torch-dreams
 torch-dreams copied to clipboard
torch-dreams copied to clipboard
Flexible Feature visualization on PyTorch, for research and art :mag_right: :computer: :brain: :art:
Torch-Dreams
Making neural networks more interpretable, for research and art.

pip install torch-dreams
Contents:
- Minimal example
- Not so minimal example
- Visualizing individual channels with
custom_func - Caricatures
- Visualize features from multiple models simultaneously
- Use custom transforms
- Feedback loops
- Custom images
- Working on models with different image normalizations
- Masked image parametrs
- Other conveniences
Minimal example
Make sure you also check out the quick start colab notebook
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.models as models
from torch_dreams.dreamer import dreamer
model = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model, device = 'cuda')
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.Mixed_5b],
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
Not so minimal example
model = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model, device = 'cuda', quiet = False)
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.Mixed_5b],
width = 256,
height = 256,
iters = 150,
lr = 9e-3,
rotate_degrees = 15,
scale_max = 1.2,
scale_min = 0.5,
translate_x = 0.2,
translate_y = 0.2,
custom_func = None,
weight_decay = 1e-2,
grad_clip = 1.,
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
Visualizing individual channels with custom_func
model = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model, device = 'cuda')
layers_to_use = [model.Mixed_6b.branch1x1.conv]
def make_custom_func(layer_number = 0, channel_number= 0):
def custom_func(layer_outputs):
loss = layer_outputs[layer_number][channel_number].mean()
return -loss
return custom_func
my_custom_func = make_custom_func(layer_number= 0, channel_number = 119)
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = layers_to_use,
custom_func = my_custom_func,
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
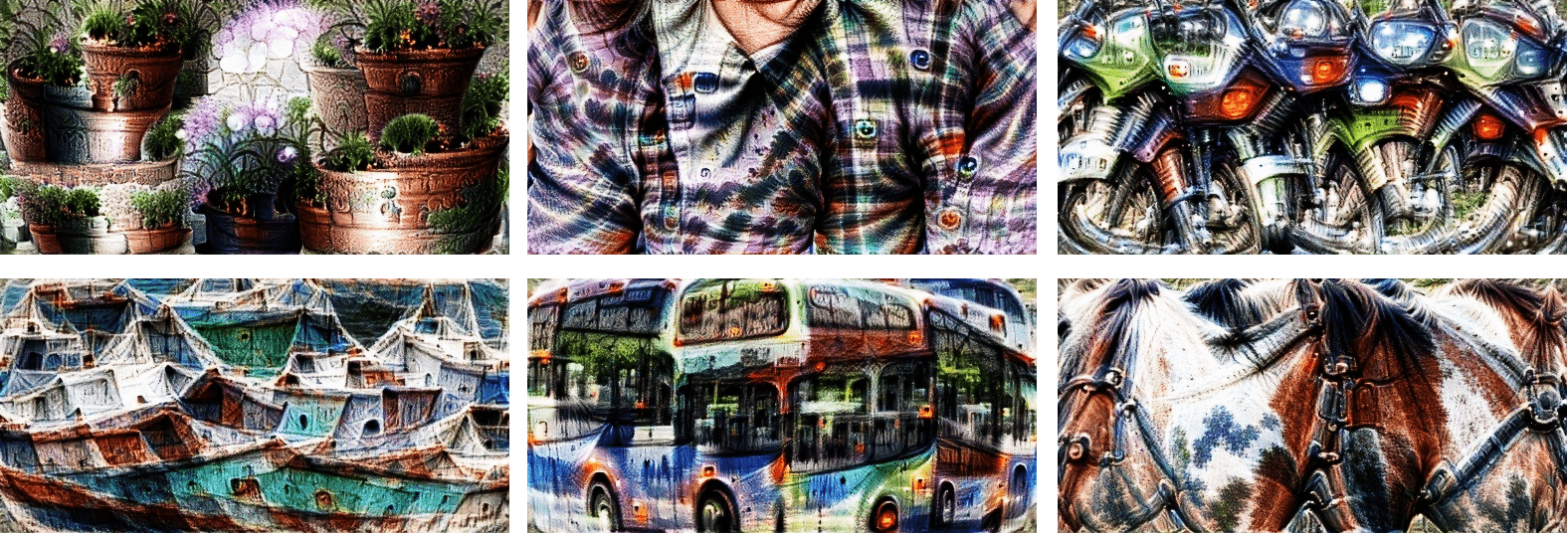
Caricatures
Caricatures create a new image that has a similar but more extreme activation pattern to the input image at a given layer (or multiple layers at a time). It's inspired from this issue

In this case, let's use googlenet
model = models.googlenet(pretrained = True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model = model, quiet= False, device= 'cuda')
image_param = dreamy_boi.caricature(
input_tensor = image_tensor,
layers = [model.inception4c], ## feel free to append more layers for more interesting caricatures
power= 1.2, ## higher -> more "exaggerated" features
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
Visualize features from multiple models simultaneously
First, let's pick 2 models and specify which layers we'd want to work with
from torch_dreams.model_bunch import ModelBunch
bunch = ModelBunch(
model_dict = {
'inception': models.inception_v3(pretrained=True).eval(),
'resnet': models.resnet18(pretrained= True).eval()
}
)
layers_to_use = [
bunch.model_dict['inception'].Mixed_6a,
bunch.model_dict['resnet'].layer2[0].conv1
]
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model = bunch, quiet= False, device= 'cuda')
Then define a custom_func which determines which exact activations of the models we have to optimize
def custom_func(layer_outputs):
loss = layer_outputs[0].mean()*2.0 + layer_outputs[1][89].mean()
return -loss
Run the optimization
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = layers_to_use,
custom_func= custom_func,
iters= 100
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
Using custom transforms:
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
model = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model, device = 'cuda', quiet = False)
my_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomAffine(degrees = 10, translate = (0.5,0.5)),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p = 0.3)
])
dreamy_boi.set_custom_transforms(transforms = my_transforms)
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.Mixed_5b],
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
You can also use outputs of one render() as the input of another to create feedback loops.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.models as models
from torch_dreams.dreamer import dreamer
model = models.inception_v3(pretrained=True)
dreamy_boi = dreamer(model, device = 'cuda', quiet = False)
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.Mixed_6c],
)
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
image_parameter= image_param,
layers = [model.Mixed_5b],
iters = 20
)
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
Using custom images
Note that you might have to use smaller values for certain hyperparameters like lr and grad_clip.
from torch_dreams.custom_image_param import custom_image_param
param = custom_image_param(image = 'images/sample_small.jpg', device= 'cuda') ## image could either be a filename or a torch.tensor of shape NCHW
image_param = dreamy_boi.render(
image_parameter= param,
layers = [model.Mixed_6c],
lr = 2e-4,
grad_clip = 0.1,
weight_decay= 1e-1,
iters = 120
)
Working on models with different image normalizations
torch-dreams generally works with models trained on images normalized with imagenet mean and std, but that can be easily overriden to support any other normalization. For example, if you have a model with mean = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5] and std = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]:
t = torchvision.transforms.Normalize(
mean = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
std = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5]
)
dreamy_boi.set_custom_normalization(normalization_transform = t) ## normalization_transform could be any instance of torch.nn.Module
Masked Image parameters
Can be used to optimize only certain parts of the image using a mask whose values are clipped between [0,1].
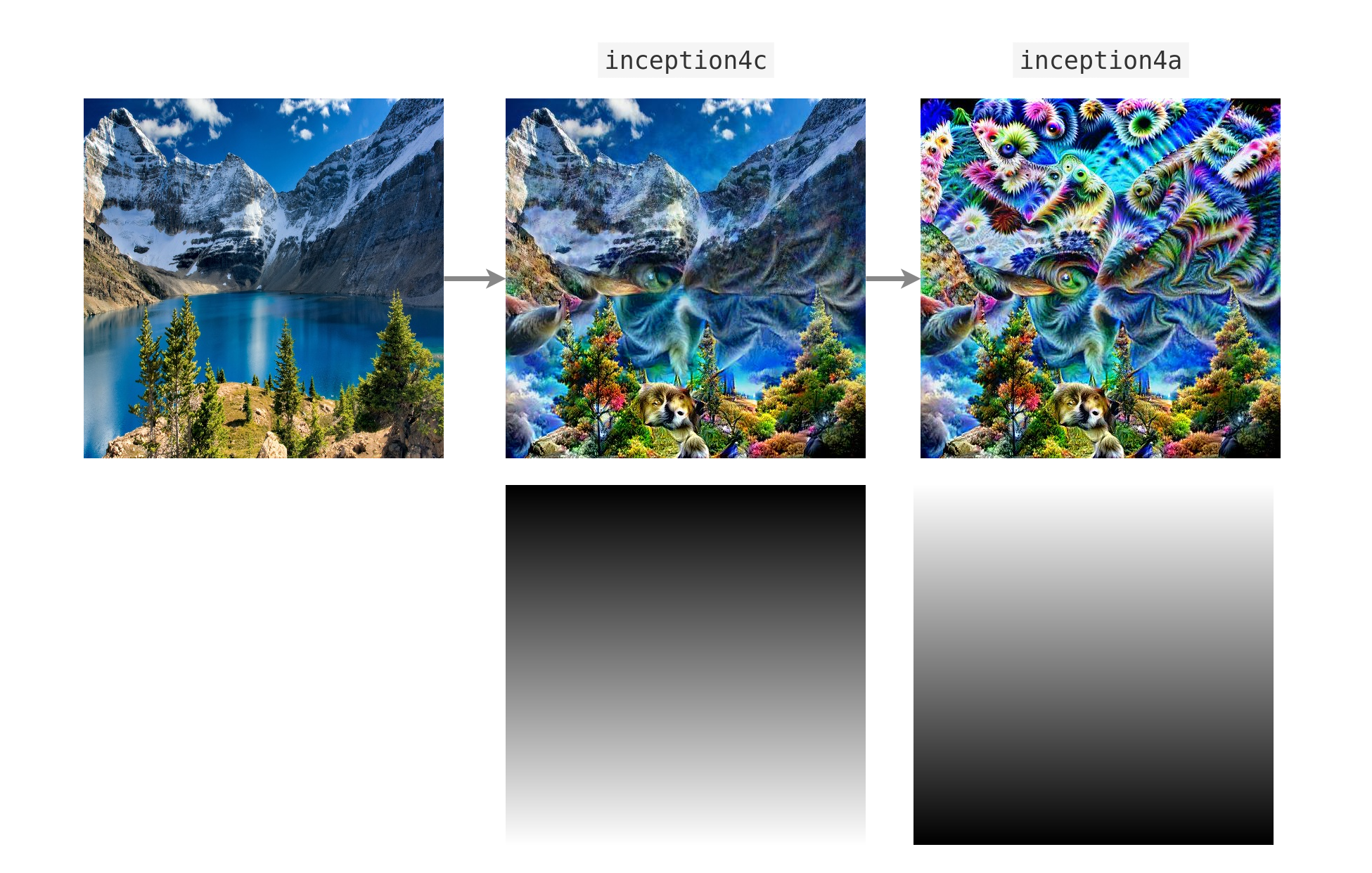
Here's an example with a vertical gradient
from torch_dreams.masked_image_param import masked_image_param
mask = torch.ones(1,1,512,512)
for i in range(0, 512, 1): ## vertical gradient
mask[:,:,i,:] = (i/512)
param = masked_image_param(
image= 'images/sample_small.jpg', ## optional
mask_tensor = mask,
device = 'cuda'
)
param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.inception4c],
image_parameter= param,
lr = 1e-4,
grad_clip= 0.1,
weight_decay= 1e-1,
iters= 200,
)
param.save('masked_param_output.jpg')
It's also possible to update the mask on the fly with param.update_mask(some_mask)
param.update_mask(mask = torch.flip(mask, dims = (2,)))
param = dreamy_boi.render(
layers = [model.inception4a],
image_parameter= param,
lr = 1e-4,
grad_clip= 0.1,
weight_decay= 1e-1,
iters= 200,
)
param.save('masked_param_output_2.jpg')
Other conveniences
The following methods are handy for an auto_image_param instance:
- Saving outputs as images:
image_param.save('output.jpg')
- Torch Tensor of dimensions
(height, width, color_channels)
torch_image = image_param.to_hwc_tensor(device = 'cpu')
- Torch Tensor of dimensions
(color_channels, height, width)
torch_image_chw = image_param.to_chw_tensor(device = 'cpu')
- Displaying outputs on matplotlib.
plt.imshow(image_param)
plt.show()
- For instances of
custom_image_param, you can set any NCHW tensor as the image parameter:
image_tensor = image_param.to_nchw_tensor()
## do some stuff with image_tensor
t = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomRotation(5)
])
transformed_image_tensor = t(image_tensor)
image_param.set_param(tensor = transformed_image_tensor)
Args for render()
-
layers(iterable): List of the layers of model(s)'s layers to work on.[model.layer1, model.layer2...] -
image_parameter(auto_image_param, optional): Instance oftorch_dreams.auto_image_param.auto_image_param -
width(int, optional): Width of image to be optimized -
height(int, optional): Height of image to be optimized -
iters(int, optional): Number of iterations, higher -> stronger visualization -
lr(float, optional): Learning rate -
rotate_degrees(int, optional): Max rotation in default transforms -
scale_max(float, optional): Max image size factor. Defaults to 1.1. -
scale_min(float, optional): Minimum image size factor. Defaults to 0.5. -
translate_x(float, optional): Maximum translation factor in x direction -
translate_y(float, optional): Maximum translation factor in y direction -
custom_func(function, optional): Can be used to define custom optimiziation conditions torender(). Defaults to None. -
weight_decay(float, optional): Weight decay for default optimizer. Helps prevent high frequency noise. Defaults to 0. -
grad_clip(float, optional): Maximum value of the norm of gradient. Defaults to 1.
Args for dreamer.__init__()
model(nn.Moduleortorch_dreams.model_bunch.Modelbunch): Almost any PyTorch model which was trained on imagenetmeanandstd, and supports variable sized images as inputs. You can pass multiple models into this argument as atorch_dreams.model_bunch.Modelbunchinstance.quiet(bool): Set toTrueif you want to disable any progress barsdevice(str):cudaorcpudepending on your runtime
Citation
@misc{mayukhdebtorchdreams,
title={Feature Visualization library for PyTorch},
author={Mayukh Deb},
year={2021},
publisher={GitHub},
howpublished={\url{https://github.com/Mayukhdeb/torch-dreams}},
}