elysia
 elysia copied to clipboard
elysia copied to clipboard
How to seperate the handlers out from inline arrow functions with context/types
So say you have:
const app = new Elysia();
async function IndexHandler() {
return "HI";
}
app.group("/app", (app) =>
app.get("/hi", IndexHandler).get("/bye", async () => "BYE")
);
app.listen("3000");
This will run without issue; the IndexHandler() function will run correct without issue. But once you add the context param like:
async function IndexHandler(context) {
return "HI";
}
This will ask for a type on the context param; and you can add IndexHandler(context: Context) but then handler function in the get() method will throw a large type error.
My question is, is there a way to seperate out the handler functions correctly with appropriate types? Or do they all need to be inline arrow functions so the types pass over?
Thanks :)
Hi, you can use Context to type the function parameter like this:
import { type Context } from 'elysia'
const a = (a: Context<any>) => {
return "A"
}
Is there a good way to do something like the following?
// app.ts
export const app = new Elysia()
.use(html())
.state('n', 123);
export MyContext = Context<???, (typeof app)['store']>;
// index.ts
import {app, MyContext} from './app'
const handler = (c: MyContext) => {
// !!! c does not have an `html` property :(
}
The second type parameter gives good type-hints for handlers that take MyContext, but I can't figure out what to put for the second generic?
I think I may have actually got it:
// app.ts
export const app = new Elysia()
.use(html())
.state('n', 123);
type App = typeof app;
type Instance = App extends Elysia<any, infer T> ? T : never;
export MyContext = Context<{}, (typeof app)['store']>;
export Handler = (ctx: MyContext & Instance["request"]) => Response | Promise<Response>;
// index.ts
import {app, MyContext} from './app'
const handler: Handler = (ctx) => {
// c has all expected properties
}
I am having the same Issue
I guess the question is more about getting the Context type for your specific app with all the plugins being used.
For example if I have the following code:
import { Context, Elysia } from "elysia"
import { html } from "@elysiajs/html"
import jwt from "@elysiajs/jwt"
import cookie from "@elysiajs/cookie"
const app = new Elysia()
.use(html())
.use(jwt({ secret: 'some secret', name: "jwt" }))
.use(cookie())
const handler = ({ cookie: { jwt: token }, jwt, set }: Context) => {
const verified = await jwt.verify(token)
console.log({ verified, token })
if (!verified) {
return (set.redirect = "/login")
} else {
return '<p>hello</p>'
}
}
app.get("/", handler)
typescript tells me that cookie and jwt does not exist on type Context because the standard Context does not know about the plugins.
But Context<typeof app> also does not work for me.
type MyContext = Parameters<Parameters<typeof app.get>[1]>[0] would match the type of the specific context but that would be very ugly.
Is there an easier way to get this type?
@langej Try my answer in this comment: https://github.com/elysiajs/elysia/issues/95#issuecomment-1714674241
I believe this is what is wanted. The "trouble" is that portions of Context can depend on route-specific type-guards, which if I'm not mistaken, is what the first generic of the Context<_, _> type captures.
I think it would be ideal if we have a utility type that infers this, something like what @jrop did
I was also tinkering with this, and got it working (at least for my use case). When I tried the above solutions, and added the handler to a path, it would cause the Elysia instance's types to break, resulting in the types of my RouteHandler breaking, etc.
// app.ts
import Elysia from "elysia";
import { login } from "./routes/login";
const app = new Elysia().derive(async (ctx) => {
return {
value: 100,
}; // Personally use this for Lucia session
});
export type RouteHandler = Parameters<typeof app.post>[1];
// Then, register the routes
app
.post("/login", login);
// routes/login.ts
import { RouteHandler } from "../app";
export const login: RouteHandler = async ({ set, session }) => {
return { ok: true };
};
I've managed to get it working (with a bit of hacky way) while working with parameters in paths. While merging the types of @jrop's and mine, I've came across some weird TypeScript problems (like circular depencency stuff) so it would be perfect if someone manages to merge this and the @jrop's solution.
InferContext<T> will still have all the properties of Elysia's original Context with the additional params property, except the state variables and decorate functions
import { Context } from 'elysia';
type SplitUrlPath<T> = T extends `${infer A}/${infer B}` ? [A, ...SplitUrlPath<B>] : T extends `${infer A}` ? [A] : [T];
type FilterUrlPath<T extends any[]> = T extends [infer Item, ...infer Rest]
? Item extends `:${infer Parameter}`
? [Parameter, ...FilterUrlPath<Rest>]
: FilterUrlPath<Rest>
: [];
type ParameterToRecord<T extends string[]> = Record<T[number], string>;
export type InferContext<T extends string> = Context<
{
params: ParameterToRecord<FilterUrlPath<SplitUrlPath<T>>>;
},
any
>;
The usage is fairly simple, just pass your handler function to Elysia and annotate your context type with InferContext<T>:
const app = new Elysia()
.get('/', getAllHandler)
.get('/:id', getSingleHandler);
function getAllHandler(ctx: InferContext<'/'>) {
ctx.params // {}
}
function getSingleHandler(ctx: InferContext<'/:id'>) {
ctx.params // { id: string }
}
I am also having this problem in below code.
import { Context, Elysia, Handler } from "elysia";
import { swagger } from "@elysiajs/swagger";
const app = new Elysia().get("/", () => "Hello Elysia").listen(3000);
app.use(swagger());
app.get("/:name", handler);
const handler = async (obj:Context<any>) => {
console.log(obj.params.name);
return `Hi, ${decodeURIComponent(obj.params.name)}`;
};
app.get("/:name", handler);
console.log(`🦊 Elysia is running at http://${app.server?.hostname}:${app.server?.port}`);
typscript showing a long error ..
Types of parameters 'obj' and 'context' are incompatible.
Type '{ body: unknown; query: Record<string, string | null>; params: Record<"name", string>; headers: Record<string, string | null>; cookie: Record<string, Cookie<any>>; set: { ...; }; path: string; request: Request; store: {}; }' is not assignable to type '{ body: any; query: Record<string, string | null>; params: never; headers: Record<string, string | null>; cookie: Record<string, Cookie<any>>; set: { ...; }; path: string; request: Request; store: {}; }'.
Types of property 'params' are incompatible.
Type 'Record<"name", string>' is not assignable to type 'never'.ts(2345)```
Sorry might be off topic but looks like you can only pass ctx only one time, so lets say my handler receives ctx but then i have another function i want to pass i get error
Sorry might be off topic but looks like you can only pass ctx only one time, so lets say my handler receives ctx but then i have another function i want to pass i get error
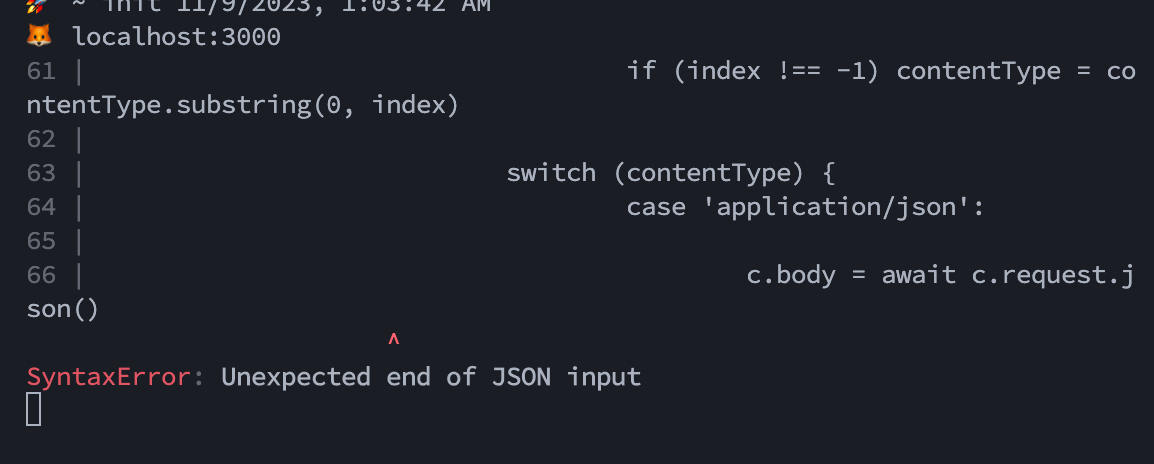
This is probably because the Request's body is a stream and it can only read once. Once you consume the body (using request.json()), that stream is drained. That means there is no more data left to read when you try to call request.json() again.
If you really want to consume request body twice, you have two options;
- Clone the request using
ctx.request.clone()in each of your functions and use the cloned request, - Save the body object on
Contextobject by extending it (haven't tested but it should work).
I ended up going a different route recently with this that I am much more happy with. The problem with my previous approach was that I was depending on what I would now consider elysia "internals" that are subject to more churn than the stable API. I've shifted to inferring the Context off of the resulting app.post(.., /* handler */ (ctx: Context) => { ... }, ...) method call:
import type { Elysia } from "elysia";
// a utility that helps us simplify the type of a record, namely
// because we are doing `Omit ... & ...`:
type SimplifyOneLevel<T> = T extends Record<string, unknown>
? { [K in keyof T]: T[K] }
: T;
//
// app.post([path], [handler]): grab the type of the handler:
type InferHandler<E extends Elysia> = Parameters<E["post"]>[1];
export type InferContext<E extends Elysia> = SimplifyOneLevel<
// For my particular use, I want to force the params to be a Record<string, string | undefined>:
// so I do `Omit<_, "params"> & { params: ... }`:
Omit<
// ...but this is the real meat of the inference:
// the type of the context is the type of the first parameter of the handler:
Parameters<InferHandler<E>>[0],
"params"
> & {
params: Record<string, string | undefined>;
}
>;
Then later in my user-space code:
import type { InferContext } from "./path/to/above/helper";
import { Elysia } from "elysia";
export const app = new Elysia()
.state("bleh1", "whackamole1")
.state("bleh2", "whackamole2")
.state("bleh3", "whackamole3");
export type Context = InferContext<typeof app>;
// Context has { ..., store: { bleh1: string; bleh2: string; bleh3: string } }
This could most likely easily be extended with @Stradi 's additions, if needed. In my particular case, I am using a different strategy for ensuring params types.
no idea?
@jrop have you found a way to achieve this with version 0.8.17?
this is my approach
import { Elysia } from "elysia";
type BeforeHandle = NonNullable<
NonNullable<Parameters<typeof transactionRoute.post>[2]>["beforeHandle"]
>;
type ParameterType<T> = T extends (context: infer U) => any ? U : never;
type ActualContextType = ParameterType<BeforeHandle>;
export const transactionRoute = new Elysia({ prefix: "/transaction" }).get(
"",
async () => "test",
{} // params from beforeHandle
);
export type InferRouteContext<
T extends Elysia<any, any, any, any, any, any, any, any>,
U extends keyof T["_routes"],
V extends keyof T["_routes"][U],
W extends keyof T["_routes"][U][V],
> = T["_routes"][U][V][W] & Omit<InferContext<T>, "params">
This has got me closest to my goal but the only issue being that I am getting a circular dependency error on the handler. Does anyone know how to get around this?
Close as documented in https://elysiajs.com/patterns/mvc.html#mvc-pattern, and export utility function for inferring context InferContext.
@SaltyAom The link is broken! :(
@SaltyAom The link is broken! :(
Just open search