spotMicro
 spotMicro copied to clipboard
spotMicro copied to clipboard
RPI not responding to keyboard commands
Hello @mike4192, A really big thank you for sharing this amazing project. I decided to implement it on a RPI4 running Ubuntu 20.04 and ROS Noetic. I used the MG996R servos, your exact same LCD, same 3D printed parts and a switching power supply (5.5 V, 8A) connected to the line. I got it assembled without any major complication. On the software part, I was able to compile the catkin_ws using catkin_tools but I had to make some minor changes:
- Add
extern "C"{#include i2c/smbus.h}toi2cpwm_controller.cpp - Modify the
CMakeLists.txtfromi2cpwm_boardpackage -> fromtarget_link_libraries(i2cpwm_board ${catkin_LIBRARIES})totarget_link_libraries(i2cpwm_board ${catkin_LIBRARIES} i2c) - Modify the python version for
spotMicroKeyboardMove.pychanging the first line from#!/usr/bin/pythonto#!/usr/bin/python3. You have also to change the functionrawInputtoinput(Pyhton 3 version of raw input) and another thing that I can't remember now.
After those changes the catkin_ws is compiled by doing catkin build. I've then changed the ROS_MASTER_URI variable to the ip address of the RPI4, port 11311. After this I was able to start the roscore on the Raspberry and list all the topic from the PC.
Following your instructions I've launched spot_micro_motion_cmd motion_cmd.launch on the RPI and everything seems OK from logs (frequency is set to 50 HZ after bus opened on the right port and servo config is loaded) and the LCD shows "State: Idle". On the PC side I start the spot_micro_keyboard_command keyboard_command.launch but when I issue the stand command nothing happens not even the LCD changes state. Nothing happens even with walk or idle command.
Echoing some topics and searching through rosnodes infos everything seems working as it meant to be.
I can tell you thath the i2cpwm_board is working because I completed the entire calibration process following your instructions (and yes, the motors move).
I cannot find the real core of conversion from calculated angles to /servos_proportional publishing.
If you are interested, we can set up a call or something to scope why and where the communication fails. This way we can have your SW implemented in ROS Noetic and Ubuntu 20.04 (a long term support, so, it's convenient i think).
Thanks for reporting this. On a surface level it seems as if the core issue is that the messages from the keyboard command node aren't making it to the motion command node running on the RPi for some reason.
When you say you echo'd the topics, were you echoing the topics on a local PC or on the RPi (via a secondary ssh session for example)? Were you echoing the command topics (like /stand_cmd)? And if so, did you see that they were indeed published when you commanded it from the keyboard command node? Did you see they were echoed on both a local PC and on the RPi?
If not already tried, can you try opening a second ssh instance to the RPi and running the keyboard command node from there? Any difference in behavior?
How do you set the ROS_MASTER_URI variable? Do you do export ROS_MASTER_URI=blah.blah.blah....? Do you do this on your controlling PC?
Also, to answer one of your questions, the conversion of angles to proportional commands occurs in the publishServoProportionalCommand method in spot_micro_motion_cmd.cpp. This method is called by the robot state instatiations (such as the stand state, or walk state), which are instantiations of the friend class SpotMicroState (such as spot_micro_stand.cpp).
Hello @mike4192,
sorry if it took me so long but I had two busy weeks. Following your suggestions, first thing I tried was to run the spot_micro_keyboard_command keyboard_command.launch on the RPi and magically the robot answered to the stand and walk commands.
After some struggling, I found that the problem was the way I set up the network in ROS. The right way is:
- Modify
~/.bashrcon RPI and PC. Addexport ROS_MASTER_URI=http://RPI_IP_ADDRESS:11311on both andexport ROS_IP=PC_IP_ADDRESS(where RPI_IP_ADDRESS is the IP of the robot and PC_IP_ADDRESS is the IP of the PC) - Modify
etc/hostsfile on both RPi and PC adding (under127.0.0.0.1 localhostline) both IP addresses with relative hostnames source ~/.bashrc
At this point I'm able to control the robot using the PC but I'm not able to see RVIZ model moving. In order to have the model in RVIZ I had to make some minor changes:
- Change the fixed frame parameter in
spot_micro.rvizfrombase_footprinttobase_link. - Add to
show_model.launchtwo nodes:<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" /><node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="state_publisher" /> - In the same file modify also the line
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py $(arg model)" />to<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro $(arg model)" />
This way the robot is shown in RVIZ but it is not moving accordingly to the real robot, well, it's really not moving at all.
Hmm, I'm not sure why your running into these issues.
For reference, below is what I have in my .bashrc file on my PC regarding ROS stuff, but I think it effectively results in the same as you have. I didn't touch anything on my RPi3, but I am using the ubiquity robotics image that was preconfigured ROS kinetic on Ubuntu 16.04. I switch the commented part below between using the RPi or local PC as the ROS master depending on what I'm running. I also didn't need to do any modifications to my /etc/hosts file.
export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://ubunturospi.local:11311 # Set IP of ros master, raspberry pi in this case
#export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://localhost:11311 # Set IP of ros master to be local machine if running here
export ROS_IP=$(hostname -I | cut -f1 -d' ') # set own ros ip environment variable
alias rosinit="source /home/mike/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash && export ROS_WORKSPACE=~/catkin_ws"
Regarding RVIZ, adding those two additional nodes to show_mode.launch is not needed to show model movement from the motion control node. For some background info, joint_state_publisher and robot_state_publisher are helper nodes included in ROS that help to broadcast transforms (TF messages) for all of the robot's links. The combination of those two nodes, along with robot description file defined by either a .urdf file or derived from a xacro file (which is one abstraction level higher, because it employs macros), allows TF frames to be broadcast from simpler joint state messages, which effectively just consist of the current angle of a joint.
This is what occurs if you launch show_and_move_model_via_gui.launch. In this case, the joint state publisher I think rebroadcasts joint state messages received via the GUI (controlled by the sliders). The robot_state_publisher node subscribes to those joint state messages, and through the robot description defined by the urdf or xacro file, broadcasts appropriate TF messages.
In my case, however, I directly publish tf messages from the spot_micro_motion_cmd_node, so joint_state_publisher and robot_state_publisher are not needed, and could infact screw things up if run simultaneously as they may also be publishing TF frames.
Can you try running all nodes on your local PC, sort of in a simulation like environment?
- Change your
.bashrcfile so ROS_MASTER_URI is set to localhost:11311, as you will be running all nodes on your PC for this test. - Open four terminals, cd to your catkin workspace, and initialize ros environment in each by sourcing setup.bash
- Launch the following:
a.
roslaunch spot_micro_motion_cmd motion_cmd.launch run_standalone:=trueb.roslaunch spot_micro_rviz show_model.launchc.roslaunch spot_micro_keyboard_command keyboard_command.launchd.rqt_graph
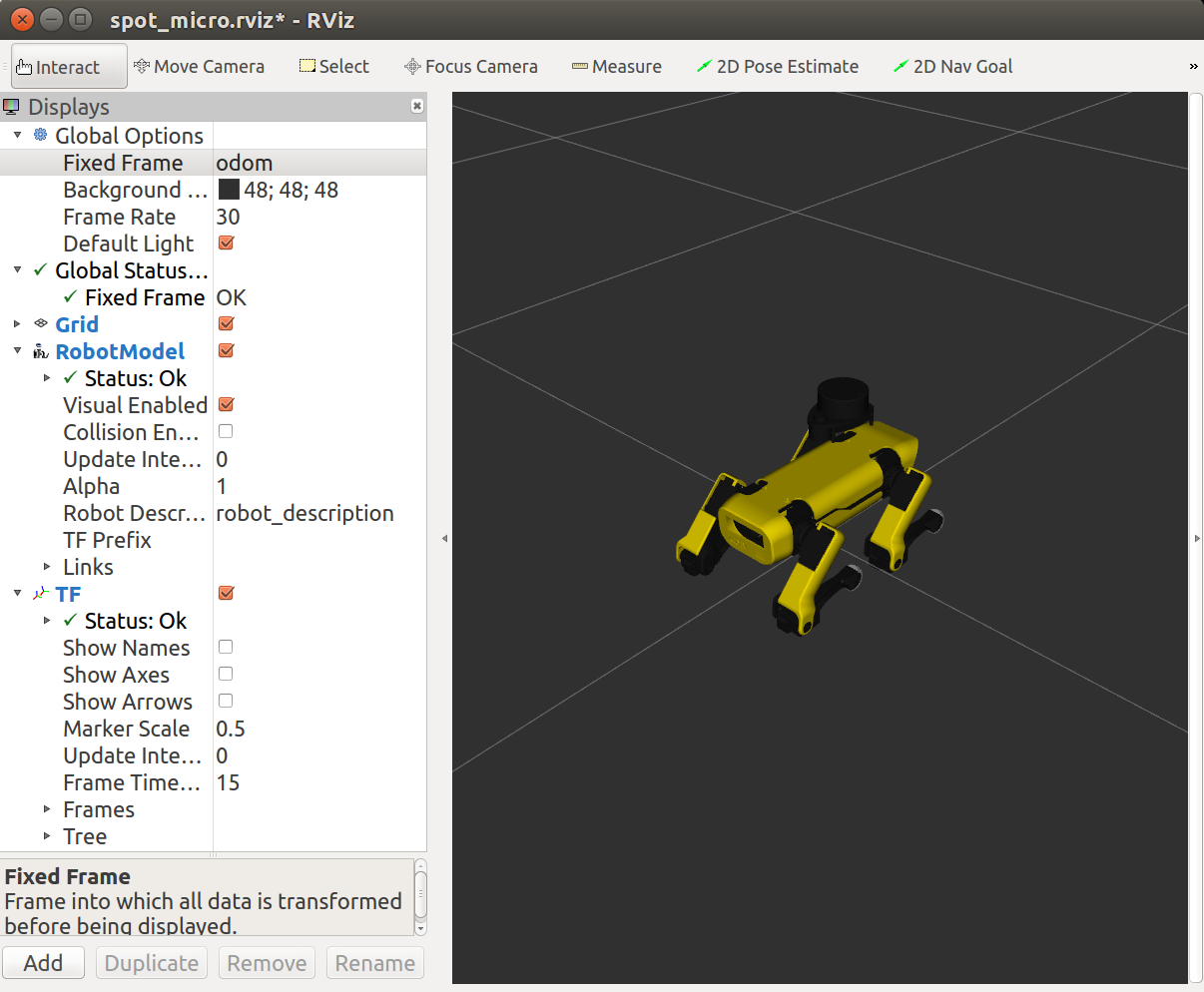
You should be able to command the robot to stand and walk through the keyboard command node, and see the corresponding motions in RVIZ. Note, you will need to switch the Fixed Frame in the top left, under Global Options from base_footprint to odom to see it actually translate around from the published odometry.
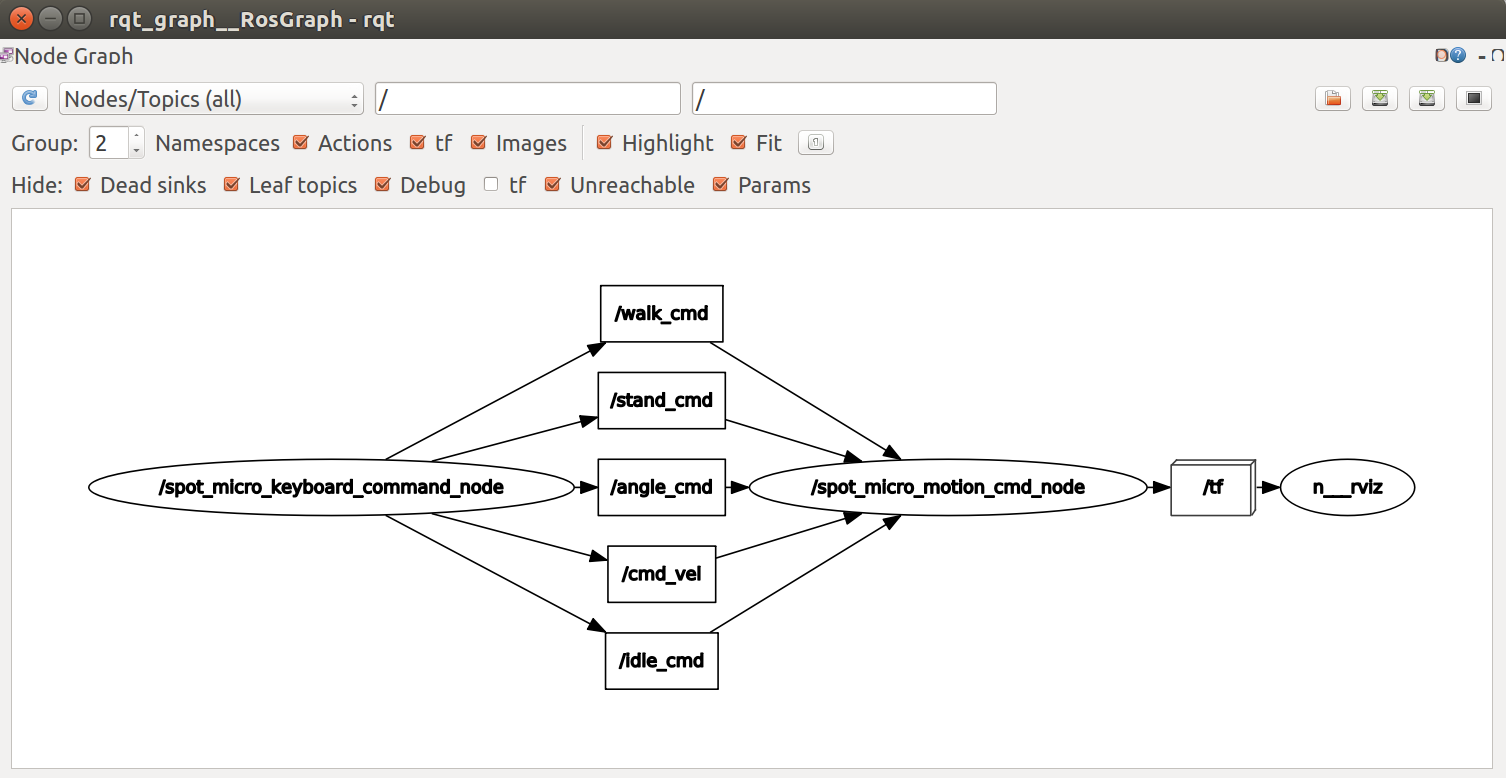
From rqt_graph, your node graph should look like the one below:
Do you see any red or yellow errors or warnings in RVIZ?
If this works, revert back your .bashrc file, and run the motion control node on the RPI4. Run RVIZ and the rqt_graph. Do you see any differences? Do you see any warnings or errors in RVIZ? If you echo the TF topic on your PC, do you see TF messages.
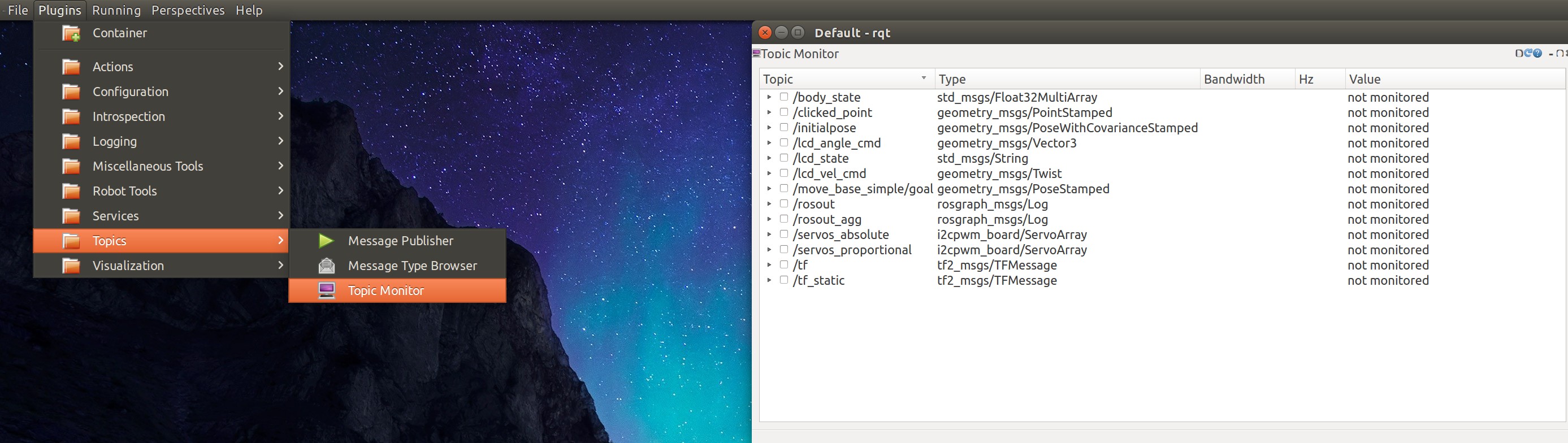
BTW, another way to help debugging is by running the topic monitor plugin after launch rqt. You can more easily monitor what messages are visible. Explore the other plugins as well.