从2-3树到红黑树/B-树/B+树(TypeScript)
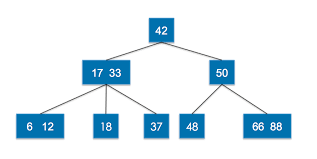
2-3查找树
为了保持查找树的平衡, 我们允许一个节点存储多个键, 一个2-3树就是允许一个节点可以有1 或 2 个节点, 对应有2个或3个子节点.
- 2- : 一个键两个链接;
- 3-: 两个键三个链接;
如下图.
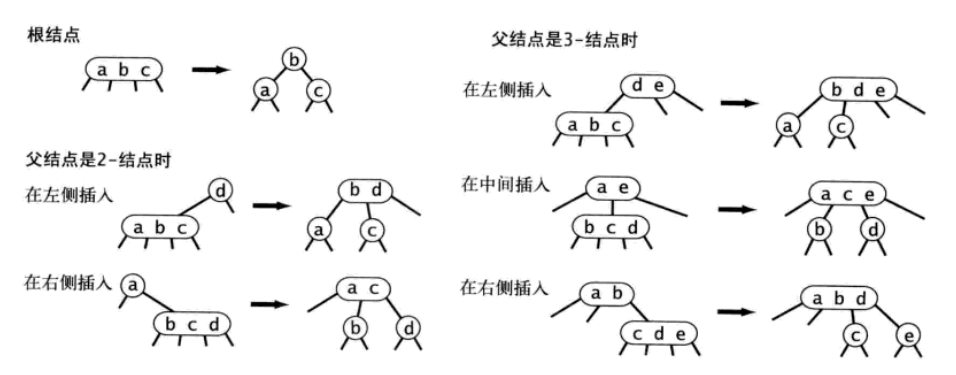
插入的时候怎么保持平衡
当未命中查找结束于一个2-节点就很简单, 直接把这个2-节点替换为3- 节点就OK了, 树还是平衡的.
当结束于3-节点 就有点麻烦, 我们可以临时构造一个4- 节点, 然后向上分解, 把中间的键移到父节点里面去, 然后分裂成2个2- 节点, 然后一直向上分解临时的4- 节点, 直到根节点, 如果根节点是临时的4- 节点向上分解, 这样树的高度就增加了1, 由于根节点分解前树的高度是不变的, 根节点分解后, 所有的叶子节点高度都加了1, 所以树还是平衡的.
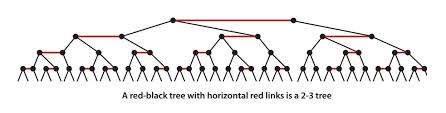
红黑树
基础
- 还是用二叉树去表示, 只是多了一个颜色属性, 当成2-3平衡树的一种等价定义.
- 红链接表示将两个2- 节点构成一个3- 节点
- 黑链接表示2-3 树中的普通节点
定义:
- 红链接均为左链接
- 没有一个节点同时和两条红链接相连
- 该树是完美黑色平衡的, 即任意空链接到根节点的路径上的黑链接数量相同
药店:
- 和 2-3 树一样, 插入的时候插入底部, 自底向上分解节点(通过左旋右旋和颜色变换)
- 如果一个节点下面两个红子节点, 将两个子节点颜色变黑, 同时将父节点的颜色由黑变红, 向上转化
- 如果根节点由红变黑, 树的高度是加1
如果把这种红黑树的红链接画平, 就是一颗2-3树
TypeScript 实现
// 比较函数
const compare = (a, b) => a - b;
const enum Color {
RED,
BLACK
}
type Key = string | number;
// 节点
class RedBlackNode {
key: Key;
value: any;
color: Color;
left: RedBlackNode | null;
right: RedBlackNode | null;
constructor(key, value, color) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.color = color;
}
}
export class RedBlackBST {
root: RedBlackNode = null;
public put(key: Key, value?: any) {
value = value || key;
this.root = this._put(this.root, key, value);
this.root.color = Color.BLACK;
}
public del(key: Key) {
if (!this.isRed(this.root.left) && !this.isRed(this.root.right)) {
this.root.color = Color.RED;
}
this.root = this._del(this.root, key);
if (this.root) {
this.root.color = Color.BLACK;
}
}
private _put(node: RedBlackNode, key: Key, value: any): RedBlackNode {
if (node === null) {
return new RedBlackNode(key, value, Color.RED);
}
const cmp = compare(key, node.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
node.left = this._put(node.left, key, value);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
node.right = this._put(node.right, key, value);
} else {
node.value = value;
}
if (this.isRed(node.right) && !this.isRed(node.left)) {
node = this.rotateLeft(node);
}
if (this.isRed(node.left) && this.isRed(node.left.left)) {
node = this.rotateRight(node);
}
if (this.isRed(node.left) && this.isRed(node.right)) {
this.flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 删除节点也是向下遍历, 确保当前节点不是2- 节点, 如果键在树的底部直接删除, 如果不在, 和二叉树一样交换右子树中最小的元素,
* 问题就转化为删除一棵根节点(右子树)不是2- 节点的最小值
* @param node
* @param key
*/
private _del(node: RedBlackNode, key: Key) {
if (compare(key, node.key) < 0) {
if (!this.isRed(node.left) && !this.isRed(node.left.left)) {
node = this.moveRedLeft(node);
}
node.left = this._del(node.left, key);
} else {
// 如果左子接点是 红 就右旋
if (this.isRed(node.left)) {
node = this.rotateRight(node);
}
// 如果是树的底部, 直接删除
if (compare(key, node.key) === 0 && node.right === null) {
return null;
}
// 不是树的底部, 确保右子节点不是2- 节点
if (!this.isRed(node.right) && !this.isRed(node.right.left)) {
node = this.moveRedRight(node);
}
// 和二叉树 一样替换右子树最小节点
if (compare(key, node.key) === 0) {
const temp = node;
node = this._min(node.right);
node.left = temp.left;
node.right = this._delMin(temp);
} else {
node.right = this._del(node.right, key);
}
}
return this.balance(node);
}
private _min(node: RedBlackNode) {
if (node.left === null) {
return node;
}
return this._min(node.left);
}
/**
* 向下转化, 保证左子节点 不是2- 节点
* @param node
*/
private _delMin(node: RedBlackNode) {
// 最左节点
if (node.left === null) {
return null;
}
// 如果 左子节点是 2- 节点, 借节点
if (!this.isRed(node.left) && !this.isRed(node.left.left)) {
node = this.moveRedLeft(node);
}
node.left = this._delMin(node.left);
return this.balance(node);
}
/**
* 从右边借节点, 让左子节点变成3- 或 4- 节点(图1)
* @param node
*/
private moveRedLeft(node: RedBlackNode) {
// 现将节点 结合成4- 节点
this.flipColors(node);
// 如果 node.right.left是红, 那就不是4- 节点
if (this.isRed(node.right.left)) {
node.right = this.rotateRight(node.right);
node = this.rotateLeft(node);
// 现在将left, right由红变黑 保证是3- 或 4- 节点, 便于理解, 也可以在后面向上配平的时候转化.
this.flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
/**
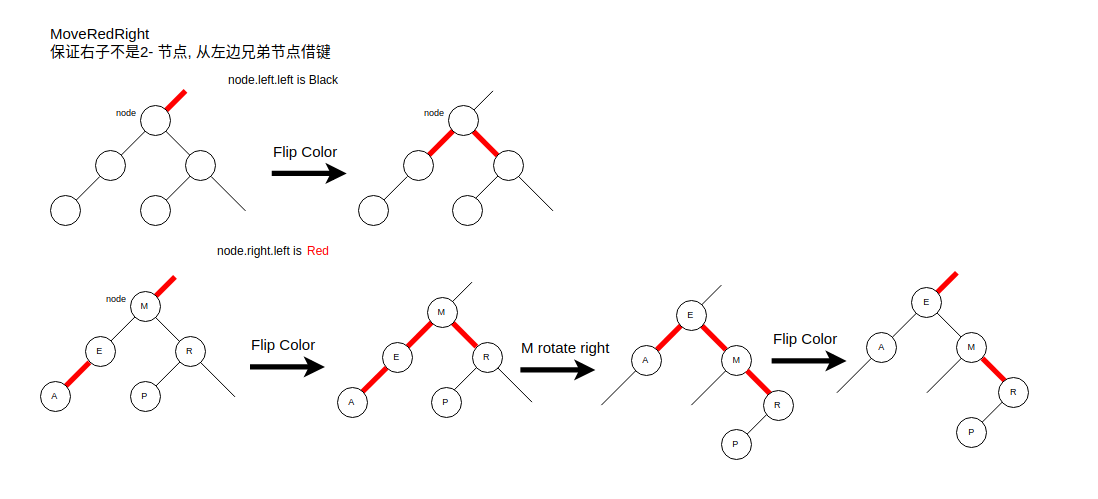
* 从左边借节点, 让右子节点变成3- 或 4- 节点(图2)
* @param node
*/
private moveRedRight(node: RedBlackNode) {
this.flipColors(node);
if (this.isRed(node.left.left)) {
node = this.rotateRight(node);
this.flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
/**
* 向上分解临时的4- 节点
* @param node
*/
private balance(node: RedBlackNode) {
if (this.isRed(node.right) && !this.isRed(node.left)) {
node = this.rotateLeft(node);
}
if (this.isRed(node.left) && this.isRed(node.left.left)) {
node = this.rotateRight(node);
}
if (this.isRed(node.left) && this.isRed(node.right)) {
this.flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
// 将红色右链接转化为左链接,
private rotateLeft(node) {
const x = node.right;
node.right = x.left;
x.left = node;
x.color = node.color;
node.color = Color.RED;
return x;
}
private rotateRight(node) {
const x = node.left;
node.left = x.right;
x.right = node;
x.color = node.color;
node.color = Color.RED;
return x;
}
private flipColors(node) {
node.color = !node.color;
node.left.color = !node.left.color;
node.right.color = !node.right.color;
}
private isRed(node) {
return node !== null && node.color === Color.RED;
}
}
图示
图1
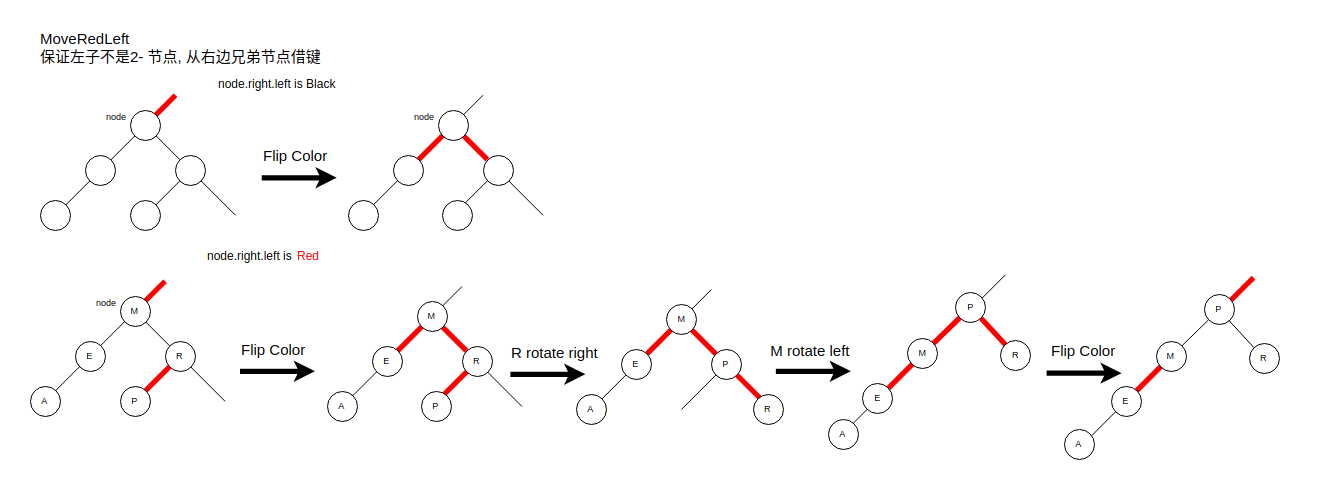 图2
图2
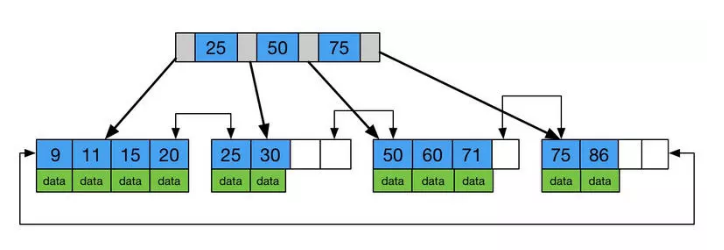
B/B+ 树
红黑树对于插入, 查找, 删除非常高效, 但是考虑到存储的话, 不那么灵了.
因为计算机访问内存和磁盘的速度差异是多个数量级.
在大量数据存储的前提下, 我们必须减少磁盘访问的次数.
但是二叉树每个节点的保存信息少, 树就比较高, 不适合磁盘操作.
就像是2-3树, 我们可以设计一个节点保存2个键表示3- 节点, 这样一次I/O的信息就多了.
当然可以不只是保存2个键值, 最好是一个节点保存的信息就是一个磁盘块的大小, 这样就尽量减少磁盘I/O.
B-树就是基于此设计. 本质就是2-3-4-N树
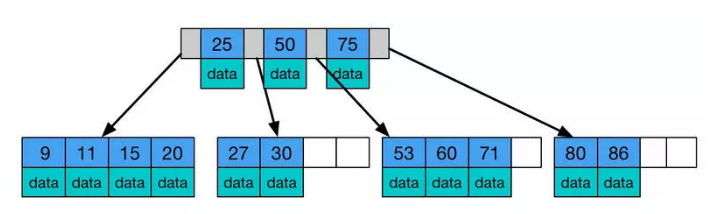
然后是B-树的问题, 为了获取一个节点的数据, 我们需要先在内存加载它的父节点, 它的父节点中同时包含了数据(或者指向数据的指针)和指向子树的指针. 但是我们其实只需要指向子树的指针而已, 所以这种包含了数据指针和子树指针的节点很难构建常驻内存的索引.
B+树就是中间节点只是保存子树的指针, 所有的数据指针下沉到在叶子节里面. 这样相对于B-树只是最下面多了一层, 但是中间节点的可用空间就多了. 这就是B+树的构建方式.