with a provided body, in form [Method, Url, Headers, ContentType, Body]:
{compose_request, {
return, [post,"http://localhost/newpost",[{"User-Agent", "Habanero/1.0"}], "text/plain", "foo=bar"]}
},
Transition must return a single value specifying the next stage to execute:
{transition, {return, sample_get}}
Erlang Support
Phases can also execute Erlang functions using the form
{
compose_request, {erlang, {my_module, my_function}}
},
Erlang functions must accept a Context parameter, e.g.
-module(my_module).
-export([my_function/1]).
my_function(Context) ->
[get, "http://localhost/index.html", [{"User-Agent", "Habanero"}]]
Javascript Support
To enable Javascript support, you must edit rebar.config and uncomment the erlang_js dependency.
{sample_get, [
{compose_request, {javascript, "function(context){
var method = 'get';
var url = 'http://localhost/index.html';
return [method, url, []];
};"}},
{transition, {return, sample_get}}
]},
Running tests
Test runs can be pre-configured as a series of worker counts over time.
{timeline, [
{5, 10},
{15, 10},
{20, 20},
{30, 20}
]},
The above example defines a 30 second test run. Points in the timeline are specified as tuples of {second, worker count}. Habanero will interpolate the worker values between points spawning or terminating workers as necessary.
You can execute a pre-configured test run via start_run()
1> habanero_coordinator:start_run().
ok
2>
Test runs can be stopped prematurely via stop_run()
1> habanero_coordinator:stop_run().
ok
2>
Ad hoc test runs can also be excecuted from via the shell as follows, the arguement to workers() is the number of workers to spawn:
1> habanero_coordinator:workers(1).
ok
2> 17:41:00.507 [info] Spawned worker <0.119.0>
Web Endpoints
Habanero exposes the following web API endpoints:
- /api/start
- Start a test run.
- /api/stop
- Stop a test run.
- /api/history
- Fetch a JSON summary of past test runs.
- /api/poll
- Fetch current telemetry data.
- /api/load?id=RUN_ID
- Fetch telemetry data for a past test run, RUN_ID is the timestamp of the prior run.