postgrest-js
 postgrest-js copied to clipboard
postgrest-js copied to clipboard
Update non-public schema
Bug report
Describe the bug
I can't seem to be able to update non-public schema tables (e.g. auth.users):
await supabase.from('auth.users').update({ phone: user.phone }).eq('id', user.id);
To Reproduce
Steps to reproduce the behavior, please provide code snippets or a repository:
- Try to update a table not in the
publicPostgreSQL schema. - See a 404 error (e.g. table
public.auth.userscould not be found).
Expected behavior
I should be able to update non-public schemas without PostgREST adding that public prefix (e.g. auth.users should update auth.users not public.auth.users which doesn't exist).
Screenshots
Here's the error response from Supabase's PostgREST API:
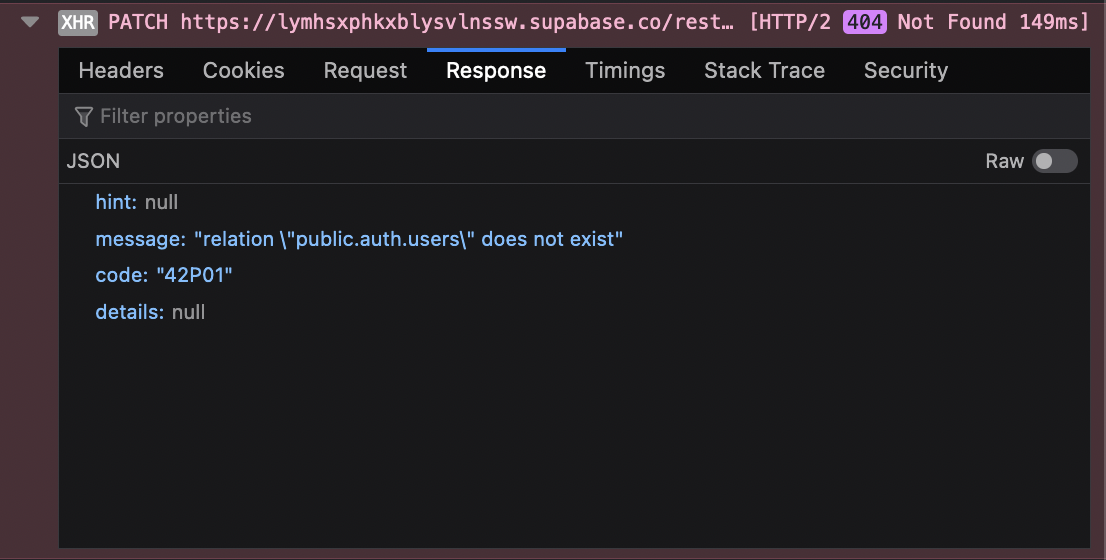
System information
- OS: macOS Big Sur
- Version of supabase-js: 1.25.2
- Version of Node.js: 16.13.0
Additional context
This would be fixed by supabase/gotrue-js#154.
The postgrest constructor actually accepts the schema option to configure which schema requests are sent to (https://supabase.github.io/postgrest-js/classes/postgrestclient.html#constructor). However, this requires the PostgREST to be configured with db-schema (https://postgrest.org/en/v8.0/api.html#switching-schemas), which is not available in Supabase platform right now. Additionally, I think the Postgres roles used by PostgREST right now do not have access to the auth schema (correct me if I'm wrong).
Edit: looks like the db-schema property was recently made available for access in Supabase platform: https://github.com/supabase/supabase/pull/2683.
As mentioned above, you can configure the setting (API settings > Exposed schemas) and set the schema property when initializing the client lib.
You also need to apply GRANTs for each custom schema. For a user-facing schema meant to be accessed via the anon key:
create schema my_schema;
grant usage on schema my_schema to postgres, anon, authenticated, service_role;
grant all on all tables in schema my_schema to postgres, anon, authenticated, service_role;
grant all on all functions in schema my_schema to postgres, anon, authenticated, service_role;
grant all on all sequences in schema my_schema to postgres, anon, authenticated, service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on tables to anon, authenticated, service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on functions to anon, authenticated, service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on sequences to anon, authenticated, service_role;
For an internal schema only meant to be accessed via the service_role key:
create schema my_schema;
grant usage on schema my_schema to service_role;
grant all on all tables in schema my_schema to postgres, service_role;
grant all on all functions in schema my_schema to postgres, service_role;
grant all on all sequences in schema my_schema to postgres, service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on tables to service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on functions to service_role;
alter default privileges for role postgres in schema my_schema grant all on sequences to service_role;
(This should be put in our docs at some point)